Develop an Integration From a Managed API¶
The top down approach of API first integration provides the capability for API developers to start creating a managed REST API first in MWARE ESB. Then the integration developer can use the same API in the ESB Integration Studio to develop the integration later on and expose it to MWARE ESB. Thereafter, the API consumers can discover the API from the marketplace, subscribe to it, and use it for application development.
The following stakeholders will be involved in implementing this process:
Stakeholders
- API Creator
- Integration developer
- API Publisher
- API Consumer
What you'll build¶
Let's work with the following user story in this tutorial.
The API developer needs to create an API first and managed it before adding the backend server implementation. The API developer creates an API via the Control Plane (Publisher Portal), creates mock implementations, and tests the API. The integration developer picks up the API definition, implements the integrations and deploys it in the Micro Integrator server. Thereafter, the API developer adds the service endpoint using ESB and publishes the created API.
Let's get started!
Step 1 - Create an API¶
Let’s create an API in MWARE ESB.
-
Sign in to the API Publisher portal.
https://localhost:9443/publisher -
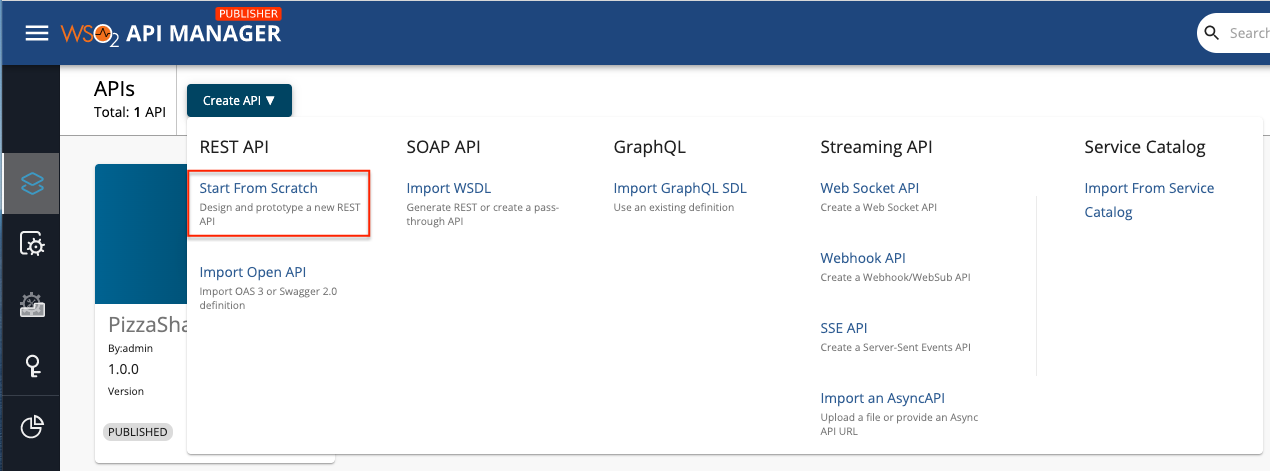
Click Create API and then click Start from Scratch.
You can use any option to create the REST API.
-
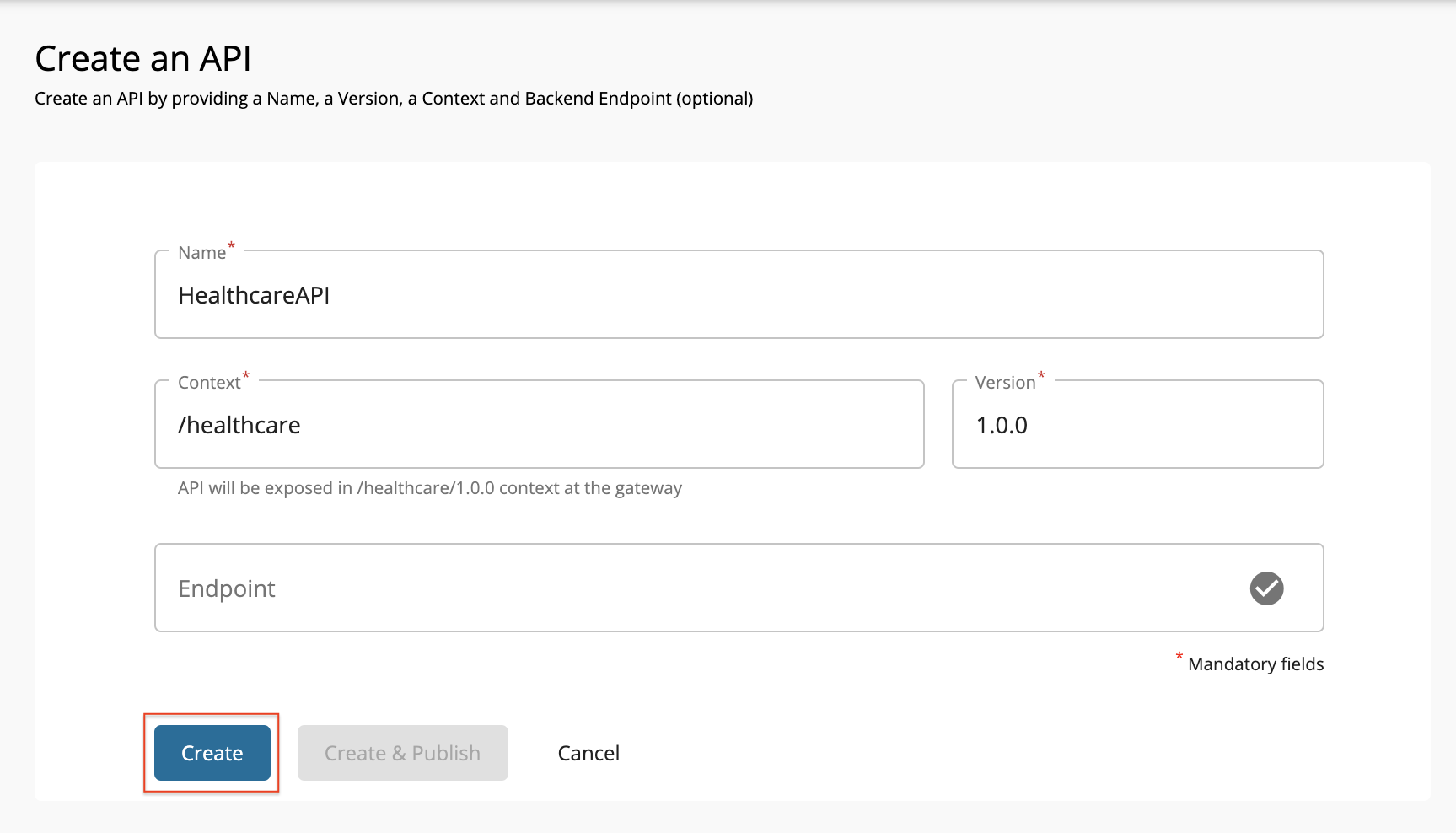
Enter the details of the API and click Create to create the REST API.
As the backend is not implemented yet, do not enter a value as the endpoint.
Field Value API name HealthcareAPI Context /healthcare Version 1.0.0 -
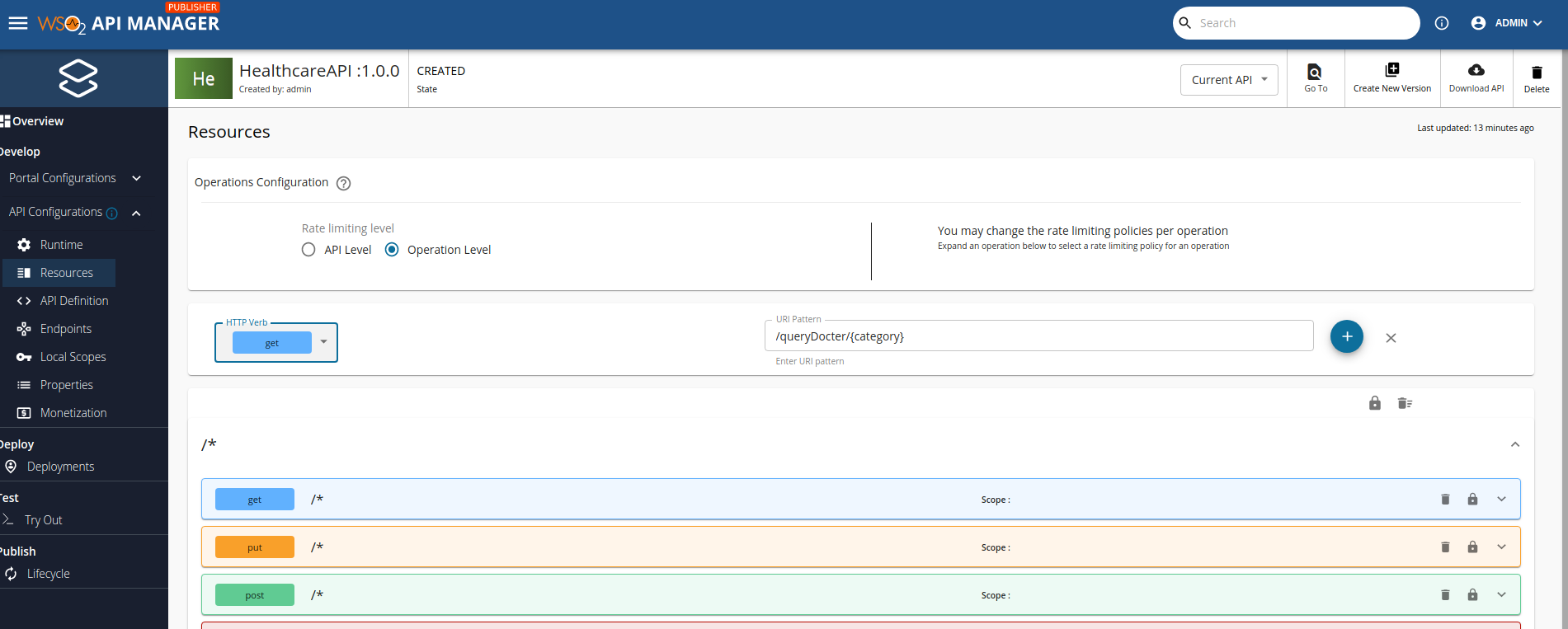
Let’s add a new GET resource named
/queryDocter/{category}to the REST API. -
You can manage the API the way you want and test out the resource by adding a Mock Implementation.
Step 2 - Develop the integration service¶
Let’s start implementing the integration for the created Healthcare REST API.
-
Download the relevant ESB Integration Studio based on your operating system.
-
Open ESB Integration Studio.
-
Click New Integration Project in the Getting Started tab as shown below.
-
Enter ServiceCatalogSample as the project name and select the following checkboxes to create the required modules.
-
Create ESB Configs.
-
Create Composite Exporter.
-
-
Click Finish.
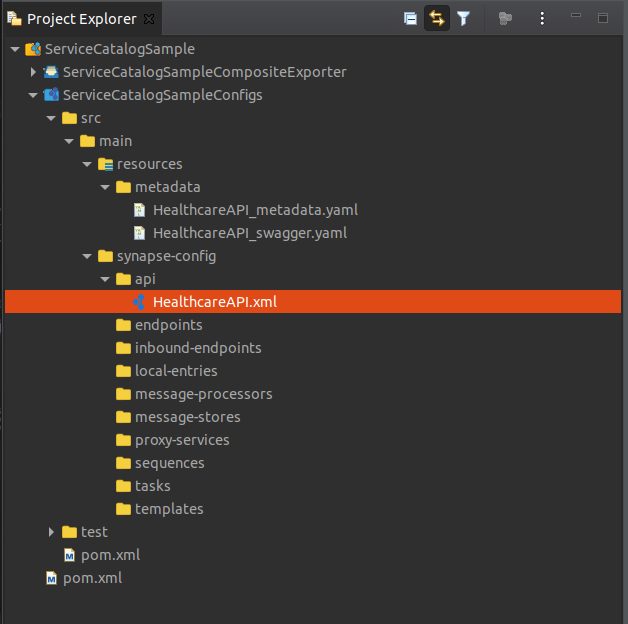
You will see the projects listed in the Project Explorer as shown below:
-
Create an Endpoint artifact.
-
Right-click on ServiceCatalogSampleConfigs in the project explorer, click New and click Endpoint.
-
Ensure that Create a New Endpoint is selected and click Next.
-
Enter the information given below to create the new endpoint.
Property Value Description Endpoint Name QueryDoctorEP The name of the endpoint. Endpoint Type HTTP Endpoint Indicates that the back-end service is HTTP. URI Template http://localhost:9090/healthcare/{uri.var.category}The template for the request URL expected by the backend service. In this case, the variable categorythat needs to be included in the request for querying doctors is represented as{uri.var.category}in the template.Method GET This indicates that you are creating this endpoint for GET requests that are sent to the back end service. Save Endpoint in ServiceCatalogSampleConfigs This is the ESB configuration module where the artifact will be saved. -
Click Finish.
-
-
Create a REST API artifact for the previously created API in the API Publisher.
-
In the project explorer, right-click on ServiceCatalogSampleConfigs, click New and click REST API.
-
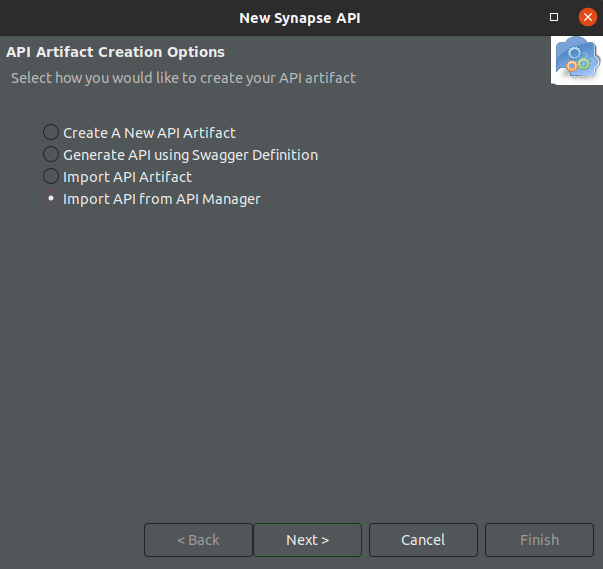
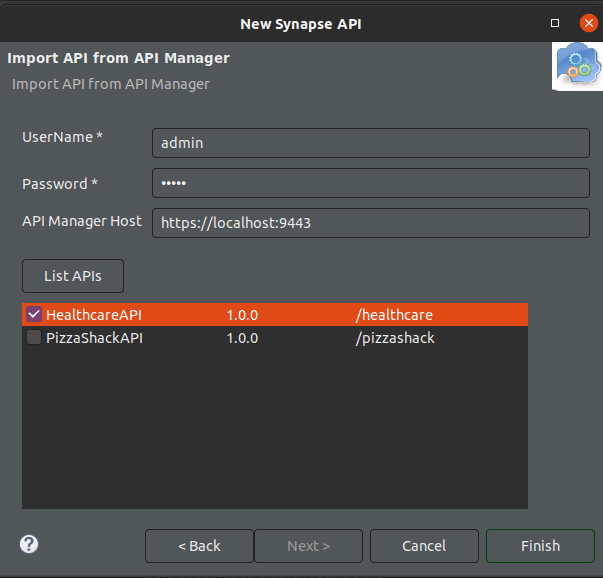
Select Import API from ESB.
-
Enter the credentials of the ESB user and ESB host URl.
For this tutorial let's use the MWARE ESB admin credentials.
Note
- MWARE ESB has introduced a new role named
Internal/integration_devfor this particular task, which can be assigned to the integration developer who will be using the Integration Studio to carryout this task. - You can create a new user and assign the
Internal/integration_devrole to the user via the carbon console in MWARE ESB.
Property Value Description Username admin Username of the ESB user. Password admin Password of the ESB user. ESB host https://localhost:9443Host Url of the ESB. - MWARE ESB has introduced a new role named
-
Click List APIs.
-
Click HealthcareAPI and click Finish.
This pulls the Swagger/OpenAPI definition file that corresponds to the API that was created in MWARE ESB.
-
-
Implement the integration solution.
Let's add a log mediator as well to the integration apart from the created endpoint.
Open the Source view of the HealthcareAPI REST API that you created and delete the existing
<inSequence >code snippet and apply the following<inSequence>.<inSequence> <log description="Request Log" level="custom"> <property name="Log Property message" value=""Welcome to HealthcareService""/> </log> <send> <endpoint key="QueryDoctorEP"/> </send> </inSequence>The code in the final file should be as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <api context="/healthcare" name="HealthcareAPI" version="1.0.0" version-type="context" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <resource methods="GET" uri-template="/querydoctor/{category}"> <inSequence> <log description="Request Log" level="custom"> <property name="Log Property message" value=""Welcome to HealthcareService""/> </log> <send> <endpoint key="QueryDoctorEP"/> </send> </inSequence> <outSequence> <respond/> </outSequence> <faultSequence/> </resource> </api>When the HealthcareAPI is created, the following two new files are created in the metadata folder.
HealthcareAPI_metadata.yaml This file contains the metadata of the integration service you created in the previous step. HealthcareAPI_swagger.yaml This Swagger file contains the OpenAPI definition of the integration service.
Step 3 - Configure service metadata¶
Let's update the metadata of the integration service.
-
Open the
HealthcareAPI_metadata.yamlfile from the project explorer. -
Update the following values in the file.
Property Value Description description API to fetch doctors for a given category. Explain the purpose of the API. serviceUrl http://localhost:8290/healthcareThis is the URL of the API when it gets deployed in the Micro Integrator. You (as the integration developer) may not know this URL during development. Therefore, you can parameterize the URL to be resolved later using environment variables. By default, the {MI_HOST}and{MI_PORT}values are parameterized with placeholders.
You can configure the serviceUrl using the following methods:-
Add the complete URL without parameters. For example:
http://localhost:8290/healthcare.
Let's use this option for this tutorial. - Parameterize using the host and port combination.
Example:http://{MI_HOST}:{MI_PORT}/healthcare. - Parameterize using a preconfigured URL.
Example:http://{MI_URL}/healthcare.
-
Add the complete URL without parameters. For example:
-
Make sure to change the
serviceUrlfromHTTPStoHTTP.This is required because the HealthcareAPI is not secured.
-
Leave the default values for the remaining parameters.
Step 4 - Configure the Micro Integrator¶
The Micro Integrator contains a client application, which automatically publishes artifacts to the Service Catalog in the API Publisher Portal.
Let's enable this client for the embedded Micro Integrator of ESB Integration Studio.
-
Click the Embedded Micro Integrator Configuration icon on the upper menu to open the dialog box.
-
Uncomment the
[[service_catalog]]section as shown below and change the API-M server configurations accordingly.[[service_catalog]] apim_host = "https://localhost:9443" enable = true username = "admin" password = "admin" -
Optionally, you can encrypt the username and password for better security:
-
Update the configuration as shown below.
[secrets] userName = "[admin]" password = "[admin]" [[service_catalog]] apim_host = "https://localhost:9443" enable = true username = "$secret{username}" password = "$secret{password}" -
Click Encrypt Secrets.
-
-
Save the configurations.
-
Optionally, inject environment variables to your Micro Integrator.
If you need to parameterize the serviceUrl in the metadata file, you must inject the parameterized values as environment variables.
The following are example placeholder values that you may have used in the serviceUrl followed by the corresponding environment variables.
{MI_HOST} : localhost {MI_PORT} : 8290 {MI_URL} : localhost:8290
Step 5 - Package the artifacts¶
Package the artifacts in your composite exporter module to be able to deploy the artifacts in the server.
-
Open the
pom.xmlfile of theServiceCatalogSampleCompositeExportermodule. -
Ensure that the following artifacts are selected in the POM file.
- HealthcareAPI
- QueryDoctorEP
-
Save the changes.
Step 6 - Build and run the service¶
Deploy the packaged artifacts in the embedded Micro Integrator:
- Right-click on the composite exporter module and click Export Project Artifacts and Run.
- Confirm that the required artifacts from the composite exporter module are selected.
-
Click Finish.
-
The artifacts are deployed in the embedded Micro Integrator and the Micro Integrator starts.
-
The integration service is also deployed in the Service Catalog during server startup.
-
You will see the following in the server start-up log.
Successfully updated the service catalog
-
Step 7 - Add the service endpoint to the API¶
Now let’s add the developed backend service to the API.
-
Sign in to the Publisher in MWARE ESB.
https://localhost:9443/publisher -
Select the previously created HealthcareAPI.
-
Click Endpoint and then click Service Endpoint Type.
-
Add the production and/or sandbox endpoint.
For this tutorial let's only add the production endpoint.
- Click the production endpoint.
- Add the production endpoint using service endpoints.
- Select the
HealthcareAPIservice endpoint from the dropdown.
- Click Save.
Step 8 - Deploy the API¶
Depoly the HealthcareAPI REST API in the Gateway. For more information, see Deploy an API.
Step 9 - Start the backend service¶
Let's start the back-end hospital service.
-
Download the JAR file of the backend service from here.
-
Open a terminal, navigate to the location where you saved the backend service.
-
Execute the following command to start the service.
java -jar Hospital-Service-JDK11-2.0.0.jar
Step 10 - Subscribe to the API and test it¶
Subscribe to the HealthcareAPI REST API and invoke it. For more information, see Test a REST API Using the Integrated API Console.
You will get the response message from the Healthcare service, if you send the category as surgery:
[
{
"name":"thomas collins",
"hospital":"grand oak community hospital",
"category":"surgery",
"availability":"9.00 a.m - 11.00 a.m",
"fee":7000.0
},
{
"name":"anne clement",
"hospital":"clemency medical center",
"category":"surgery",
"availability":"8.00 a.m - 10.00 a.m",
"fee":12000.0
},
{
"name":"seth mears",
"hospital":"pine valley community hospital",
"category":"surgery",
"availability":"3.00 p.m - 5.00 p.m",
"fee":8000.0
}
]Now, check the Console tab of ESB Integration Studio and you will see the following message:
INFO - LogMediator message = "Welcome to HealthcareService"