Mock Implementation with API Gateway¶
Let's create a Prototype API that has a mock implementation of JavaScript snippets auto-generated based on the OpenAPI specification, and invoke it via Publisher and Developer Portals to test it out.
Note
This is not supported when Choreo Connect is used as the Gateway.
Step 1 - Create the interface of the API¶
Note the following when creating an interface for the API.
- You can create either a new API or a new version of an existing API for this purpose.
- Leave the endpoint field empty since the gateway will be acting as a backend using the javascript definitions we provide.
For this example, let's follow steps 1 to 5 in the Create a REST API from an OpenAPI Definition - basic flow guide to create the basic structure of the API interface using the following details.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| OpenAPI URL | https://petstore3.swagger.io/api/v3/openapi.json |
| Name | SwaggerPetstore |
| Context | /v3 |
| Version | 1.0.6 |
| Endpoint | Leave the endpoint field empty. |
Step 2 - Implement the API¶
The MWARE ESB Mock Implementation allows you to generate a mock payload based on an API definition that will mock the API responses. You can prototype an API using the inbuilt JavaScript engine without having to write the JavaScript implementation for each resource manually.
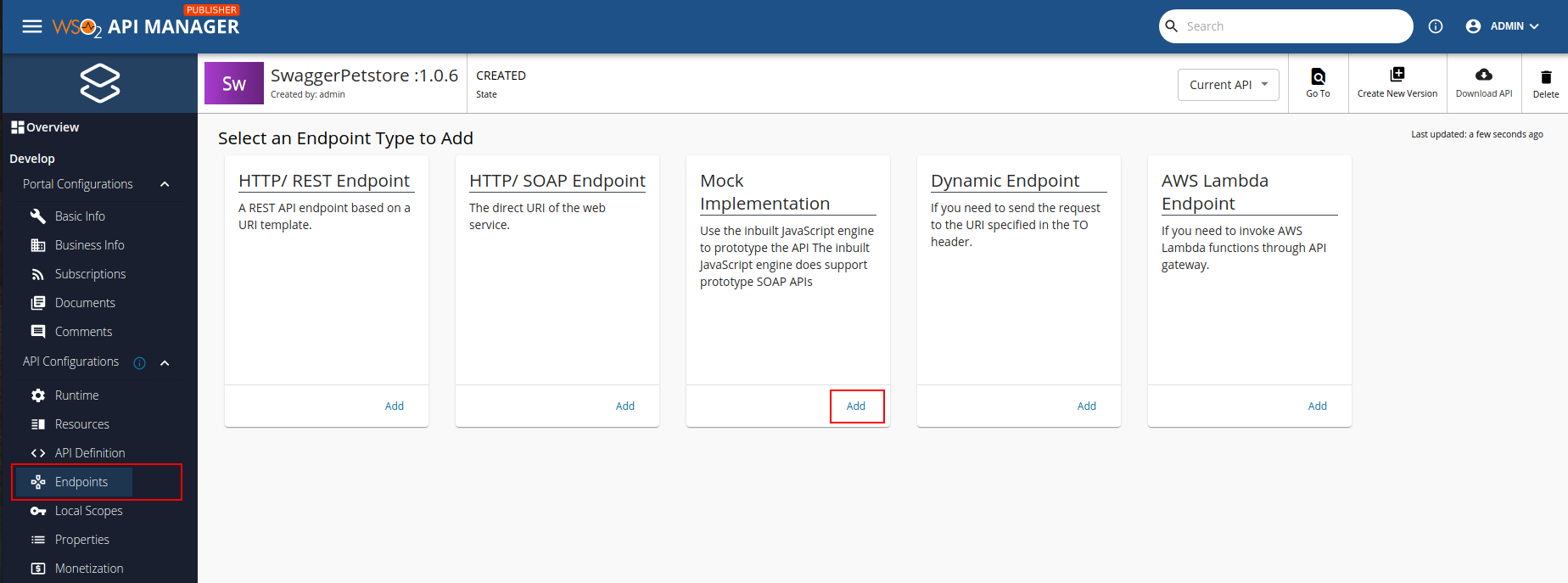
Follow the instructions below to add a mock implementation to the API:
-
Navigate to API Configurations and click Endpoints to navigate to the Endpoints page in the Publisher.
-
Select Mock Implementation as the endpoint type and click Add.
-
View the inline script that has been generated.
Click and expand any of the methods that contain a sample/mock payload.
Let's click on the
GET /pet/{petId}method.The example response defined in the OpenAPI definition is set as the mock response payload. You can modify the generated inline scripts as required.
Click here to view the inline Mock Implementation script.
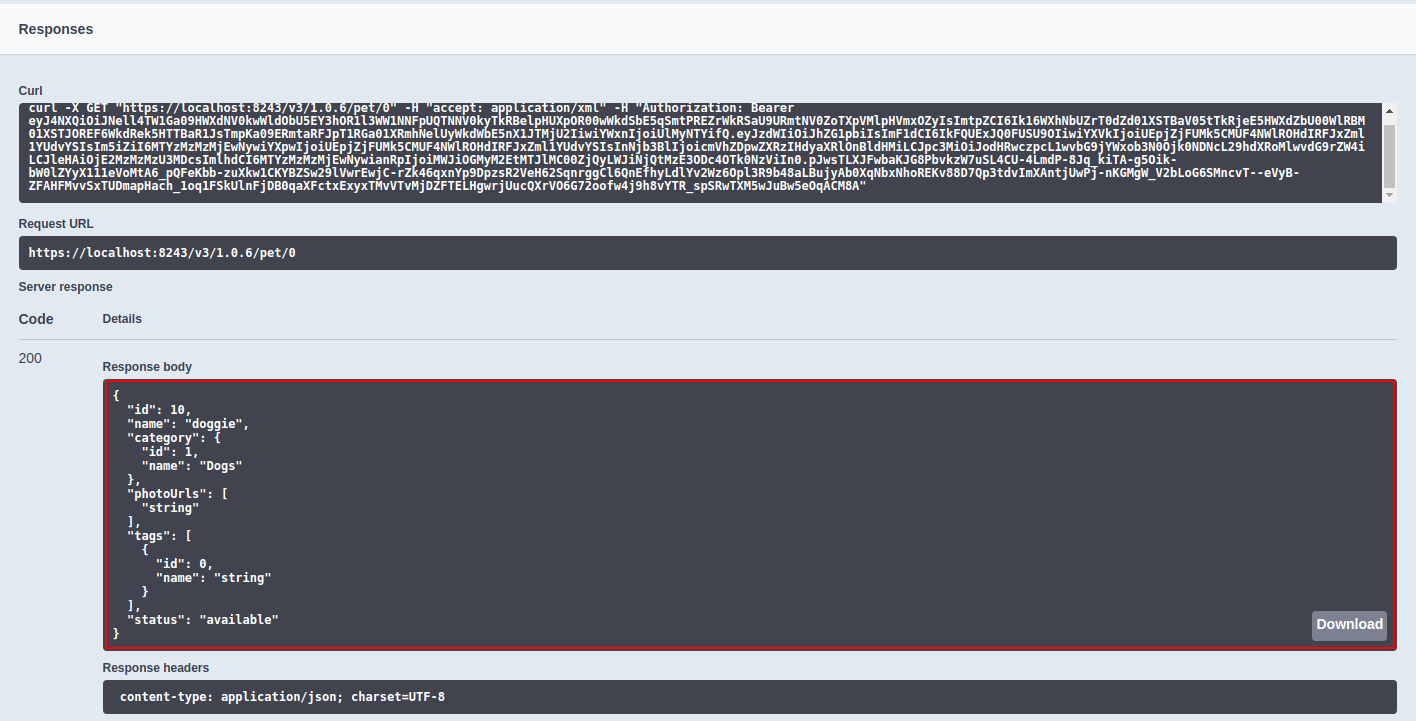
responses[200]["application/json"] = { // Mock response payload stored as a variable "id" : 10, "name" : "doggie", "category" : { "id" : 1, "name" : "Dogs" }, "photoUrls" : [ "string" ], "tags" : [ { "id" : 0, "name" : "string" } ], "status" : "available" }; mc.setProperty('CONTENT_TYPE', 'application/json'); // Set the content type of the payload to the message context mc.setPayloadJSON(response200json); // Set the new payload to the message context -
Modify the sample/mock payload as required.
For more information, see Inline Script Methods.
For example, let's modify the inline script for the
GET /pet/{petId}method by setting a path parameter entered by the user to a variable that will satisfy a condition and set a response accordingly.Tip
The RESET button appears after a change is made to the script. When pressed, the script will revert to the originally generated script.
Click here to view the modified inline Mock Implementation script.
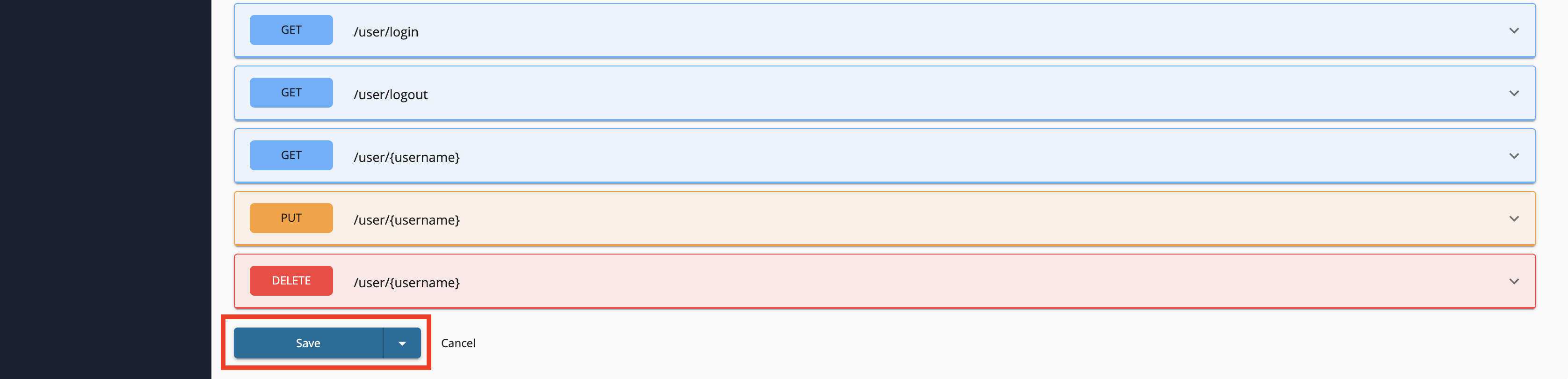
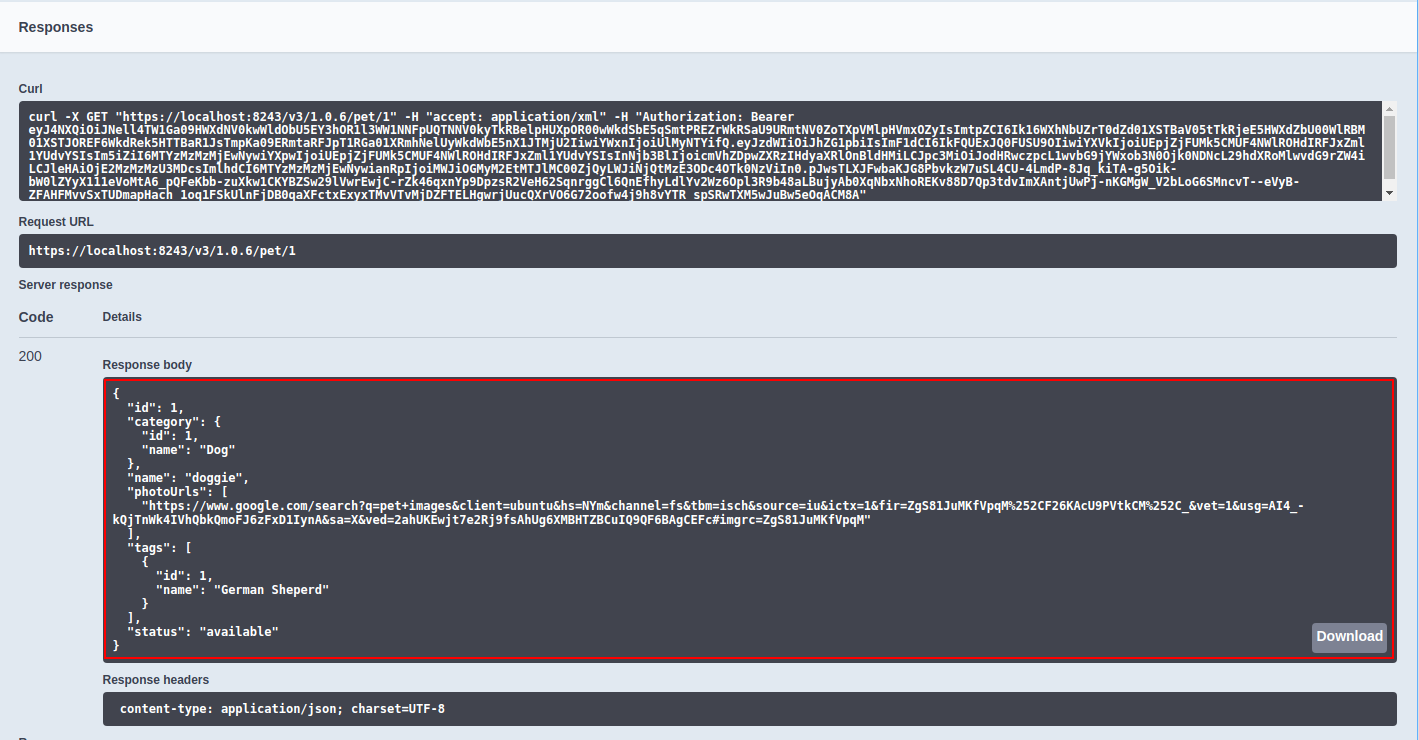
// **GENERATED CODE** // var responseCode = mc.getProperty('query.param.responseCode'); var responseCodeSC; var responses = []; if (!responses[200]) { responses [200] = []; } responses[200]["application/json"] = { "id" : 10, "name" : "doggie", "category" : { "id" : 1, "name" : "Dogs" }, "photoUrls" : [ "string" ], "tags" : [ { "id" : 0, "name" : "string" } ], "status" : "available" }; // **MANUALLY ADDED CODE** // if (mc.getProperty('uri.var.petId') == 1) { // Get the path parameter 'petID' to check the condition responses[200]["application/json"] = { "id" : 1, "category" : { "id" : 1, "name" : "Dog" }, "name" : "doggie", "photoUrls" : [ "https://www.google.com/search?q=pet+images&client=ubuntu&hs=NYm&channel=fs&tbm=isch&source=iu&ictx=1&fir=ZgS81JuMKfVpqM%252CF26KAcU9PVtkCM%252C_&vet=1&usg=AI4_-kQjTnWk4IVhQbkQmoFJ6zFxD1IynA&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjt7e2Rj9fsAhUg6XMBHTZBCuIQ9QF6BAgCEFc#imgrc=ZgS81JuMKfVpqM" ], "tags" : [ { "id" : 1, "name" : "German Sheperd" } ], "status" : "available" } } if (!responses[400]) { responses[400] = []; } responses[400]["application/json"] = ""; if (!responses[404]) { responses[404] = []; } responses[404]["application/json"] = ""; responses[501] = []; responses[501]["application/json"] = { "code" : 501, "description" : "Not Implemented"} if (responseCode == null) { responseCode = 200; } if (!responses[responseCode]) { if (responses["default"]) { responseCode = "default" } else { responseCode = 501; } } if (responseCode === "default") { responseCodeSC = mc.getProperty('query.param.responseCode'); } else { responseCodeSC = responseCode; } mc.setProperty('CONTENT_TYPE', 'application/json'); // Set the content type of the payload to the message context mc.setProperty('HTTP_SC', responseCodeSC + ""); mc.setPayloadJSON(responses[responseCode]["application/json"]); // Set the new payload to the message context -
Click Save to save the endpoint configurations in the API.
Step 3 - Deploy the API¶
Deploy the API in order to make the API available in the respective Gateway.
Step 4 - Test the API via the Publisher¶
Once deployed to the Gateway, you can test the REST type APIs via the Publisher Portal.
Step 5 - Publish the API as a Prototype¶
Important
- By default, from MWARE ESB 4.1.0 onwards, security is enabled for all the resources of the Prototype API. As a result, you need a subscription to invoke the API.
-
Skip this step if you have disabled security for all the resources in the API.
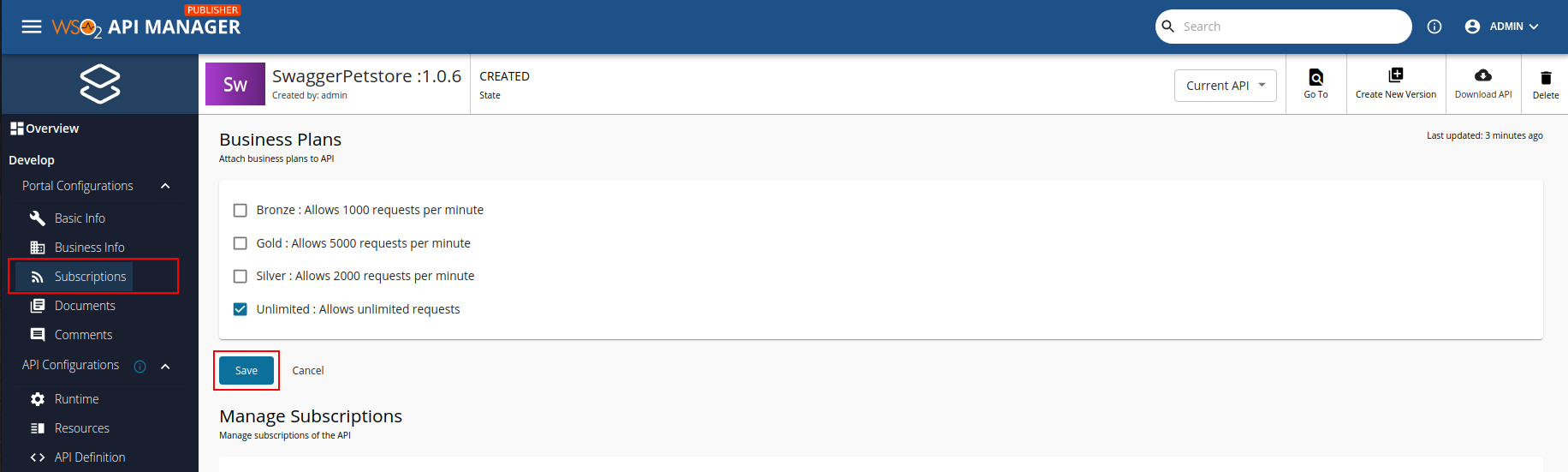
Follow the instructions below to attach Business Plans to the API.
-
Navigate to Portal Configurations and click Subscriptions.
-
Select the required Business Plans and click Save.
-
Follow the instructions below to publish the API to the Developer Portal as a Prototype:
-
Navigate to the Lifecycle page listed under Publish.
For both options, When creating an API with the Mock Implementation and When creating an API with an actual backend URL, you will have the option to either promote your API to the PRE-RELEASED state or to the PUBLISHED state in the API lifecycle.
-
Click Pre-Release to publish the API as a Prototype API to the Developer Portal
Step 6 - Invoke the API¶
-
Click View in Dev Portal to navigate to the Developer Portal.
Note
If you have enabled security for the prototype API, follow the Subscribe to an API guide to subscribe and obtain an access token to invoke the prototype API.
-
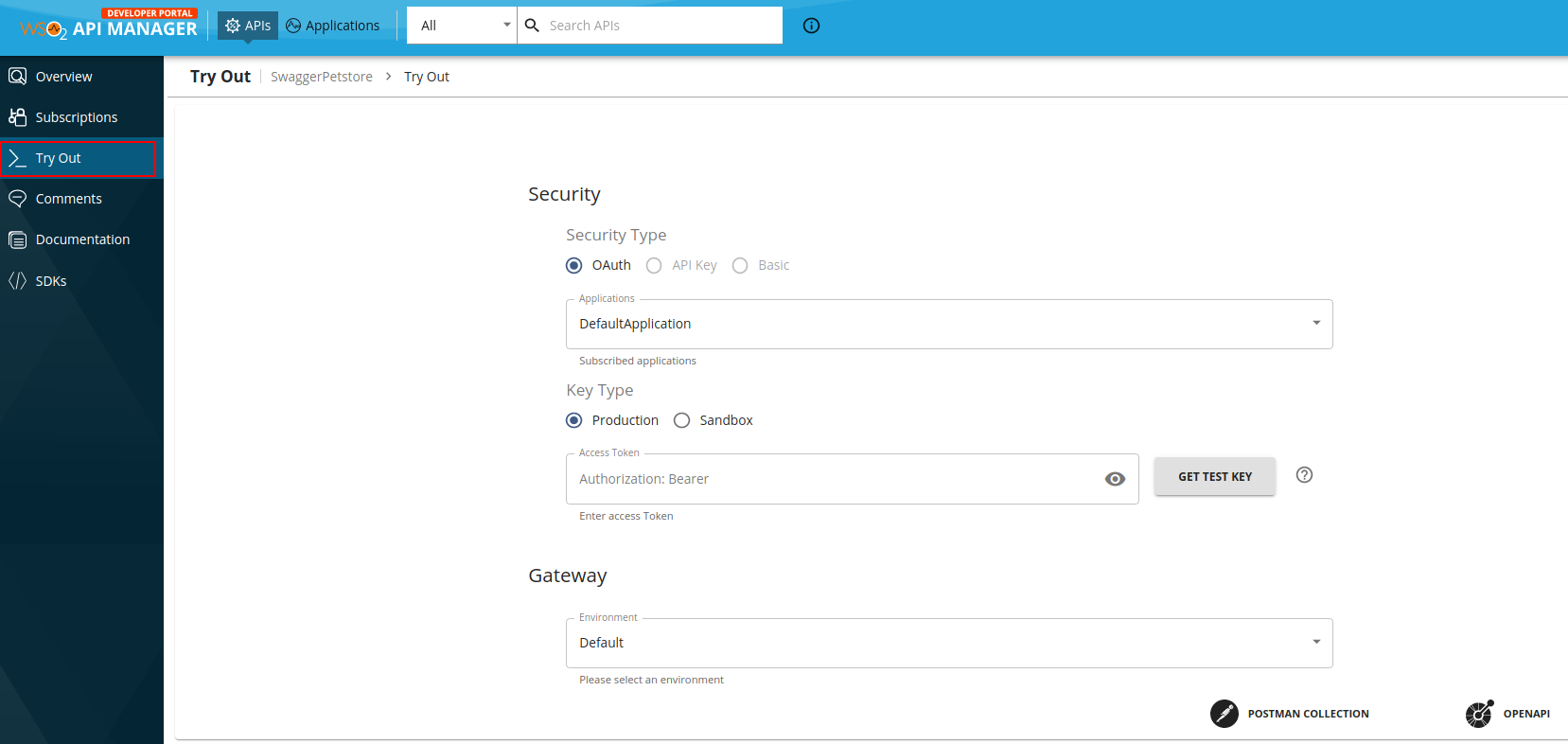
Click Try Out to navigate to the API Console.
-
If you have enabled security, you can either use the access token that you got from the above step or use the GET TEST KEY option.
Note
Skip this step if you have disabled security for the API, and leave the Access Token field empty.
-
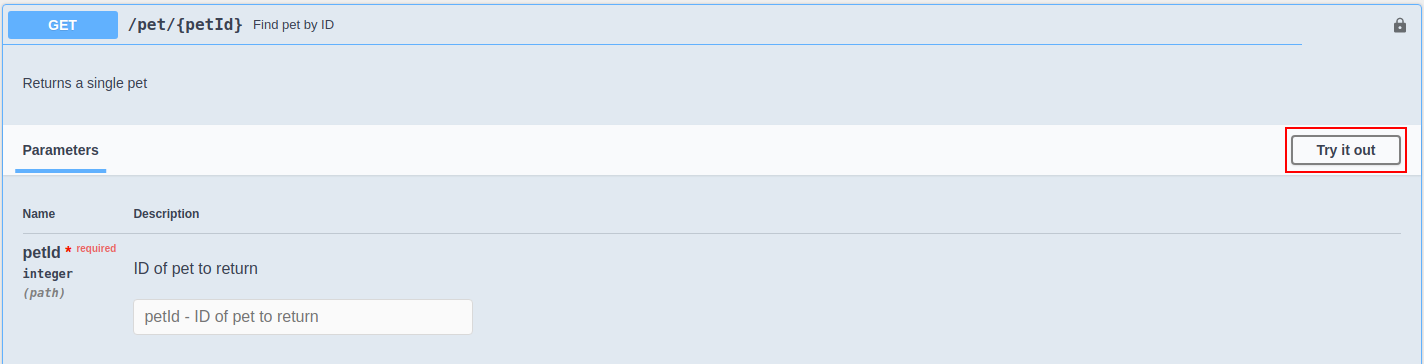
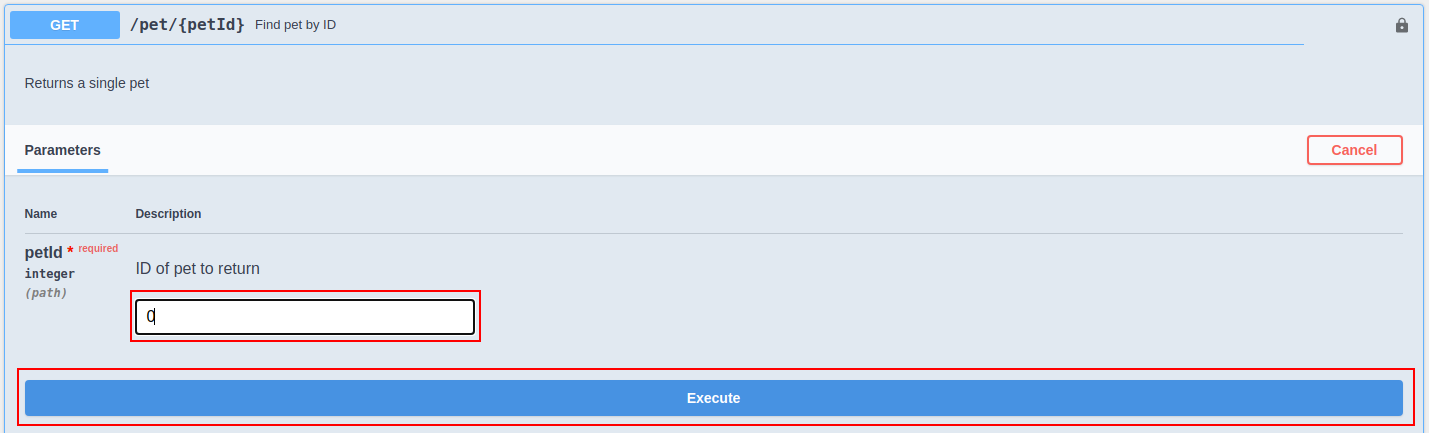
Expand any method and click Try it out.
-
Enter the value for the parameter and click Execute to invoke the API.
Note
The payload that you gave as a JSON/XML output appears in the response for each respective parameter provided.
Additional Information¶
Inline Script Methods¶
The following table lists down the mc. methods that you can use to invoke functions in the inline script. You can use these functions to access the Synapse predefined in a script variable named mc. The mc variable represents an implementation of the MessageContext, named ScriptMessageContext.java, which contains the following methods that you can access within the script as mc.methodName.
| Return? | Method Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | getPayloadXML() |
This gets an XML representation of SOAP body payload. |
| No | setPayloadXML(payload) |
This sets the SOAP body payload from XML. |
| Yes | getEnvelopeXML() |
This gets the XML representation of the complete SOAP envelope. |
| No | setTo(reference) |
This is used to set the value that specifies the receiver of the message. |
| Yes | setFaultTo(reference) |
This is used to set the value that specifies the receiver of the faults relating to the message. |
| No | setFrom(reference) |
This is used to set the value that specifies the sender of the message. |
| No | setReplyTo(reference) |
This is used to set the value that specifies the receiver of the replies to the message. |
| Yes | getPayloadJSON() |
This gets the JSON representation of a SOAP Body payload. |
| No | setPayloadJSON(payload) |
This sets the JSON representation of a payload obtained via the getPayloadJSON() method and sets it in the current message context. |
| Yes | getProperty(name) |
This gets a property from the current message context. |
| No | setProperty(key, value) |
This is used to set a property in the current message context. The previously set property values are replaced by this method. |
See Also¶
Learn more on the concepts that you need to know when creating a Prototype API:
- Endpoints
- API Security
- Rate Limiting
- Life Cycle Management
- API Monetization
- API Visibility
- API Documentation
- Custom Properties