Synapse Handlers¶
This section gives an introduction to what a handler is and describes how you can write a synapse handler by walking you through a basic example.
What is a Synapse Handler?¶
Synapse Handlers can be used to process requests in a scenario where you have multiple requests and each request needs be processed in a specific manner. A Handler defines the interface that is required to handle the request and concreteHandlers are to handle requests in a specific manner based on what needs to be done with regard to each type of request. The diagram below illustrates this.
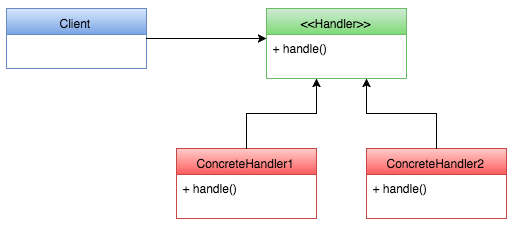
Synapse handler is the interface used to register server response callbacks. Synapse handler provides the abstract handler implementation that executes the request in flow, request out flow, response in flow and response out flow. The diagram below is an illustration of how the specified flows execute in the abstract handler implementation.
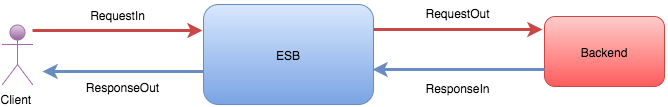
-
Request in flow This executes when the request reaches the synapse engine.
public boolean handleRequestInFlow(MessageContext synCtx); -
Request out flow This executes when the request goes out of the synapse engine.
public boolean handleRequestOutFlow(MessageContext synCtx); -
Response in flow This executes when the response reaches the synapse engine.
public boolean handleResponseInFlow(MessageContext synCtx); -
Response out flow This executes when the response goes out of the synapse engine.
public boolean handleResponseOutFlow(MessageContext synCtx);
The diagram below illustrates the basic component structure of ESB Micro Integrator and how the flows mentioned above execute in the request path and the response path.
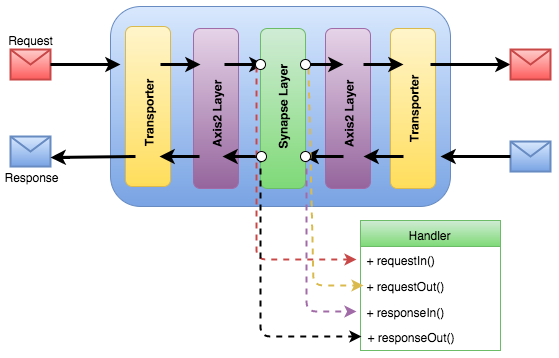
Now that you understand what a handler is, let's see how you can write a concrete Synapse handler.
Step 1: Writing a concrete Synapse handler¶
The easiest way to write a concrete Synapse handler is to extend the org.apache.synapse.AbstractSynapseHandler class. You can also write a concrete Synapse handler by implementing org.apache.synapse.SynapseHandler, which is the SynapseHandler interface.
Following is an example Synapse handler implementation that extends the org.apache.synapse.AbstractSynapseHandler class:
public class TestHandler extends AbstractSynapseHandler {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(TestHandler.class);
@Override
public boolean handleRequestInFlow(MessageContext synCtx) {
log.info("Request In Flow");
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean handleRequestOutFlow(MessageContext synCtx) {
log.info("Request Out Flow");
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean handleResponseInFlow(MessageContext synCtx) {
log.info("Response In Flow");
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean handleResponseOutFlow(MessageContext synCtx) {
log.info("Response Out Flow");
return true;
}
}Step 2: Deploying the Synapse handler¶
To deploy your custom synapse handler in ESB Micro Integrator, bundle the artifact as a JAR file (with either the .jar or .xar format), and add it to the MI_HOME/lib/ directory. Be sure to restart the server after adding the files.
Step 3: Engaging the Synapse handler¶
To engage the deployed Synapse handler, you need to add the following configuration to the deployment.toml file.
[synapse_handlers]
<handlerName>.enabled = true
<handlerName>.class = "<packageName>.<handlerName>"