K8s Deployment Sample 1: Hello World Scenario¶
Let's define a basic Hello World scenario using ESB Micro Integrator and deploy it on your Kubernetes environment.
Prerequisites¶
- Install and set up ESB Integration Studio.
- Install a Kubernetes cluster and v1.11+ client. Alternatively, you can run Kubernetes locally via Minikube.
- Install Docker.
- Install the Kubernetes API Operator.
Step 1 - Create the integration solution¶
Let's use an integration template in ESB Integration Studio to generate a sample integration solution that returns a 'Hello World' response when invoked.
- Open ESB Integration Studio.
-
In the Getting Started view, select the Hello Kubernetes template.
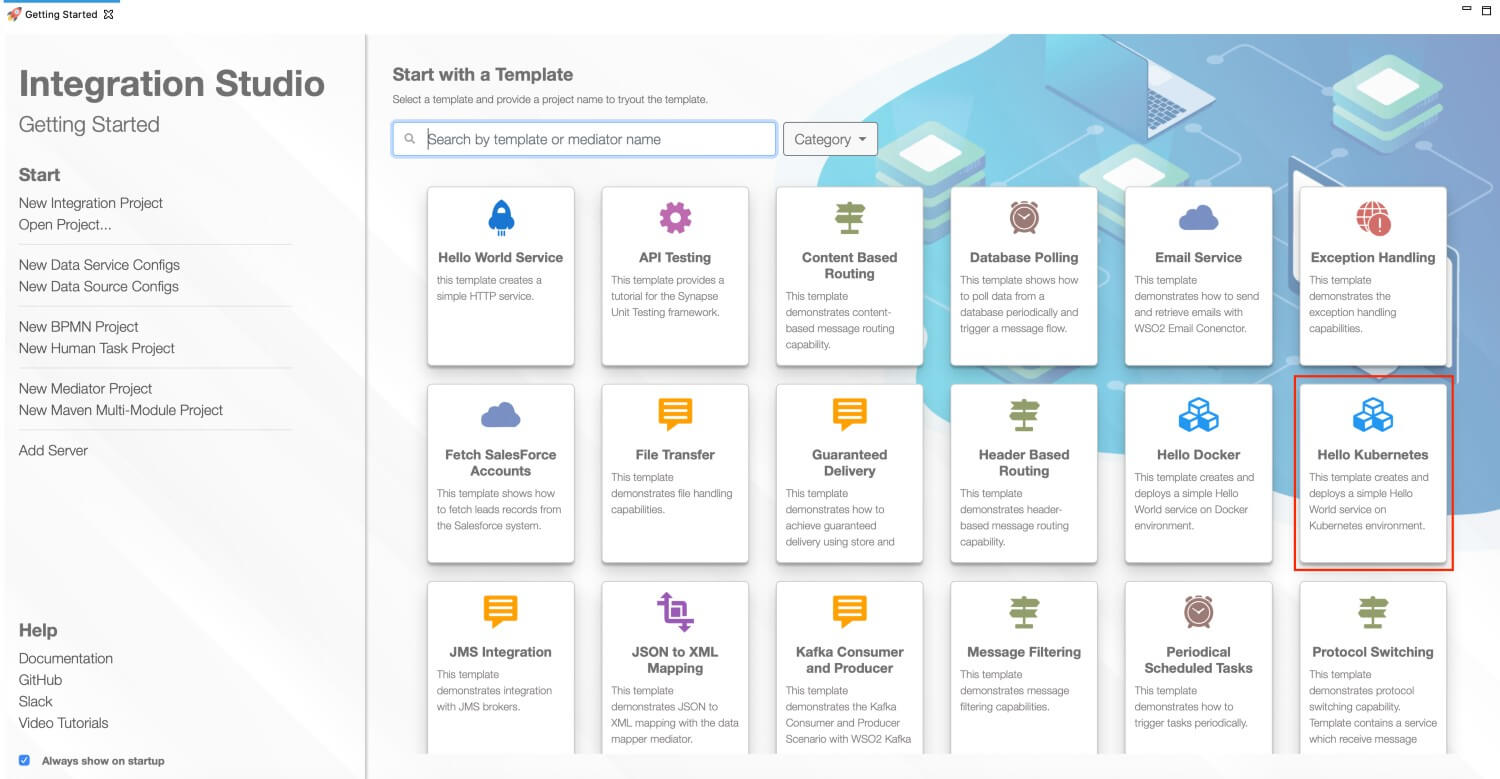
-
Give a project name and click Finish.
This generates the complete integration project with the 'Hello World' solution, which is ready to be deployed in Kubernetes.

Step 2 - Build and Push the Docker image¶
Note
Be sure to start your Docker instance before building the image. If Docker is not started, the build process will fail.
There are two ways to build a Docker image of the integration solution and push it to your Docker registry:
-
Using Maven:
Before you begin
You need Maven 3.5.2 or a later version when you build the Docker image manually (without using ESB Integration Studio).
- Open a terminal and navigate to the integration project.
-
Execute the following command.
Be sure to specify the user name and password of the correct Docker registry.
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true -Ddockerfile.username={username} -Ddockerfile.password={password}
This will build the Docker image and then push it to the specified Docker registry.
-
Using ESB Integration Studio:
-
Open the pom.xml file in the Kubernetes project as shown below.

-
Ensure that the composite exporter is selected under Dependencies.
- In the Target Repository field, enter the name of the Docker registry to which you will push a Docker image.
- Click Build & Push to build the image and push to the Docker registry.
-
In the dialog box that opens, enter the credentials of your Docker registry to which the image should be pushed.
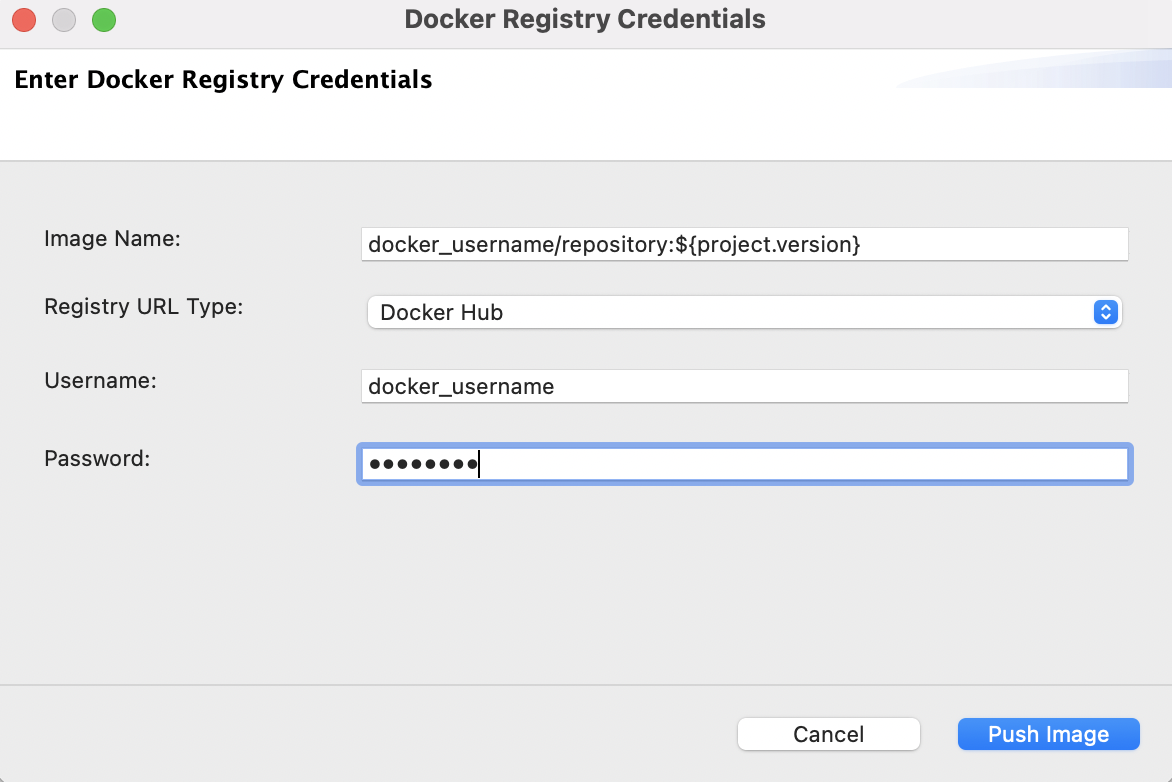
-
Click Push Image.
-
Run the docker image ls command to verify that the Docker image is created.
Step 3 - Deploy the solution in K8s¶
Info
Before you begin, the API Kubernetes Operator should be installed in your Kubernetes environment.
Follow the steps given below.
- Open the
integration_cr.yamlfile from the Kubernetes exporter in ESB Integration Studio. -
See that the integration details of the
hello-worldsolution are updated. Be sure to add the image name in the following format:docker_user/repository:tagapiVersion: "wso2.com/v1alpha2" kind: "Integration" metadata: name: "hello-world" spec: image: "<Docker image for the Hello World Scenario>" deploySpec: minReplicas: 1 -
Open a terminal and start the Kubernetes cluster.
-
Navigate to the location of your
integration_cr.yamlfile and execute the following command to deploy the integration solution in the Kubernetes cluster:kubectl apply -f integration_cr.yaml
When the integration is successfully deployed, it should create the hello-world integration, hello-world-deployment, hello-world-service, and ei-operator-ingress as follows:
Tip
The ei-operator-ingress is not created if you have disabled the ingress controller.
kubectl get integration
NAME STATUS SERVICE-NAME AGE
hello-world Running hello-service 2m
kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hello-world-deployment 1/1 1 1 2m
kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hello-world-service ClusterIP 10.101.107.154 <none> 8290/TCP 2m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 2d
k8s-api-operator ClusterIP 10.98.78.238 <none> 443/TCP 1d
kubectl get ingress
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
api-operator-ingress wso2ei.ingress.wso2.com 10.0.2.15 80, 443 2mStep 4 - Test the deployment¶
Let's invoke the service without going through the ingress controller.
-
Apply port forwarding as shown below. This will allow you to invoke the service without going through the Ingress controller:
kubectl port-forward service/hello-world-service 8290:8290 -
Invoke the service as follows:
curl http://localhost:8290/HelloWorld
You will receive the following response:
{"Hello":"World"}%