ISO8583 Inbound Endpoint Example¶
In the real world, financial scenarios are happening among thousands of banking systems and networks. In this situation, one system needs to act as a message publisher and another system needs to be capable of receiving messages. Once the message is received, further processing actions are performed based on the logic that is implemented in the internal system.
The ISO8583 inbound endpoint of ESB acts as a message consumer. The ISO8583 inbound endpoint is a listening inbound endpoint that can consume ISO8583 standard messages. It then converts the messages to XML format and injects messages to a sequence in the integration runtime.
What you'll build¶
This scenario demonstrates how the ISO8583 inbound endpoint works as an ISO8583 message consumer. In this scenario, to generate ISO8583 messages we use a sample Java client program here inside the banking network functionality simulates using the test client program.
The ISO8583 inbound endpoint listens on port 5000 and acts as a ISO8583 standard message consumer. When a sample Java client connects on port 5000, the ISO8583 inbound endpoint consumes ISO8583 standard messages, converts the messages to XML format, and then injects messages to a sequence in the integration runtime.
See ISO8583 connector configuration for more information. However, for simplicity of this example, we will just log the message. You can extend the sample as required using ESB mediators.
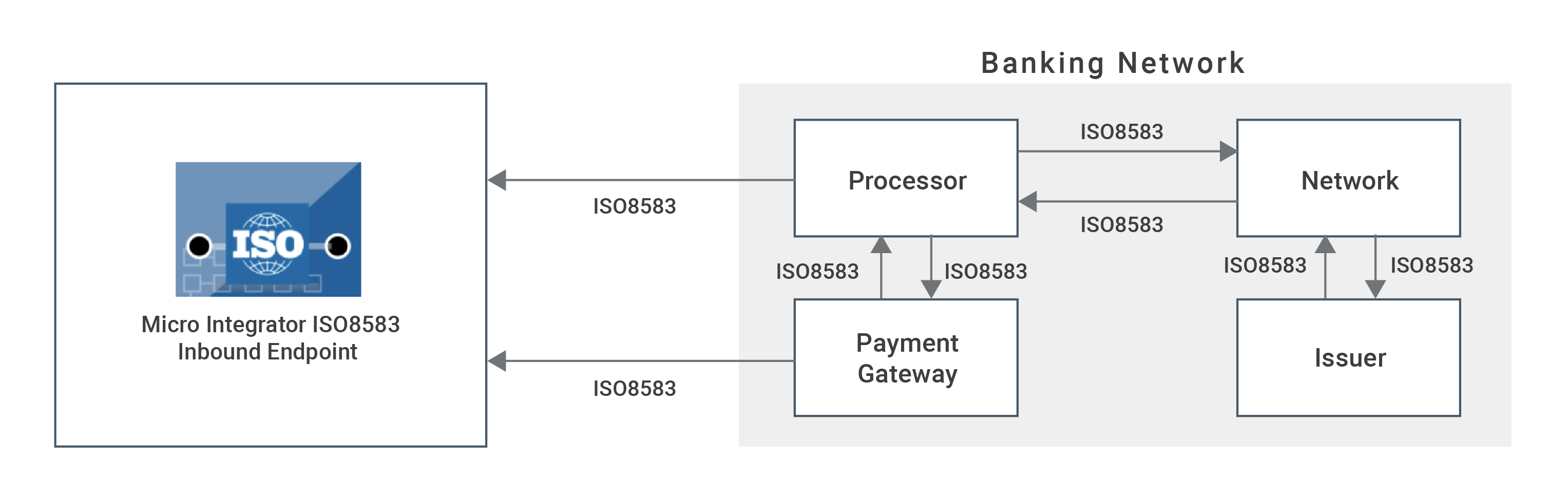
The following diagram illustrates all the required functionality of the ISO8583 inbound operations that you are going to build.
For example, while transferring bank and financial sector information using the ISO85883 message format among the banking networks, the message receiving can be done by using inbound endpoints. The ISO8583 inbound endpoint of ESB acts as an ISO8583 message receiver. You can inject that message into the mediation flow for getting the required output.
Configure inbound endpoint using ESB Integration Studio¶
-
Download ESB Integration Studio. Create an Integration Project as below.
-
Right click on Source -> main -> synapse-config -> inbound-endpoints and add a new custom inbound endpoint.
-
Click on Inbound Endpoint in design view and under
propertiestab, update class name toorg.wso2.carbon.inbound.iso8583.listening.ISO8583MessageConsumer. -
Navigate to the source view and update it with the following configuration as required.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><inboundEndpoint xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="custom_listener" sequence="requestISO" onError="fault" class="org.wso2.carbon.inbound.iso8583.listening.ISO8583MessageConsumer" suspend="false">
<parameters>
<parameter name="inbound.behavior">listening</parameter>
<parameter name="sequential">true</parameter>
<parameter name="coordination">true</parameter>
<parameter name="port">5000</parameter>
<parameter name="isProxy">false</parameter>
</parameters>
</inboundEndpoint>In this example for simplicity we will just log the message, but in a real world use case, this can be any type of message mediation.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><sequence xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="requestISO" onError="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="Log_Message for ISO8583 Inbound Endpoint" value="Message received from sample1-source"/>
</log>
</sequence>Exporting Integration Logic as a CApp¶
CApp (Carbon Application) is the deployable artefact on the integration runtime. Let us see how we can export integration logic we developed into a CApp. To export the Solution Project as a CApp, a Composite Application Project needs to be created. Usually, when a solution project is created, this project is automatically created by Integration Studio. If not, you can specifically create it by navigating to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Distribution -> Composite Application Project.
-
Right click on Composite Application Project and click on Export Composite Application Project.
-
Select an Export Destination where you want to save the .car file.
-
In the next Create a deployable CAR file screen, select inbound endpoint and sequence artifacts and click Finish. The CApp will get created at the specified location provided in the previous step.
Deployment¶
-
Navigate to the connector store and search for
ISO8583. Click onISO8583 Inbound Endpointand download the .jar file by clicking onDownload Inbound Endpoint. Copy this .jar file into/lib folder. -
Download jpos-1.9.4.jar, jdom-1.1.3.jar, and commons-cli-1.3.1.jar and add it to
/lib folder. -
Copy the exported carbon application to the
/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps folder. -
Start the integration server.
Testing¶
- Run Test Client program. Use a ISO8583 standard message as input;
0200B220000100100000000000000002000020134500000050000001115221801234890610000914XYRTUI5269TYUI021ABCDEFGHIJ 1234567890 Expected response
[2020-03-26 15:47:26,003] INFO {org.apache.synapse.mediators.builtin.LogMediator} - To: , MessageID: urn:uuid:FB34DB1FB26FB57D561585217845823, Direction: request, Log_Message for ISO8583 Inbound Endpoint = Message received from sample1-source, Envelope:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope">
<soapenv:Body>
<ISOMessage>
<header>AHc=</header>
<data>
<field id="0">0200</field>
<field id="3">201345</field>
<field id="4">000000500000</field>
<field id="7">0111522180</field>
<field id="11">123489</field>
<field id="32">100009</field>
<field id="44">XYRTUI5269TYUI</field>
<field id="111">ABCDEFGHIJ 1234567890</field>
</data>
</ISOMessage>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>