Kubernetes API Operator¶
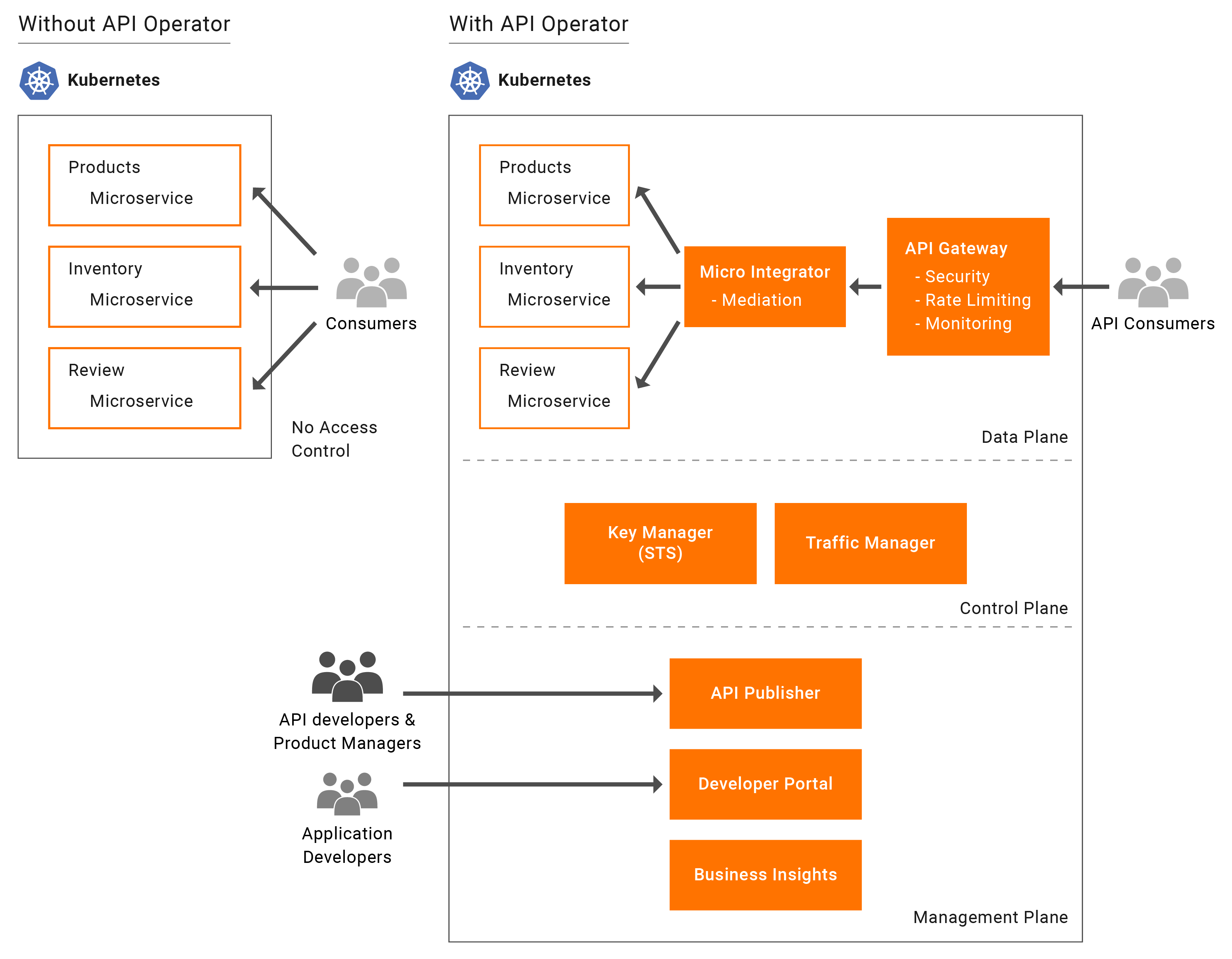
As microservices are increasingly being deployed on Kubernetes, the need to expose these microservices as well documented, easy to consume, managed APIs are becoming important to develop great applications. The API operator for Kubernetes makes APIs a first-class citizen in the Kubernetes ecosystem. Similar to deploying microservices, you can now use this operator to deploy APIs for individual microservices or compose several microservices into individual APIs. With this users will be able to expose their microservice as managed API in Kubernetes environment without any additional work.
The API operator for Kubernetes provides first-class support for Micro Integrator deployments in the Kubernetes ecosystem. It uses the Integration custom resource (integration_cr.yaml file) that is available in the Kubernetes project (exported from ESB Integration Studio) and deploys the integration in your Kubernetes environment.
Note
If you are using native Kubernetes for complex or custom scenarios, note that the ESB Kubernetes API Operator does not support such improvements. You need to use native Kubernetes and Helm charts instead for those cases.
How the API Operator works¶
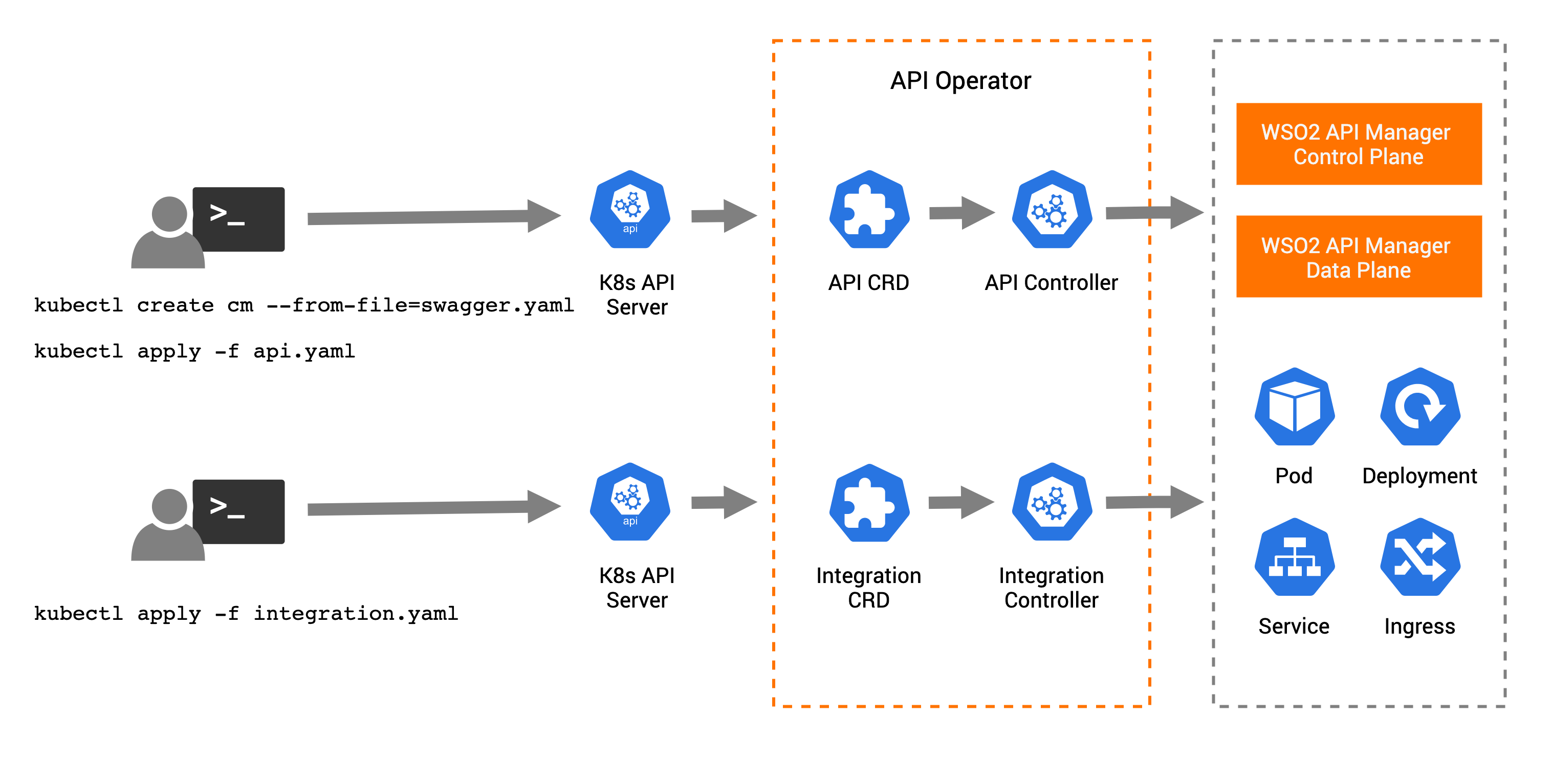
Using kubectl command-line tool, users can manage APIs and Integration custom resources in Kubernetes environments as follows.
Deploy APIs¶
The high-level steps for deploying APIs in Kubernetes using the API K8s Operator is as follows:
- Deploy an API project or OpenAPI definition in a config map in Kubernetes
- Deploy api.yaml file which is the API custom resource definition (CRD) for the API.
- In the API, you should refer to the config map which has the API project or OpenAPI definition.
- The API Operator takes control of the API CRD.
- The API controller in the API Operator creates the relevant artifacts for deploying in the ESB control plane and data plane.
- Based on the deployment options, API controller deploys the API in the ESB control plane or data plane.
For more information and instructions, see Deploying APIs.
Deploy Integrations¶
The high-level steps for deploying integrations in Kubernetes using the API K8s Operator is as follows:
- Deploy integration.yaml file which is the Integration custom resource definition (CRD) for the Integration project.
- The API Operator takes control of the Integration CRD.
- The Integration controller in the API Operator creates and deploys the relevant Kubernetes artifacts such as deployment, service, ingress, and horizontal pod autoscaler in the Kubernetes environment.
For more information and instructions, see Deploying Integrations.
Custom Resources¶
API¶
API holds the API related information. Users can provide a configmap name for swaggerConfigMapName, paramsValues and certsValues. The swaggerConfigMapName holds the API project or OpenAPI definition file. The paramsValues and certsValues holds the apictl project parameter configs and the certificate files for the API respectively.
apiVersion: wso2.com/v1alpha2
kind: API
metadata:
name: petstore-api
spec:
swaggerConfigMapName: petstore-cm
paramsValues: params-cm
certsValues: certs-cmIntegration¶
Integration holds the integration project-related information. Users can define the docker image name, deployment specification, autoscale configurations, service-related information, and environment variables for the integration project.
apiVersion: wso2.com/v1alpha2
kind: Integration
metadata:
name: test-integration
spec:
image: sajithagimash/test:1.0.0
deploySpec:
minReplicas: 1
requestCPU: "500m"
reqMemory: "512Mi"
cpuLimit: "2000m"
memoryLimit: "2048Mi"
autoScale:
enabled: "true"
maxReplicas: 3
expose:
passthroPort: 8290
inboundPorts:
- 8000
env:
- name: DEV_ENV_USER_EP
value: "https://reqres.in/api"TargetEndpoint¶
TargetEndpoint holds the endpoint-related information. Users can define the application protocol, ports, deployment specification and the running mode for the endpoint.
apiVersion: wso2.com/v1alpha2
kind: TargetEndpoint
metadata:
name: products-privatejet
labels:
app: wso2
spec:
applicationProtocol: http
ports:
- name: prod-ep
port: 80
targetPort: 9090
deploy:
name: products-pj-service
dockerImage: pubudu/products:1.0.0
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 3
requestCPU: "60m"
reqMemory: "32Mi"
cpuLimit: "120m"
mode: privateJetAPI K8s Operator configurations¶
The configurations of the K8s API Operator are stored in K8s secrets and configmaps. Users can change the configurations by changing the secrets and config maps in K8s.
API Controller¶
Control deploying to the API microgateway and ESB.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: api-controller-config
data:
# Deploy the API to Microgateway
deployAPIToMicrogateway: "true"
# Deploy the API to ESB
deployAPIToAPIManager: "false"API-M configurations¶
Configure key manager endpoints, API publisher endpoint, ssl verification, and secret name for ESB credentials.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: apim-config
data:
# The following 3 endpoints are related to importing API to ESB
# ESB Keymanager/DCR endpoint
apimKeymanagerEndpoint: "https://localhost:9443"
# ESB Publisher endpoint
apimPublisherEndpoint: "https://localhost:9443"
# ESB token endpoint
apimTokenEndpoint: "https://localhost:9443/oauth2/token"
# Skip verification for the REST API invocations. If "false", you need to provide the cert
insecureSkipVerify: "true"
# Secret name containing ESB credentials and cert
apimCredentialsSecret: "apim-secret"
# Enable configurations for retrieving API and subscription data from ESB.Choreo Connect configurations¶
Configure adapter connection URL and SSL verification.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: envoy-mgw-configs
data:
mgwAdapterHost: "https://adapter.default:9843"
# Skip verification for Microgateway Adapter endpoint call. If "false", you need to provide the cert
mgwInsecureSkipVerify: "true"API-M secrets¶
Configure credentials related to ESB and API Microgateway using K8s secrets as below. The input values should be Base64 encoded.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: apim-secret
type: Opaque
data:
# Base64 encoded username, password, and, cert secret name for ESB
username: YWRtaW4=
password: YWRtaW4=
cert_security: YXBpbS1jZXJ0LXNlY3JldA==apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: apim-cert-secret
data:
# Base64 encoded public cert of ESB instance
apim.pem: <BASE 64 ENCODED PUBLIC CERT>
type: OpaqueapiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: envoymgw-adapter-secret
type: Opaque
data:
# Base64 encoded username and password for Envoy MGW Adapter
username: YWRtaW4=
password: YWRtaW4=
mgwCertSecretName: ZW52b3ltZ3ctY2VydC1zZWNyZXQ=apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: envoymgw-cert-secret
data:
# Base64 encoded public cert of Microgateway Adapter
adapter.pem: <BASE 64 ENCODED PUBLIC CERT>
type: OpaqueIntegration Controller¶
Configure Integration custom resource-related configurations.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: integration-config
data:
reconcileInterval: "10"
autoIngressCreation: "true"
enableAutoScale: "false"
minReplicas: "1"
maxReplicas: "5"
# Auto Scaling Configurations
hpaMetrics: |
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
# K8s Probes
livenessProbe: |
tcpSocket:
port: 8290
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
readinessProbe: |
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 9201
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5Integration Ingress configurations¶
Configure Ingress configurations for Integration services.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: integration-ingress-config
data:
ingress.properties: |
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: false
ingressResourceName: "api-operator-ingress"
#Define whether ingress to use http or https endpoint of operator deployment
ingressTransportMode: "https"
#Define the hostname of the ingress
ingressHostName : "wso2ei.ingress.wso2.com"
#Define the secret name for TLS certificate
#tlsSecretName: ""