Working with Message Builders and Formatters¶
Overview¶
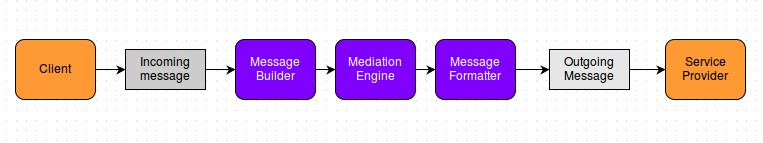
When a message comes in to ESB Micro Integrator, the receiving transport selects a message builder based on the message's content type. It uses that builder to process the message's raw payload data and convert it into SOAP. Conversely, when sending a message out from Micro Integrator, a message formatter is used to build the outgoing stream from the message. As with message builders, the message formatter is selected based on the message's content type. Given below is the typical workflow:
You can use the messageType property to change the message's content type as it flows through the Micro Integrator. For example, if the incoming message is in JSON format and you want to transform it to XML, you could add the messageType property before your mediators in the configuration:
<property name="messageType" value="application/xml" scope="axis2"/>Default message builders and formatters¶
Listed below are the default message builders and formatters that are enabled for ESB Micro Integrator by default:
application_xml = "org.apache.axis2.builder.ApplicationXMLBuilder"
form_urlencoded = "org.apache.synapse.commons.builders.XFormURLEncodedBuilder"
multipart_form_data = "org.apache.axis2.builder.MultipartFormDataBuilder"
text_plain = "org.apache.axis2.format.PlainTextBuilder"
application_json = "org.wso2.micro.integrator.core.json.JsonStreamBuilder"
json_badgerfish = "org.apache.axis2.json.JSONBadgerfishOMBuilder"
text_javascript = "org.apache.axis2.json.JSONBuilder"
octet_stream = "org.wso2.carbon.relay.BinaryRelayBuilder"
application_binary = "org.apache.axis2.format.BinaryBuilder"form_urlencoded = "org.apache.synapse.commons.formatters.XFormURLEncodedFormatter"
multipart_form_data = "org.apache.axis2.transport.http.MultipartFormDataFormatter"
application_xml = "org.apache.axis2.transport.http.ApplicationXMLFormatter"
text_xml = "org.apache.axis2.transport.http.SOAPMessageFormatter"
soap_xml = "org.apache.axis2.transport.http.SOAPMessageFormatter"
text_plain = "org.apache.axis2.format.PlainTextFormatter"
application_json = "org.wso2.micro.integrator.core.json.JsonStreamFormatter"
json_badgerfish = "org.apache.axis2.json.JSONBadgerfishMessageFormatter"
text_javascript = "org.apache.axis2.json.JSONMessageFormatter"
octet_stream = "org.wso2.carbon.relay.ExpandingMessageFormatter"
application_binary = "org.apache.axis2.format.BinaryFormatter"Configuring message builders/formatters¶
Handling message relay¶
If you want to enable message relay, so that messages of a specific content type are not built or formatted but simply pass through the Micro Integrator, you can specify the message relay builder (for the required content types) in the deployment.toml file (stored in the MI_HOME/conf directory) as shown below.
[[custom_message_formatters]]
class = "org.wso2.carbon.relay.BinaryRelayBuilder"
content_type = "application/json/badgerfish"
[[custom_message_builders]]
class = "org.wso2.carbon.relay.BinaryRelayBuilder"
content_type = "application/json/badgerfish"See Configuring Message Relay.
Handling messages with no content type¶
To ensure that messages with no content type are handled gracefully, add the following to the deployment.toml file (stored in the MI_HOME/conf directory).
[[custom_message_builders]]
content_type = "empty/content"
class="org.wso2.carbon.relay.BinaryRelayBuilder"
[[custom_message_formatters]]
content_type = "empty/content"
class="org.wso2.carbon.relay.ExpandingMessageFormatter"
[transport]
default_content_type = "empty/content"Handling text/csv messages¶
There is no default builder or formatter for messages with the text/csv content type. If you just want to pass these messages through the Micro Integrator, you can configure the message relay builder and formatter.
The following default message builder configurations allow you to access the content inside the request/response payload when the content type is CSV.
[message_builders]
text_plain = "org.apache.axis2.format.PlainTextBuilder"
[message_formatters]
text_plain = "org.apache.axis2.format.PlainTextFormatter"When a text/csv message comes into the Micro Integrator, the log will include an entry similar to the following, and you can observe that the CSV data is placed inside the payload:
[2013-05-09 13:59:03,478] INFO - LogMediator To: , WSAction: urn:mediate, SOAPAction: urn:mediate, MessageID: urn:uuid:5B9A211341DCC368241368088143463, Direction: request, Envelope: <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?><soapenv:envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"><soapenv:body><text xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/commons/ns/payload">charitha,wso2,colombo chamara,wso2G,galle </text></soapenv:body></soapenv:envelope>Handling illegal XML characters in plain text payloads¶
Plain text payloads that contain illegal XML characters (such as
unicodes) will not be successfully processed by the Micro Integrator. Therefore, you
must configure the system to replace the illegal characters in the
payload with an actual character. To enable this configuration, add the
parameter shown below (with a suitable unicode value) to the
XMLOutputFactory.properties file (stored in the
MI_HOME/ directory). If this file does not exist in
your product by default, be sure to create a new file.
When this configuration is enabled, all the illegal characters found in a payload will be replaced with the actual character that is represented by the unicode value that you specify for the parameter. The below example uses whitespaces (represented by by the ' \u0020' unicode value) to replace illegal characters in payloads.
com.ctc.wstx.outputInvalidCharHandler.char=\u0020Validating JSON messages¶
If you want the JSON builder to validate JSON messages that are received by the Micro Integrator, the following property should be added to the deployment.toml file. This validation ensures that erroneous JSON messages are rejected by the Micro Integrator.
[[transport.http]]
force_json_validation=falseWriting a custom Message Builder and Formatter¶
In addition to using the default message builders and formatters in ESB Micro Integrator, you can create your own custom message builders and formatters.
Custom message builder¶
Let's look at how to create a custom message builder using a sample scenario where you need to Base64 encode an XML entry field. In this sample, you retrieve the text content from the payload and then Base64 encode the text. This is then converted to SOAP, and the content is then processed in the ESB Micro Integrator mediation flow.
-
You will first need to write a class implementing the
org.apache.axis2.builder.Builderinterface in the Axis2 Kernel module and then override theprocessDocumentmethod. Within theprocessDocumentmethod, you can define your specific logic to process the payload content as required and then convert it to SOAP format.package org.test.builder; import org.apache.axiom.om.OMAbstractFactory; import org.apache.axiom.om.OMElement; import org.apache.axiom.om.impl.OMNodeEx; import org.apache.axiom.om.impl.builder.StAXBuilder; import org.apache.axiom.om.impl.builder.StAXOMBuilder; import org.apache.axiom.om.util.StAXParserConfiguration; import org.apache.axiom.om.util.StAXUtils; import org.apache.axiom.soap.SOAPBody; import org.apache.axiom.soap.SOAPEnvelope; import org.apache.axiom.soap.SOAPFactory; import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault; import org.apache.axis2.Constants; import org.apache.axis2.builder.Builder; import org.apache.axis2.context.MessageContext; import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; import javax.xml.stream.XMLStreamException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.PushbackInputStream; public class CustomBuilderForTextXml implements Builder{ public OMElement processDocument(InputStream inputStream, String s, MessageContext messageContext) throws AxisFault { SOAPFactory soapFactory = OMAbstractFactory.getSOAP11Factory(); SOAPEnvelope soapEnvelope = soapFactory.getDefaultEnvelope(); PushbackInputStream pushbackInputStream = new PushbackInputStream(inputStream); try { int byteVal = pushbackInputStream.read(); if (byteVal != -1) { pushbackInputStream.unread(byteVal); javax.xml.stream.XMLStreamReader xmlReader = StAXUtils.createXMLStreamReader(StAXParserConfiguration.SOAP, pushbackInputStream, (String) messageContext.getProperty(Constants.Configuration.CHARACTER_SET_ENCODING)); StAXBuilder builder = new StAXOMBuilder(xmlReader); OMNodeEx documentElement = (OMNodeEx) builder.getDocumentElement(); documentElement.setParent(null); String elementVal = ((OMElement) documentElement).getText(); byte[] bytesEncoded = Base64.encodeBase64(elementVal.getBytes()); ((OMElement) documentElement).setText(new String(bytesEncoded )); SOAPBody body = soapEnvelope.getBody(); body.addChild(documentElement); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (XMLStreamException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return soapEnvelope; } } -
Create a JAR file of this class and add it into the classpath of the Axis2 installation, i.e., the
MI_HOME/libfolder. -
To enable your custom message builder for content type text/xml, add the following line in the deployment.toml file:
[[custom_message_builders]] content_type = "text/xml" class="org.test.builder.http.CustomBuilderForTextXml"
Custom message formatter¶
Similarly, you can write your own message formatter to manipulate the outgoing payload from the ESB Micro Integrator.
When creating a custom message formatter, you will need to create a class implementing the org.apache.axis2.transport.MessageFormatter interface and then override the writeTo method. You can implement your logic within the writeTo method. Let's use the org.apache.axis2.transport.http.HTMLMessageFormatter class to implement the org.apache.axis2.transport.MessageFormatter interface.
To enable this custom message formatter for content type text/html, add the following configuration to the deployment.toml file:
[[custom_message_formatters]]
content_type = "text/html"
class="org.apache.axis2.transport.http.HTMLMessageFormatter"The class name used in the above line should be the name used for the class when writing the formatter.
Top