Publishing Data¶
This guide covers how ESB Streaming Integrator publishes data to destinations and messaging systems.
Publishing data to destinations¶
Publishing to destinations involve using transports such as HTTP, TCP, email, etc., where the data is sent to an endpoint that is available to listen to messages and respond.
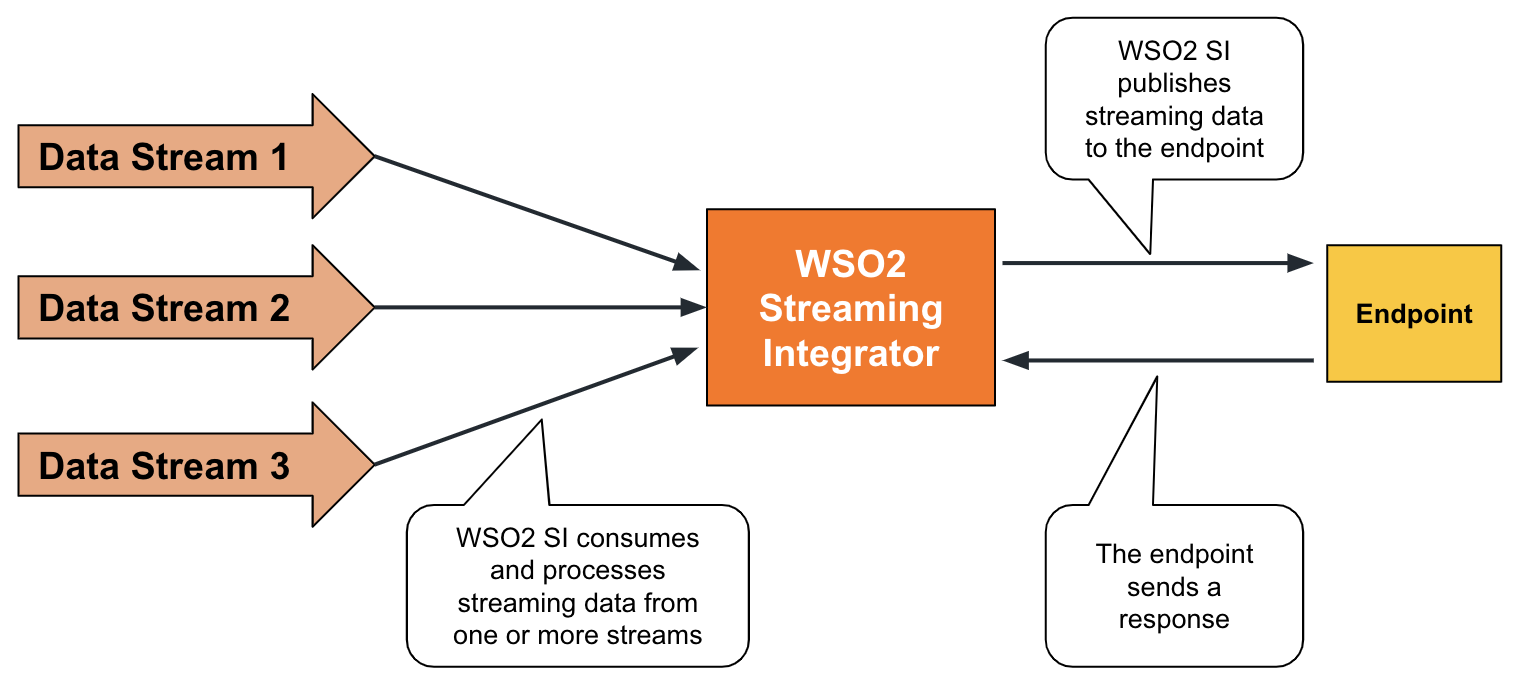
To understand this, consider a warehouse that needs to publish each stock update to a specific endpoint so that the stock can be monitored by the warehouse manager. To address this requirement via the ESB Streaming Integrator, you can define an output stream and connect a sink to it as shown below. In this example, let's use an HTTP sink.
@sink(type = 'http', publisher.url = 'http://stocks.com/stocks',
@map(type = 'json'))
define stream StockStream (symbol string, price float, volume long);The above sink configuration publishes all the events in the StockStream output stream to the http://stocks.com/stocks HTTP URL in JSON format.
Try it out¶
To try out the above example, follow the steps below:
-
Open a new file and copy the following Siddhi Application to it.
@App:name("PublishStockUpdatesApp") define stream InputStream (symbol string, price float, volume long); @sink(type = 'http', publisher.url = 'http://localhost:5005/stocks', @map(type = 'json')) define stream StockStream (symbol string, price float, volume long); from InputStream select * insert into StockStream;
Save the Siddhi application.
This Siddhi application publishes stock updates as HTTP events via the http sink in the previous example.
-
To monitor whether the HTTP events generated via the
PublishStockUpdatesAppSiddhi application are getting published to thehttp://localhost:5005/stocksURL as specified, create and save another Siddhi Application as follows:@App:name('ListenToStockUpdatesApp') @source(type = 'http', receiver.url = "http://localhost:5005/stocks", @map(type = 'json')) define stream StockStream (symbol string, price float, volume long); @sink(type = 'log', prefix = "Stock Updates", @map(type = 'passThrough')) define stream OutputStream (symbol string, price float, volume long); @info(name = 'query1') from StockStream select * insert into OutputStream;This Siddhi application listens for events in the
http://localhost:5005/stocksendpoint and logs them in the Streaming Integrator Tooling console. -
Start both the Siddhi applications. To do this, open each siddhi application and click the Play icon.

-
Simulate an event with the following values for the
InputStreamstream of thePublishStockUpdatesAppSiddhi application. For instructions to simulate events, see Testing Siddhi Applications - Simulating Events.Attribute Value symbol ABCprice 100volume 20As a result, the
ListenToStockUpdatesSiddhi applications prints the following log in the Streaming Integrator Tooling Console.[2020-10-28_10-59-20_463] INFO {io.siddhi.core.stream.output.sink.LogSink} - Stock Updates : Event{timestamp=1603862960462, data=[ABC, 100.0, 20], isExpired=false}
Supported transports¶
ESB Streaming Integrator supports the following transport types to send messages to destinations.
| Transport | Supporting Siddhi Extension |
|---|---|
http |
http |
tcp |
tcp |
email |
|
grpc |
grpc |
Thrift |
Supported mappers¶
Mappers determine the format in which the event is published. For information about transforming events by changing the format in which the data is published, see Transforming Data.
The following are the supported mappers when you publish data to destinations.
| Transport | Supporting Siddhi Extension |
|---|---|
json |
json |
xml |
xml |
text |
text |
avro |
avro |
binary |
binary |
Publishing data to messaging systems¶
ESB Streaming Integrator allows you to publish data to messaging systems such as Kafka, JMS, NATS, GooglePubSub, etc. so that you can expose streaming data to applications that cannot read streaming data, but are able to subscribe for data in messaging systems.
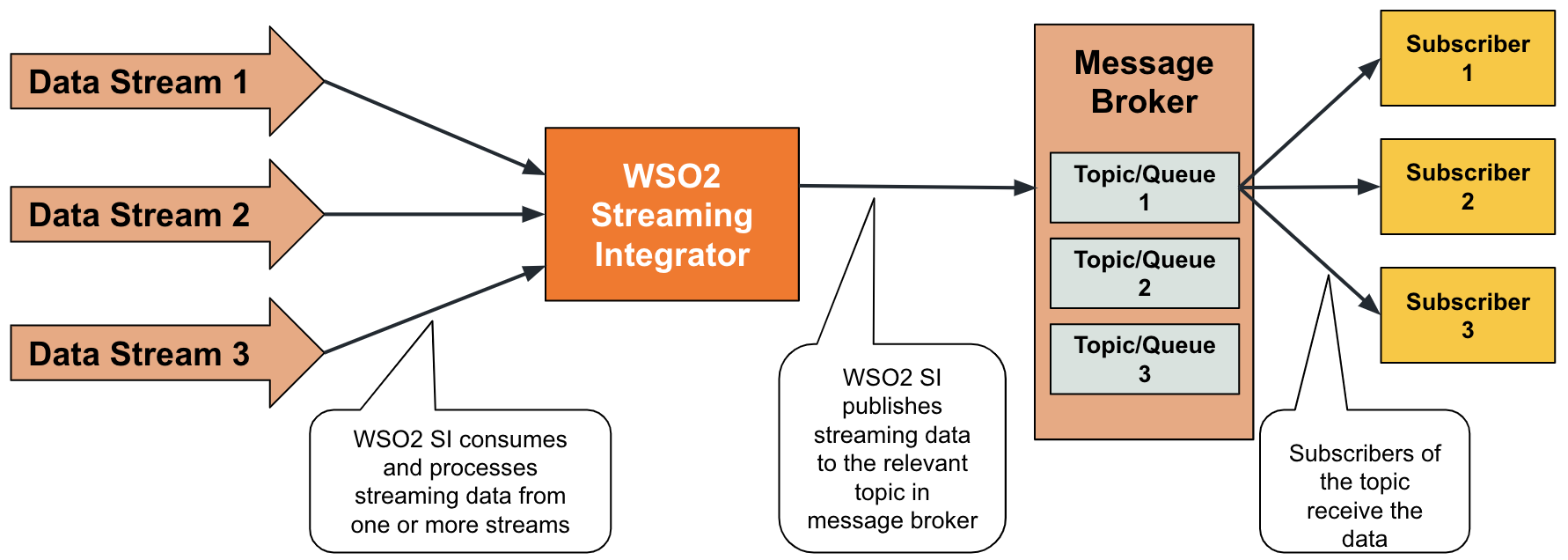
To understand this, consider a scenario where temperature readings from a sensor are published into a Kafka topic so that other devices that need to consume that data can subscribe for it. You can address this requirement via ESB Streaming Integrator by defining an output stream and then connecting a sink to it as shown in the example below.
@sink(type = 'kafka', bootstrap.servers = "localhost:9092", topic = "temperature",
@map(type = 'json'))
define stream PublishTemperatureStream (temperature int);The above sink configuration of the kafka type publishes all the events in the PublishTemperatureStream stream to a Kafka topic named temperature running in the localhost:9092 server. The messages are published in json format.
Try it out¶
To try out the example in the previous subtopic, follow the steps below:
-
Download the Kafka broker from the Apache site and extract it. This directory is referred to as
<KAFKA_HOME>from here on. -
Start Kafka as follows:
-
First, start a zoo keeper node. To do this, navigate to the
<KAFKA_HOME>directory and issue the following command.sh bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties -
Next, start a Kafka server node. To do this, issue the following command from the same directory.
sh bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties -
To create a Kafka topic named
temperature, issue the following command from the same directory.bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic temperature
-
-
Prepare ESB Streaming Integrator Tooling to publish data to a Kafka topic as follows:
-
Start and access ESB Streaming Integrator Tooling.
-
Download and install the Kafka extension to it. For instructions, see Installing Siddhi Extensions.
-
Open a new file and add the following Siddhi application to it.
Save the Siddhi application.@App:name('TemperaturePublishingApp') @sink(type = 'kafka', bootstrap.servers = "localhost:9092", topic = "temperature", @map(type = 'json')) define stream PublishTemperatureStream (temperature int); define stream TemperatureStream (temperature int); from TemperatureStream select * insert into PublishTemperatureStream;
The above Siddhi application includes the sink configuration from the previous example. The Siddhi query takes all the input events in the
TemperatureStreamstream and inserts them into thePublishTemperatureStreamstream so that they can be published to thetemperatureKafka topic via the connected source.-
Start the Siddhi application by clicking the Play icon in the top panel for it.

-
Simulate an event for the
TemperatureStreamstream of theTemperaturePublishingAppSiddhi application. In this example, let's enter30as the value for thetemperatureattribute.For instructions to simulate events, see Testing Siddhi Applications - Simulating Events.
-
To retrieve the events published to the Kafka topic, issue the following command from
<KAFKA_HOME>bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic temperature --from-beginningYou can see the following in the Kafka consumer log.
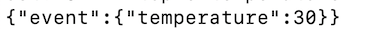
-
Supported messaging systems¶
ESB Streaming Integrator allows you to publish messages to the following messaging system via Siddhi extensions.
| Transport | Supporting Siddhi Extension |
|---|---|
kafka |
kafka |
NATS |
NATS |
Google Pub/Sub |
Google Pub/Sub |
rabbitmq |
rabbitmq |
jms |
jms |
mqtt |
mqtt |
sqs |
sqs |
Supported mappers¶
Mappers determine the format in which the event is published. For information about transforming events by changing the format in which the data is published, see Transforming Data.
The following are the supported mappers when you publish data to destinations.
| Transport | Supporting Siddhi Extension |
|---|---|
json |
json |
xml |
xml |
text |
text |
avro |
avro |
binary |
binary |