Streaming Integration Overview¶
This section helps you to understand streaming integration and how to perform it with ESB Streaming Integrator in less than 30 minutes
First, let's understand the concept of streaming integration. For this, let's consider an example of a sweet factory where the system publishes the production details after each production run. The details published include the name of the sweet and the amount produced.
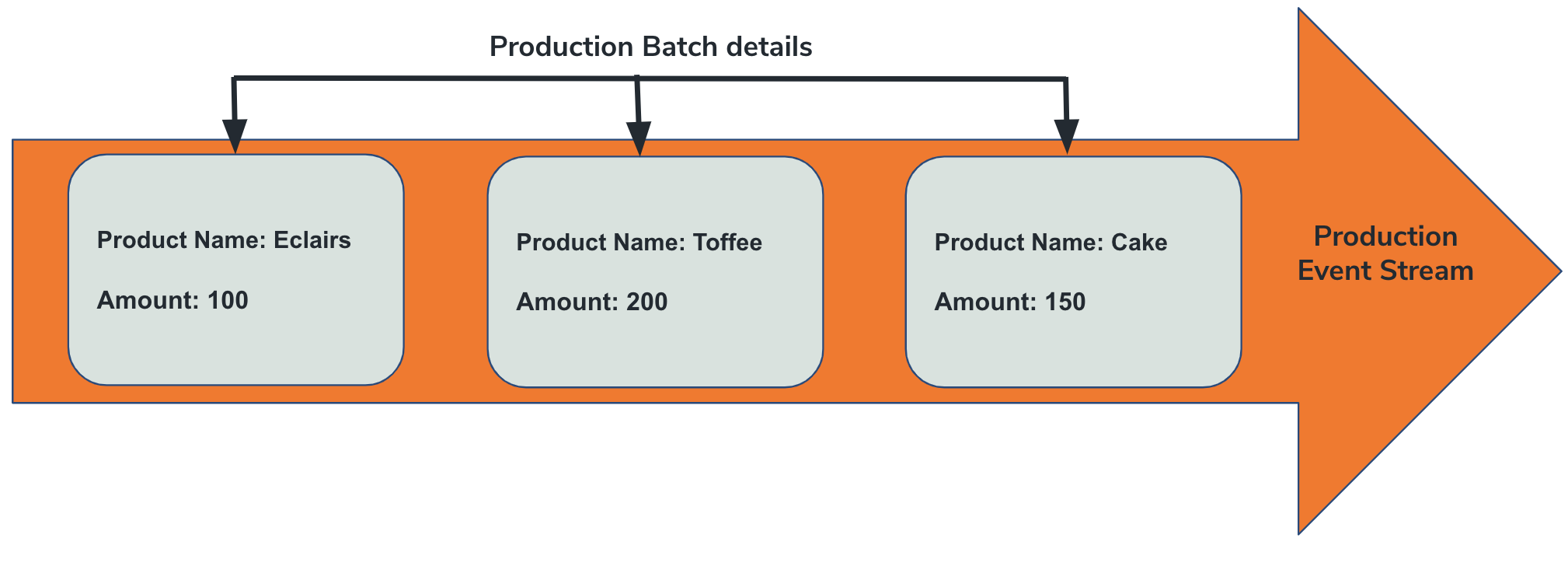
Each production run that reports the name of the sweet and the amount is an event.
Many such events form a stream.
In Streaming typically involves handling data received/published via streams in high speed and high volume. In this example, there can be multiple factories in several locations that results in a few production runs being reported in a given second.
ESB Streaming Integrator allows data to be received from multiple sources such as files, databases, cloud-based applications, and streaming messaging systems (such as Kafka) in a streaming manner. It uses the Siddhi Query Language, to process this data, and then publishes the results in a streaming manner to multiples destinations such as files, databases, cloud-based applications, and streaming messaging systems in a streaming manner.
Streaming Integration involves processing streaming data and incorporating them into integration flows so that action can be taken based on the output derived. In this example, you may want to filter production details relating to a specific sweet.
To understand how Streaming Integration is performed via the ESB Streaming Integrator, follow the sections below.
Step 1: Download Streaming Integrator and Dependencies
Step 2: Create the Siddhi Application
Step 3: Deploy the Siddhi Application
Step 4: Run the Siddhi Application
Step 5: Update the Siddhi Application
Step 6: Handle Errors
Step 7: Monitor Statistics