Securing APIs by Auditing API Definitions¶
API Security has become an important concern in recent times as organizations are more cautious about exposing raw, sensitive data via APIs. Therefore, it is important that APIs adhere to the OpenAPI Specification (OAS) to ensure API security.
MWARE ESB has partnered with 42Crunch, the only enterprise API security platform, to bring in the ability to conduct a security audit on the OpenAPI Specification definition and to obtain an audit report.
Step 1 - Enable Audit API¶
Step 1.1 - Obtain API token and collection ID¶
Follow the instructions below to obtain the API token and collection ID from 42Crunch:
-
Navigate to the 42Crunch platform and register or sign in.
-
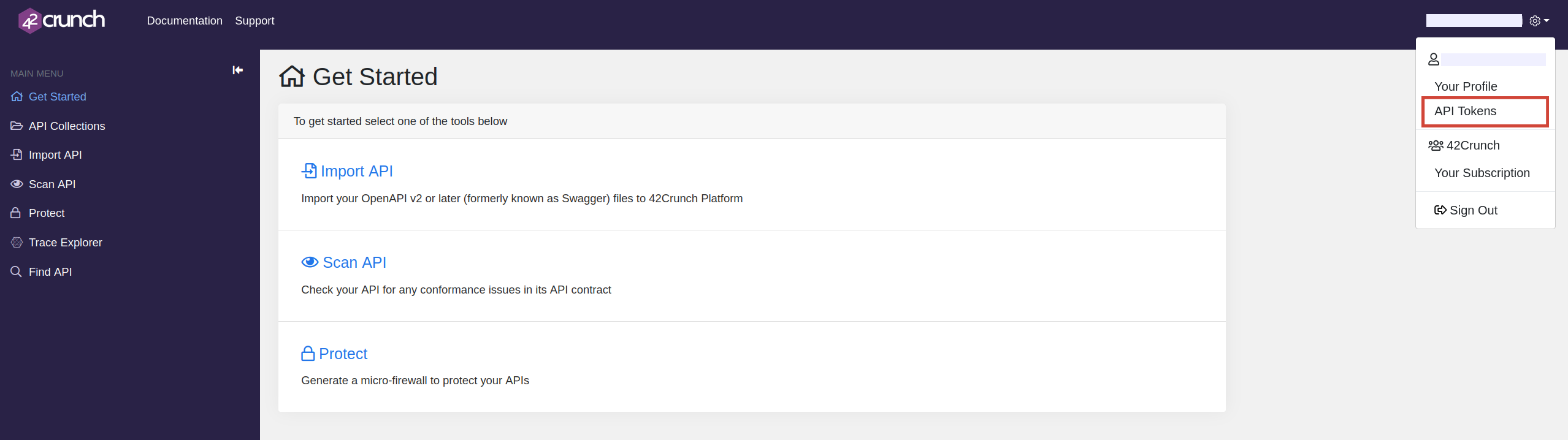
Click Settings.
-
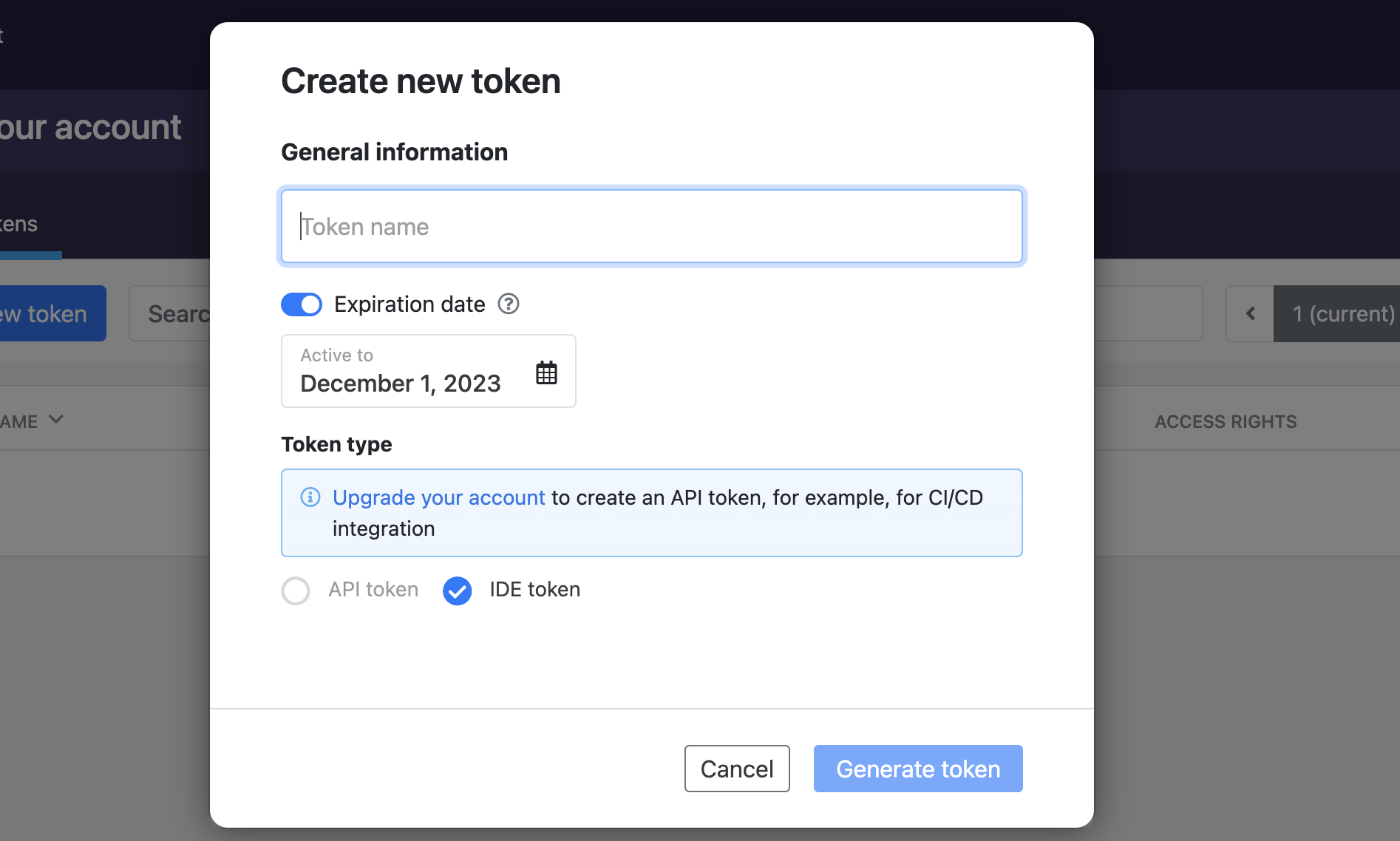
Click API Tokens and click Create New Token.
-
Upgrade the account to access the API token type
-
Enter a name for the token and select API Contract Security Audit as the token access right.
When working with API Audit, you only need to select the API Contract Security Audit permission.
-
Click Generate Token.
Note
The generated API Token can be viewed only once. Make sure to copy it and save it in a safe place for future reference.
-
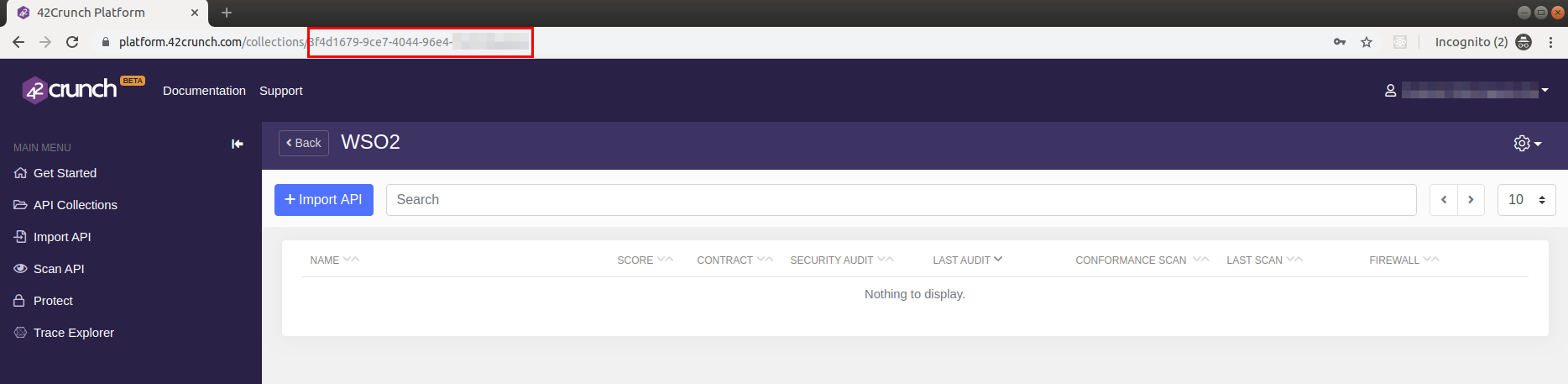
Click either API Collections in the left navigation bar or click + New Collection at the bottom of the left navigation to create a collection.
A Collection in this context is a folder hosted on 42Crunch containing all the APIs that are to be audited.
-
Copy the Collection ID from the URL of the browser as highlighted below and save it in a safe place for reference.
Step 1.2 - Configure MWARE ESB¶
You need to add the API Token and Collection ID properties inside the configuration files in MWARE ESB in order to configure MWARE ESB with the retrieved properties. Use one of the following methods to carry out this process.
Enable Audit API for all tenants¶
-
Navigate to the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile. -
Add the following configuration to the file and save the changes.
[security_audit] api_token="{api-token}" collection_id="{collection-id}" global=true[security_audit] api_token="c21404ea-p13x-1swq-013a-pur90605uiwl" collection_id="a5213vyo-6tre-560u-p04h-p0inb98i0gt1" global=trueTip
Set the global property to false to disable the feature for all other tenants except the super tenant.
-
Restart the MWARE ESB server.
Enable Audit API for a single tenant¶
Tip
For more information on creating a tenant, see Managing Tenants.
-
Navigate to the Admin Console https://localhost:9443/admin and sign in with your tenant credentials.
-
Go to Settings > Advanced.
-
Add the following configuration to the JSON file and save it.
SecurityAuditConfig: { "apiToken": "{api-token}", "collectionId": "{collection-id}", "overrideGlobal": true }SecurityAuditConfig: { "apiToken": "c21404ea-p13x-1swq-013a-pur90605uiwl", "collectionId": "a5213vyo-6tre-560u-p04h-p0inb98i0gt1", "overrideGlobal": true } -
Restart the MWARE ESB server.
Note
If you define a value for the overrideGlobal property, it will override the global property value, which is under the [security_audit] section in the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile.
Important : If both the overrideGlobal and global properties are set to false, API Security Audit will be disabled even if the API Token and Collection ID is provided.
Step 2 - Audit an API¶
-
Navigate to the API Publisher.
-
Click on the API that you need to audit.
-
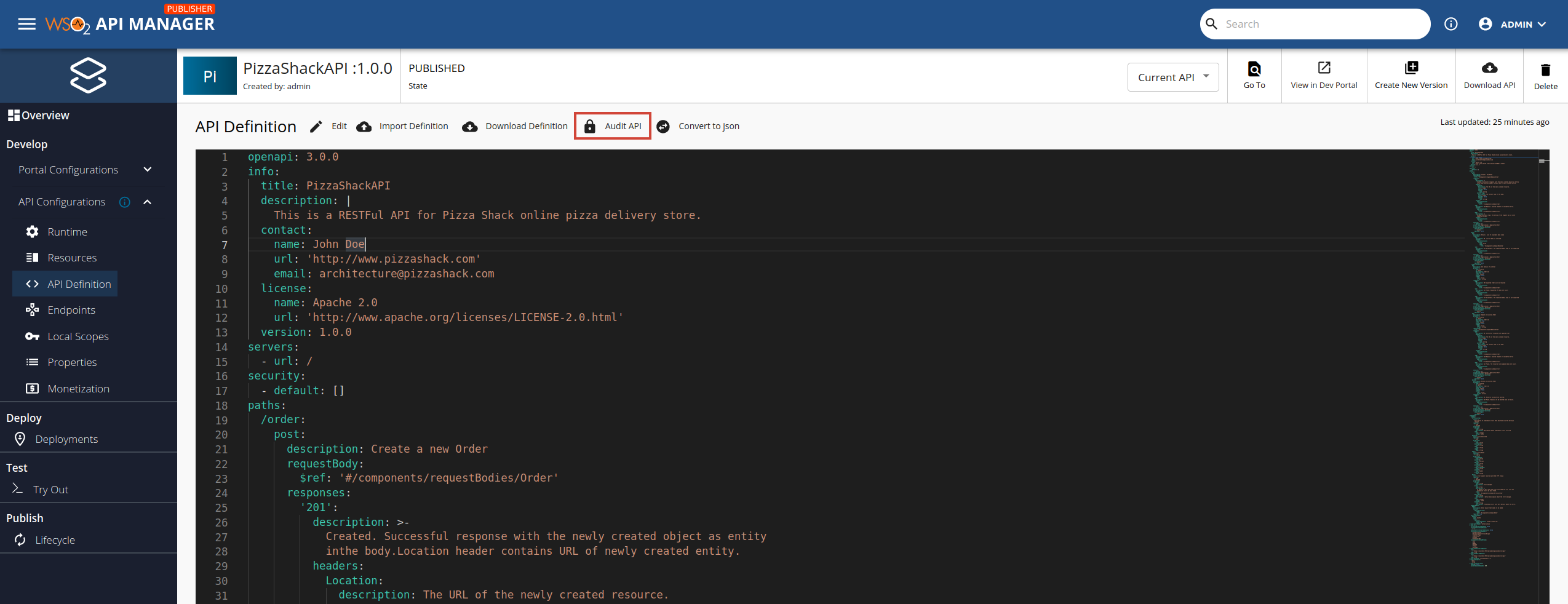
Go to API Definitions.
The Audit API button will only appear if API Auditing is enabled.
-
Click Audit API.
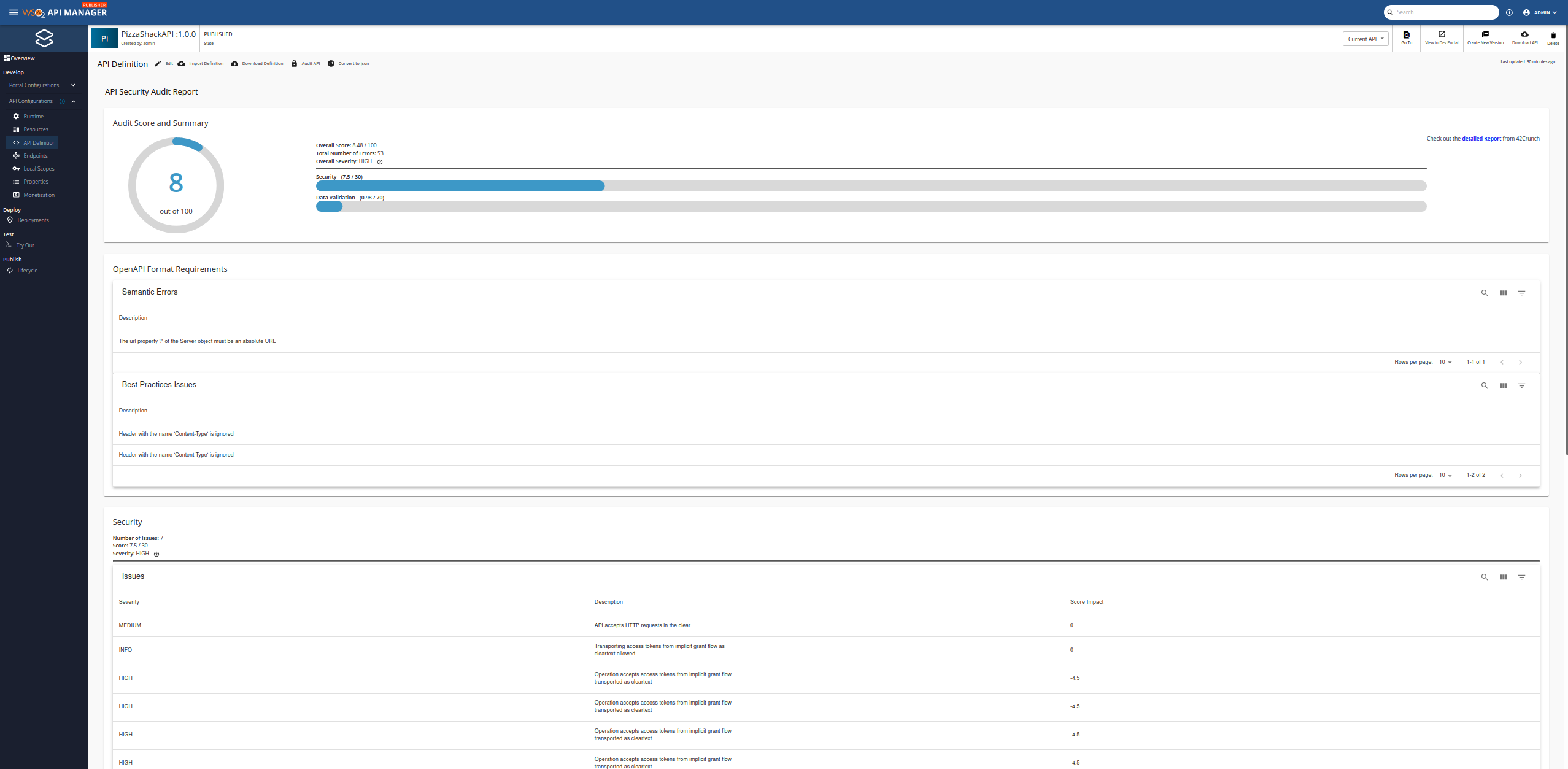
At the end of the audit, an audit report is displayed.
For more information on the details provided in the report, see Audit report sections
Audit report sections¶
There are four sections to the Audit Report:
Audit score and summary¶
This section provides the following information.
- Overall score, out of 100, given to the API Definition.
- The total number of errors.
- Overall severity of vulnerabilities present in the API Definition.
- Scores given to the Security and Data Validation sections.
Info
The OpenAPI format requirements are not taken into account when calculating the score for the Audit Report.
OpenAPI format requirements¶
This category presents any issues that exist due to the API Definition not adhering to the OpenAPI specification. OpenAPI format requirements are divided into the following three categories.
-
Structural Errors
These errors occur when the API's structure does not comply with the Open API format.
-
Semantic Errors
OpenAPI contracts that are structurally correct may have issues with the semantics of the fields in them. For example, the API could include an invalid email and URL formats, or inconsistent property formats across the API definition.
-
Best Practices Issues
The OpenAPI specification includes requirements, which are not mandatory but are highly recommended. Issues in this section will be shown in the report if those recommended requirements do not exist in the API definition.
Note
The API will not be audited if there are Structural Errors. Therefore, Structural Errors have to be fixed using the built-in Swagger Editor before attempting to audit the API again.
Security¶
This category presents security issues identified by checking the API against the security best practices such as Authentication, Authorization, and Transport.
Data validation¶
This category presents issues that arise due to inadequate validation of input and output in an API Definition such as flaws in parameters, response headers, response definition, and schemas.
Breakdown of severity levels¶
The severity level of an issue allows distinguishing between the most and least dangerous issues easier and is separated into five different levels:
-
INFO
The lowest severity level. Represents a threat that potentially is unlikely to cause damage should it be executed.
-
LOW
It represents a threat that could potentially cause damage but is lower priority.
-
MEDIUM
Reminiscent of a threat that needs attending to and could have moderately damaging effects should it be executed.
-
HIGH
It represents a threat that could potentially cause great damage if executed and needs to be attended to and fixed before the former levels.
-
CRITICAL
The highest severity level. It represents a threat that could have devastating and wide-spread consequences if executed. These threats should be fixed immediately.