Quick Start Guide - Integration¶
Let's get started with ESB Micro Integrator by running a simple integration use case in your local environment.
Before you begin...¶
-
Install Java SE Development Kit (JDK) version 11 and set the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable.Info
For information on the compatible JDK types and setting the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable for different operating systems, see Setup and Install. -
Go to the ESB Micro Integrator web page, click Download, and then click Zip Archive to download the Micro Integrator distribution as a ZIP file.
-
Optionally, navigate to the ESB Tooling web page, and download ESB Integration Studio.
Info
For more information, see the installation instructions.
-
Download the sample files. From this point onwards, let's refer to this directory as
<mi-qsg-home>. - Download curl or a similar tool that can call an HTTP endpoint.
- Optionally, go to the MWARE ESB website, click TRY IT NOW, and then click Zip Archive to download the ESB distribution as a ZIP file.
What you'll build¶
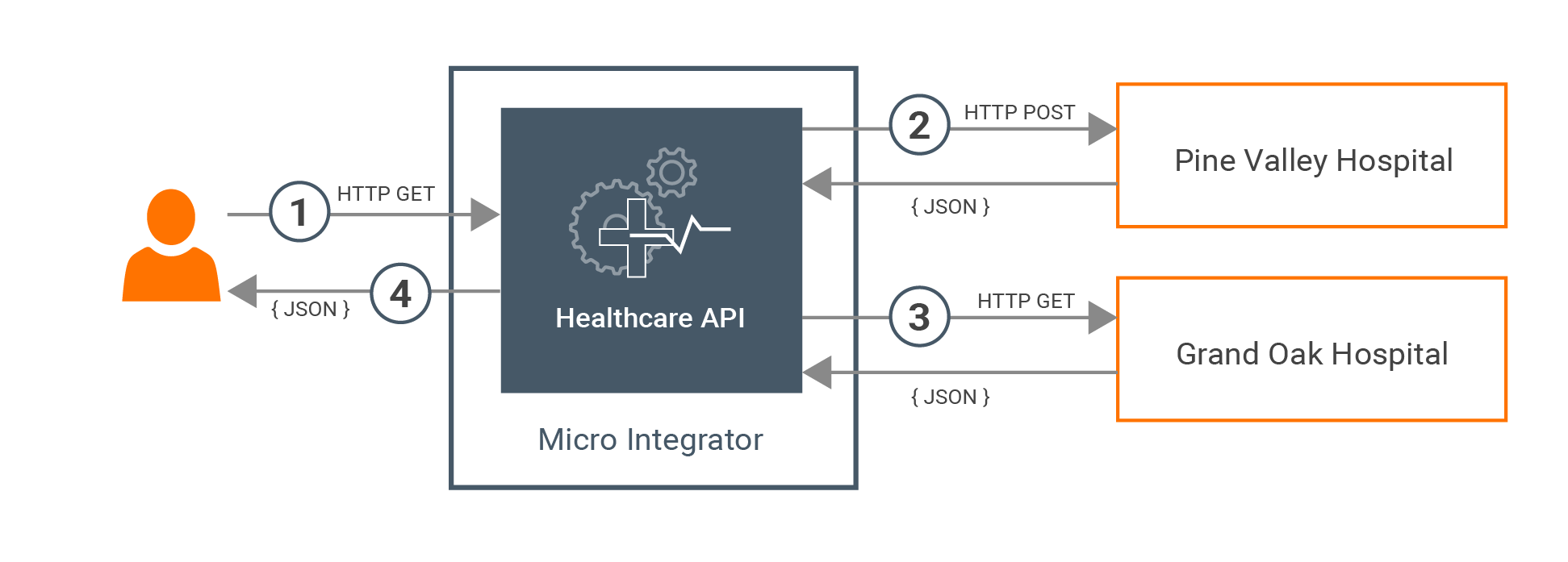
This is a simple service orchestration scenario. The scenario is about a basic healthcare system where the Micro Integrator is used to integrate two back-end hospital services to provide information to the client.
Most healthcare centers have a system that is used to make doctor appointments. To check the availability of the doctors for a particular time, users typically need to visit the hospitals or use each and every online system that is dedicated to a particular healthcare center. Here, we are making it easier for patients by orchestrating those isolated systems for each healthcare provider and exposing a single interface to the users.
!!! Tip
You may export` <mi-qsg-home>/HealthcareIntegrationProject` to Integration Studio to view the project structure.In the above scenario, the following takes place:
-
The client makes a call to the Healthcare API created using Micro Integrator.
-
The Healthcare API calls the Pine Valley Hospital back-end service and gets the queried information.
-
The Healthcare API calls the Grand Oak Hospital back-end service and gets the queried information.
-
The response is returned to the client with the required information.
Both Grand Oak Hospital and Pine Valley Hospital have services exposed over the HTTP protocol.
The Pine Valley Hospital service accepts a POST request in the following service endpoint URL.
http://<HOST_NAME>:<PORT>/pineValley/doctorsThe Grand Oak Hospital service accepts a GET request in the following service endpoint URL.
http://<HOST_NAME>:<PORT>/grandOak/doctors/<DOCTOR_TYPE>The expected payload should be in the following JSON format:
{
"doctorType": "<DOCTOR_TYPE>"
}Let’s implement a simple integration solution that can be used to query the availability of doctors for a particular category from all the available healthcare centers.
Step 1 - Set up the workspace¶
To set up the integration workspace for this quick start guide, we will use an integration project that was built using ESB Integration Studio:
-
Extract the downloaded ESB Micro Integrator and sample files into the same directory location.
-
Navigate to the
<mi-qsg-home>directory. The following project files and executable back-end services are available in the<mi-qsg-home>. -
HealthcareIntegrationProject/HealthcareIntegrationProjectConfigs: This is the ESB Config module with the integration artifacts for the healthcare service. This service consists of the following REST API:
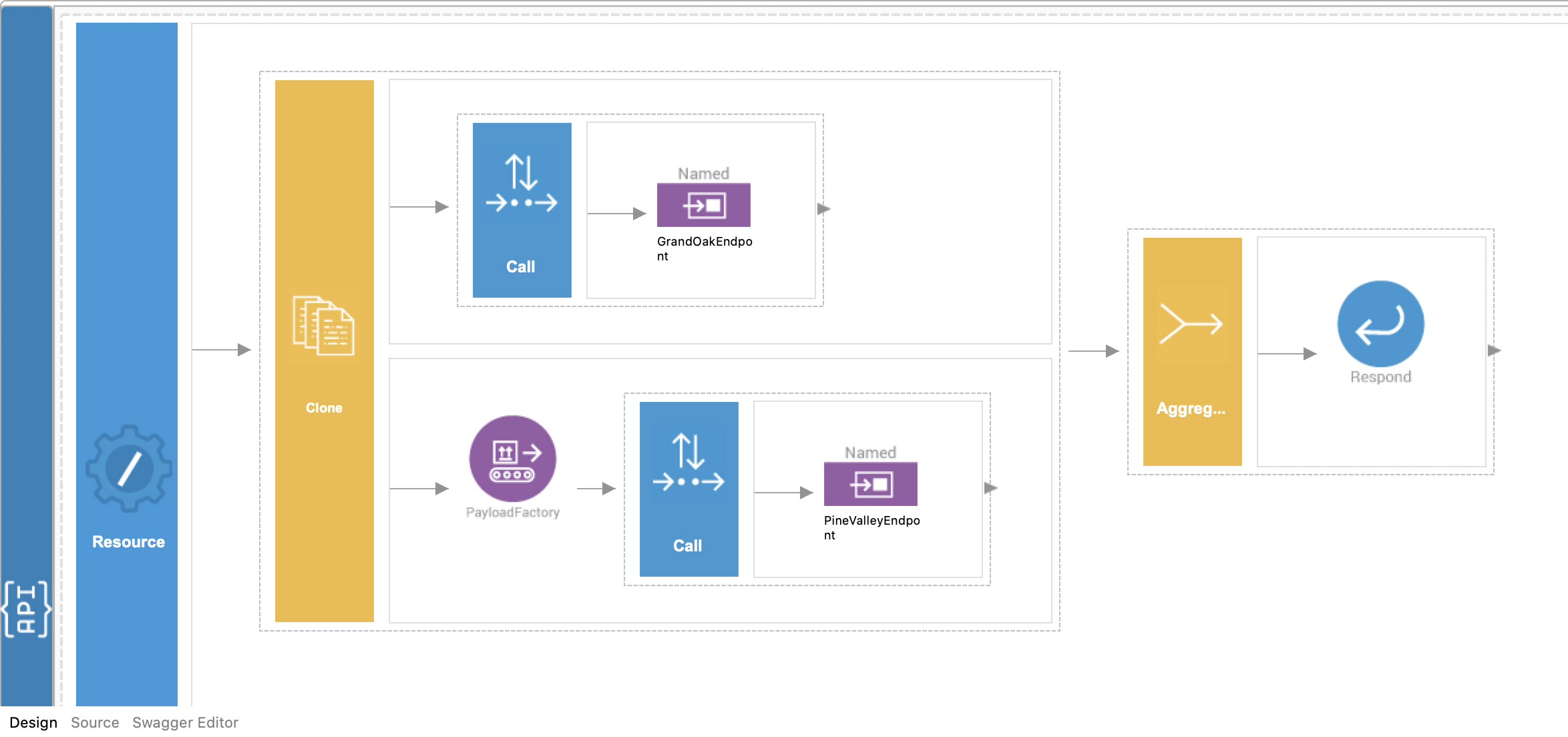
HealthcareAPI.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <api context="/healthcare" name="HealthcareAPI" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <resource methods="GET" uri-template="/doctor/{doctorType}"> <inSequence> <clone> <target> <sequence> <call> <endpoint key="GrandOakEndpoint"/> </call> </sequence> </target> <target> <sequence> <payloadFactory media-type="json"> <format>{ "doctorType": "$1" }</format> <args> <arg evaluator="xml" expression="$ctx:uri.var.doctorType"/> </args> </payloadFactory> <call> <endpoint key="PineValleyEndpoint"/> </call> </sequence> </target> </clone> <aggregate> <completeCondition> <messageCount max="-1" min="-1"/> </completeCondition> <onComplete aggregateElementType="root" expression="json-eval($.doctors.doctor)"> <respond/> </onComplete> </aggregate> </inSequence> <outSequence/> <faultSequence/> </resource> </api>It also contains the following two files in the metadata folder.
Tip
This data is used later in this guide by the API management runtime to generate the managed API proxy.
HealthcareAPI_metadata.yaml This file contains the metadata of the integration service. The default serviceUrl is configured as http://localhost:8290/healthcare. If you are running Micro Integrator on a different host and port, you may have to change these values.HealthcareAPI_swagger.yaml This Swagger file contains the OpenAPI definition of the integration service. -
HealthcareIntegrationProject/HealthcareIntegrationProjectCompositeExporter: This is the Composite Application Project folder, which contains the packaged CAR file of the healthcare service.
-
Backend: This contains an executable .jar file that contains mock back-end service implementations for the Pine Valley Hospital and Grand Oak Hospital.
-
bin: This contains a script to copy artifacts and run the backend service.
Step 2 - Running the integration artifacts¶
Follow the steps given below to run the integration artifacts we developed on a Micro Integrator instance that is installed on a VM.
-
Run
run.sh/run.batscript in<mi-qsg-home>/binbased on your operating system to start up the workspace.- Open a terminal and navigate to the
<mi-qsg-home>/binfolder. -
Execute the relevant OS specific command:
sh run.shrun.batTip
The script assumes
MI_HOMEand<mi-qsg-home>are located in the same directory. It carries out the following steps.- Start the back-end services.
Two mock hospital information services are available in the `DoctorInfo.jar` file located in the `<mi-qsg-home>/Backend/` directory. To manually start the service, open a terminal window, navigate to the `<mi-qsg-home>/Backend/` folder, and use the following command to start the services: ```bash java -jar DoctorInfo.jar ```- Deploy the Healthcare service.
Copy the CAR file of the Healthcare service (HealthcareIntegrationProjectCompositeExporter_1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.car) from the `<mi-qsg-home>/HealthcareIntegrationProject/HealthcareIntegrationProjectCompositeExporter/target/` directory to the `<MI_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps` directory.
- Open a terminal and navigate to the
-
Start the Micro Integrator.
- Execute the relevant command in a terminal based on the OS:
sh micro-integrator.shmicro-integrator.bat -
(Optional) Start the Dashboard.
If you want to view the integration artifacts deployed in the Micro Integrator, you can start the dashboard. The instructions on running the MI dashboard is given in the installation guide:
You can now test the HealthcareIntegrationService that you just generated.
Step 3 - Testing the integration service¶
-
Invoke the healthcare service.
Open a terminal and execute the following curl command to invoke the service:
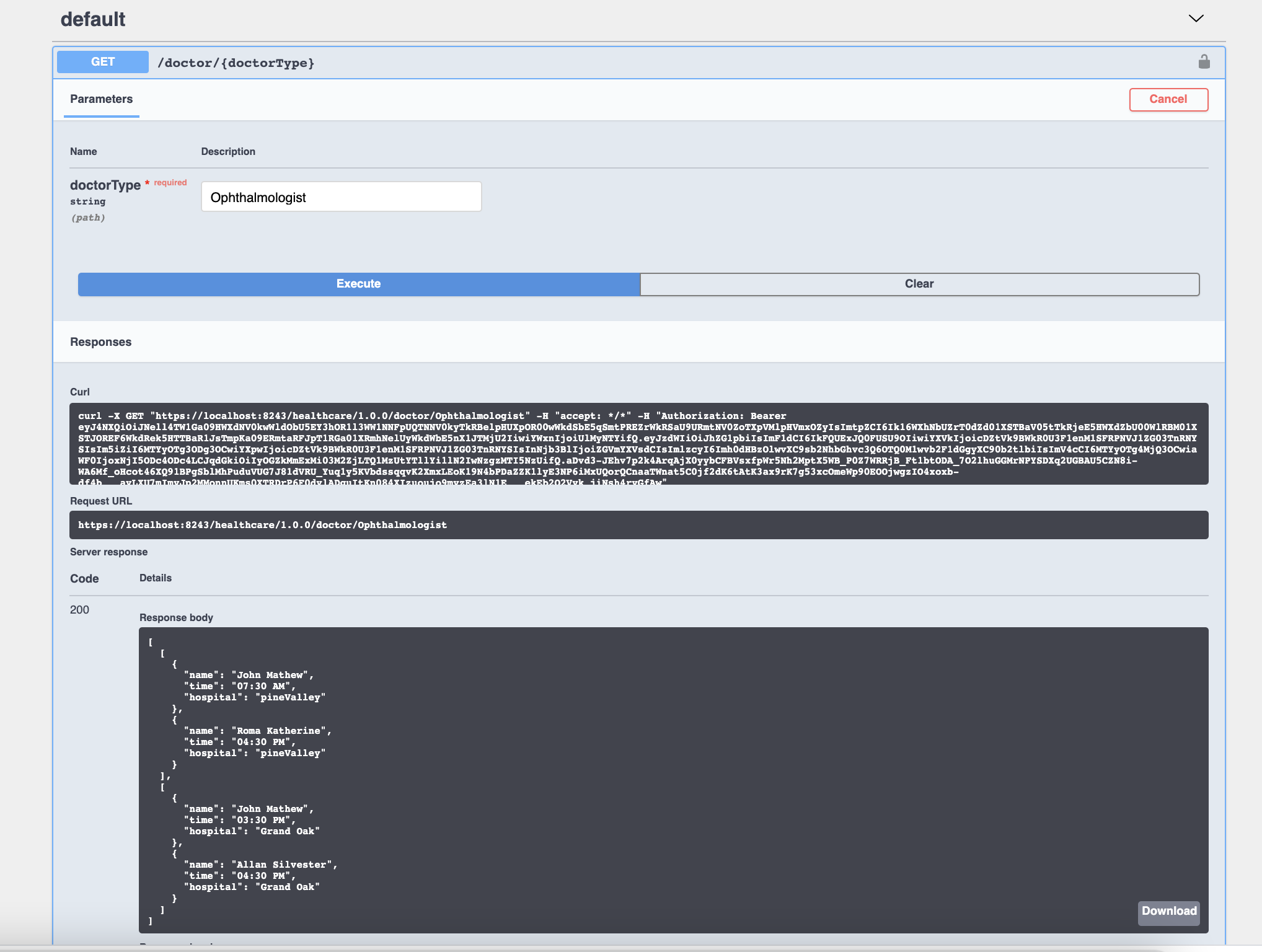
curl -v http://localhost:8290/healthcare/doctor/OphthalmologistUpon invocation, you should be able to observe the following response:
Congratulations! Now you have created your first integration service. Optionally, you can follow the steps given below to expose the service as a Managed API in ESB.[ [ { "name":"John Mathew", "time":"03:30 PM", "hospital":"Grand Oak" }, { "name":"Allan Silvester", "time":"04:30 PM", "hospital":"Grand Oak" } ], [ { "name":"John Mathew", "time":"07:30 AM", "hospital":"pineValley" }, { "name":"Roma Katherine", "time":"04:30 PM", "hospital":"pineValley" } ] ]
Exposing an Integration Service as a Managed API¶
The REST API you deployed in the Micro Integrator is an integration service for the ESB. Now, let's look at how you can expose the integration service to the API Management layer and generate a managed API by using the service.
Step 1 - Expose your integration as a service¶
-
Start the ESB runtime:
- Extract the ESB ZIP file.
-
Start MWARE ESB:
Open a terminal, navigate to the
<API-M_HOME>/bindirectory, and execute the relevant command../api-manager.shapi-manager.bat --run
-
Update and start the Micro Integrator runtime:
-
Stop the Micro Integrator.
-
Uncomment the following configuration from the
<MI_HOME>/conf/deployment.tomlfile of the Micro Integrator.Tip
The default username and password for connecting to the API gateway is
admin:admin.[[service_catalog]] apim_host = "https://localhost:9443" enable = true username = "admin" password = "admin" -
Start the Micro Integrator again.
You will see the following in the server start-up log.
Successfully updated the service catalog
-
-
Access the integration service from the API Publisher:
-
Sign in to the API Publisher:
https://localhost:9443/publisherTip
Use
adminas the user name and password. -
Select the Services from the menu.
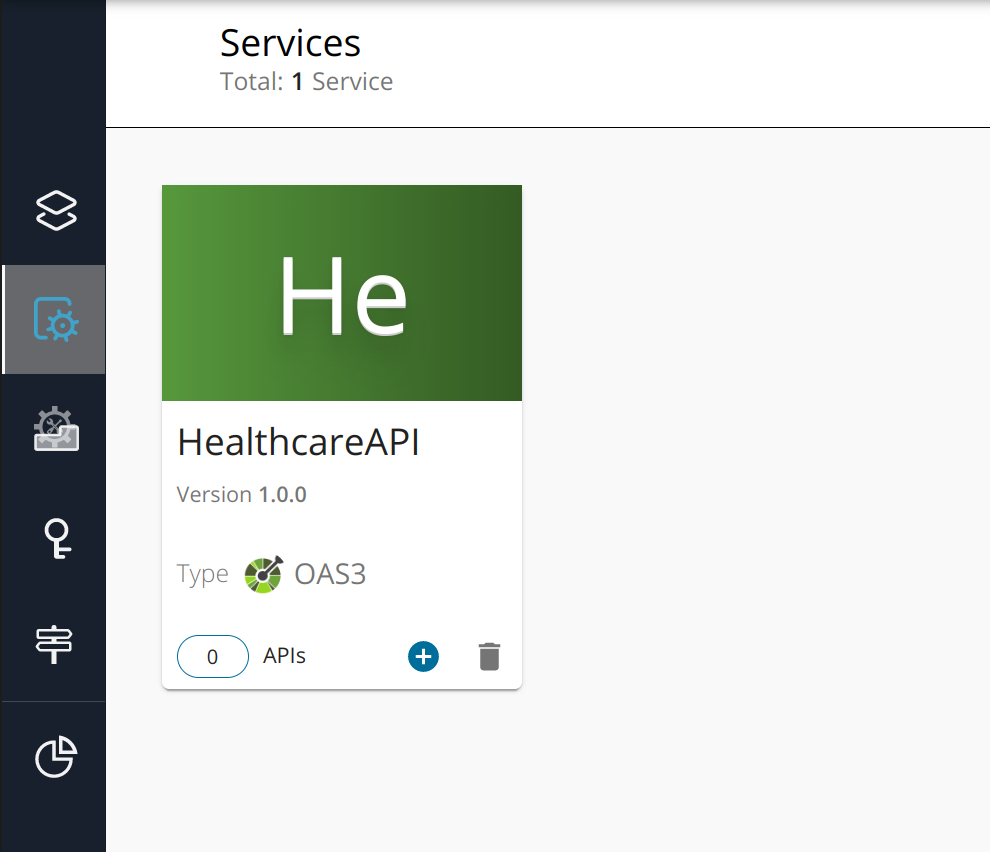
-
See that the
HealthcareAPIis listed as a service.
Step 2 - Create a managed API using the Integration Service¶
-
-
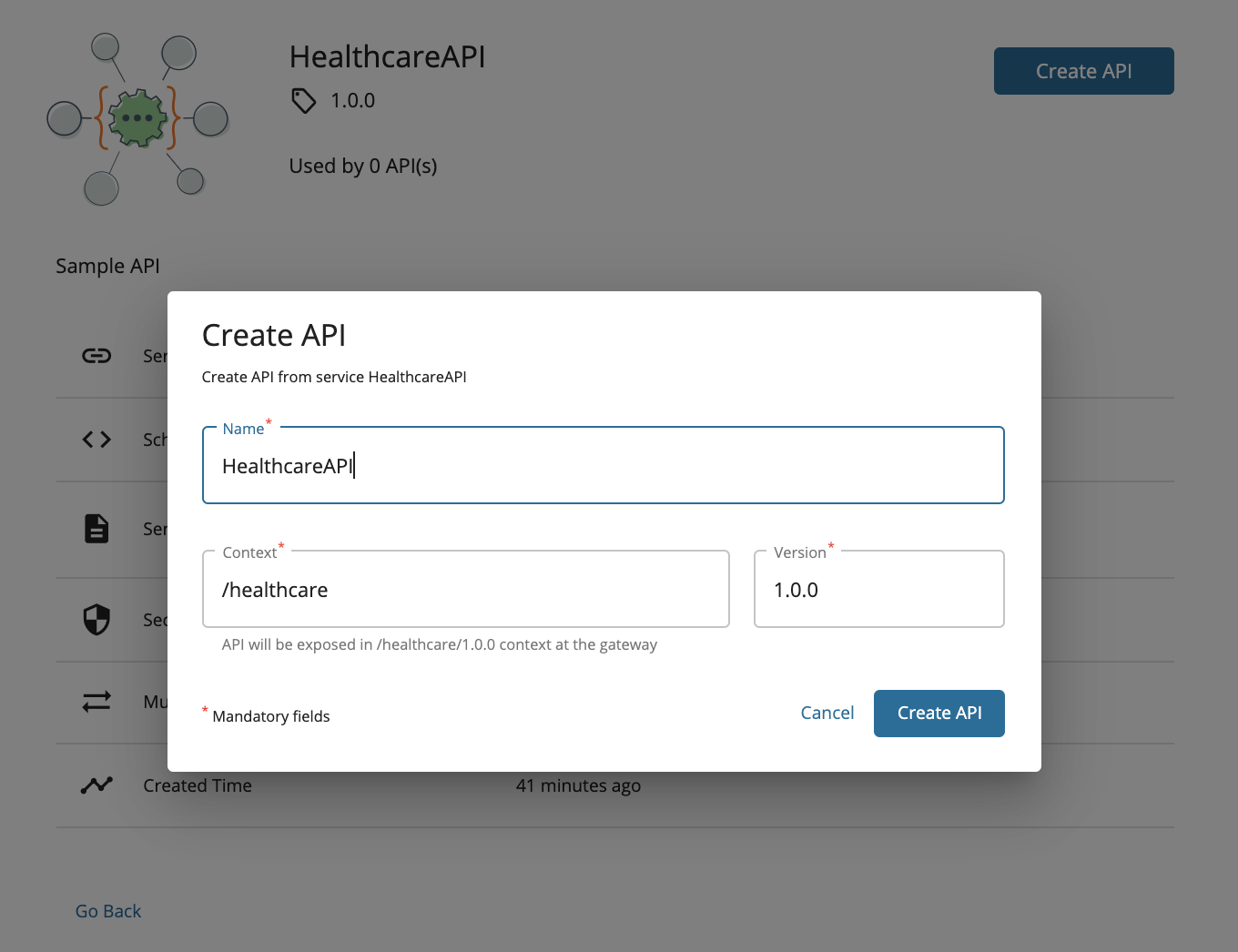
Click on the
HealthcareAPIthat is in the service catalog. -
Click Create API.
This opens the Create API dialog box with the API details that are generated based on the service.
-
Update the API name, context, and version if required, and click Create API.
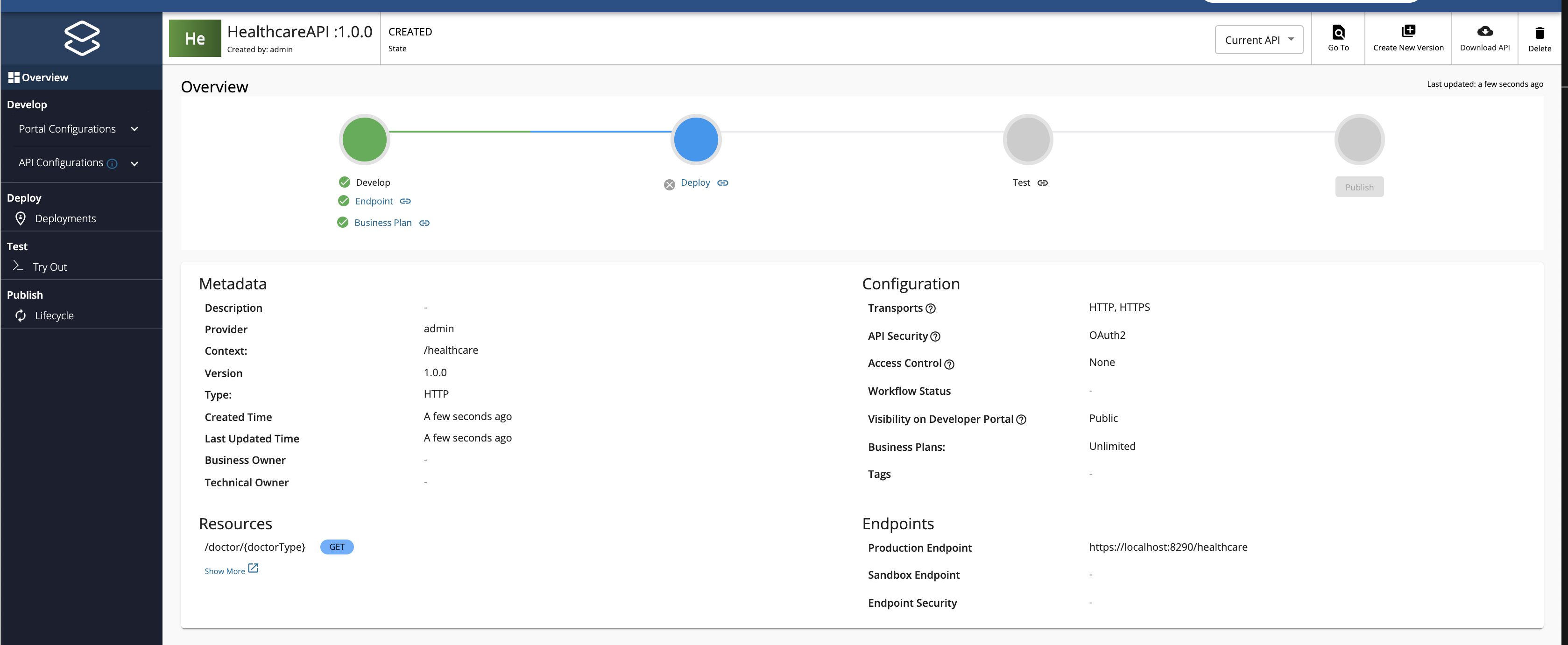
The overview page of the API that you just created appears.
-
Navigate to Develop -> API Configurations -> Endpoints from the left menu. You will see that Service Endpoint is already selected and the production endpoint is already provided.
Select the
Sandbox Endpoint, add the endpointhttp://localhost:8290/healthcare, and Save. -
Update the portal configurations and API configurations as required.
Now, you have successfully created an API using the service.
Step 3 - Publish the managed API¶
-
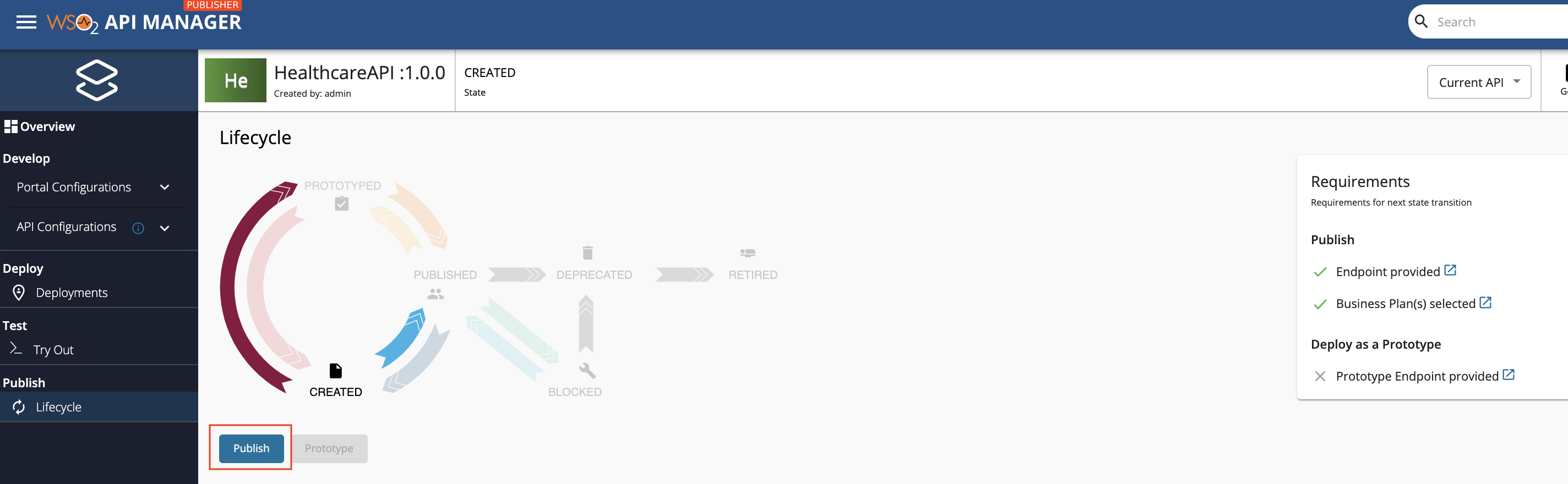
Navigate to Deployments and click Deploy to create a revision to deploy in the default Gateway environment.
-
Navigate to Lifecycle and click Publish to publish the API in the Gateway environment.
If the API is published successfully, the lifecycle state will shift to PUBLISHED.
Step 4 - Invoke the Managed HealthcareAPI via Developer Portal¶
-
Navigate to the Developer Portal by clicking on the
View In Dev Portalat the top menu. -
Sign in using the default username/password
admin/admin. You will be redirected to the APIs. -
Under APIs, you will see the published
HealthcareAPI. Click on it to navigate to the Overview of the API. -
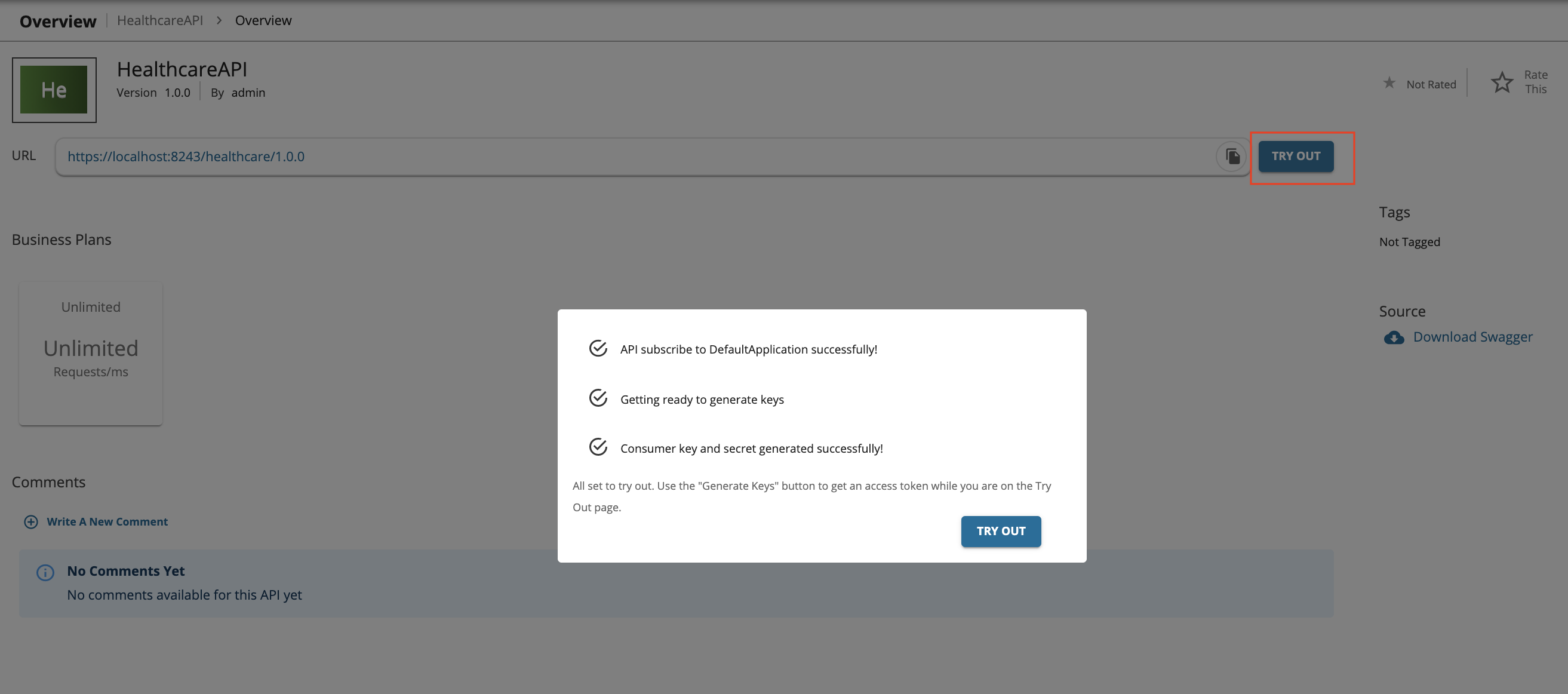
Click
Try Out. This will create a subscription to the API usingDefault Application. -
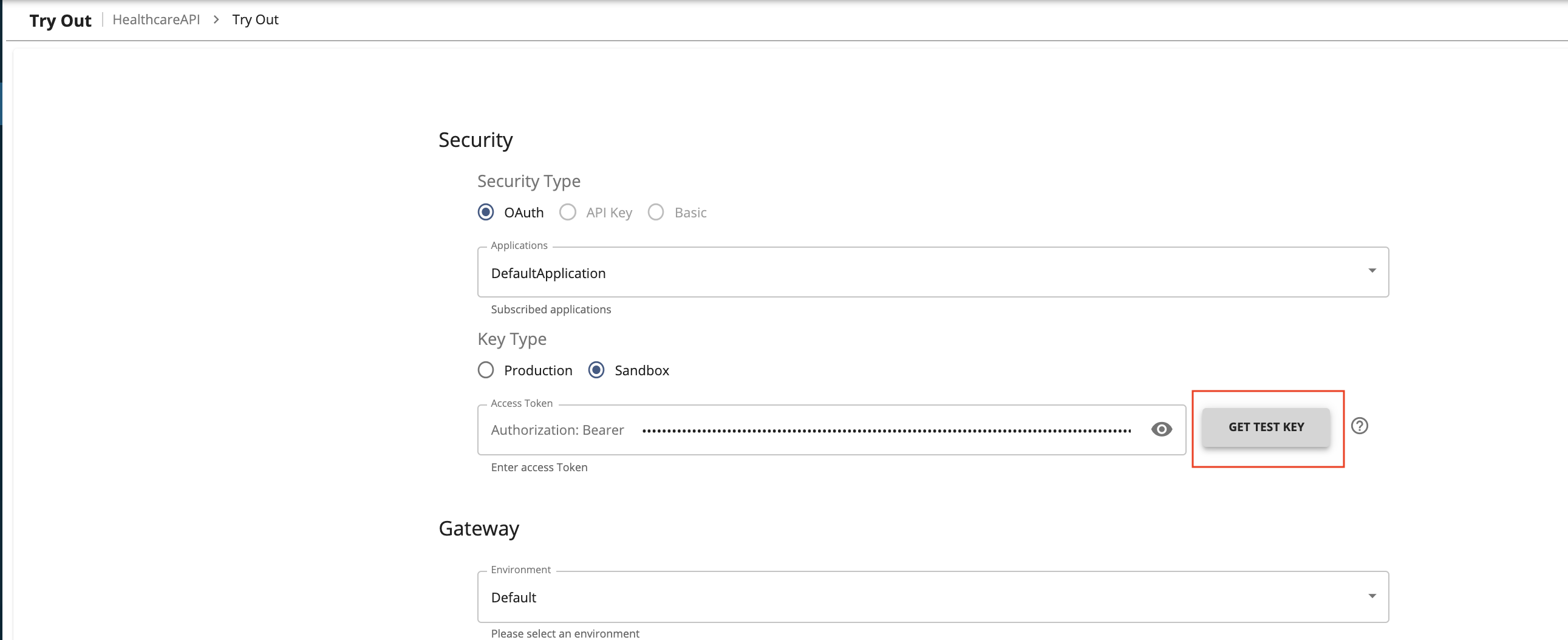
Click
GET TEST KEYto get a test token to invoke the API. -
Click GET resource
/doctor/{doctorType}. Click on Try It Out. EnterOphthalmologistin the doctorType field and click Execute.
What's next?¶
- Develop your first integration solution.
- Try out the examples available in the Integrate section of our documentation.
- Try out the entire developer guide on Exposing an Integration Service as a Managed API.
- Try out the entire developer guide on Exposing an Integration SOAP Service as a Managed API.