Google Spreadsheet Connector Example¶
The Google Sheets API lets users to read and modify any aspect of a spreadsheet. The ESB Google Spreadsheet Connector allows you to access the Google Spreadsheet API Version v4 from an integration sequence. It allows users to read/write any aspect of the spreadsheet via the spreadsheets collection. It has the ability to do spreadsheet operations and spreadsheet data operations.
What you'll build¶
This example explains how to use Google Spreadsheet Connector to create a Google spreadsheet, write data to it, and read it. Further, it explains how the data in the spreadsheet can be edited.
It will have three HTTP API resources, which are insert, read and edit.
-
/insert: The user sends the request payload, which includes the name of the spreadsheet, the sheet names, and what data should be inserted to which sheet and which range of cells. This request is sent to the integration runtime by invoking the Spreadsheet API. It creates a spreadsheet with specified data in the specified cell range.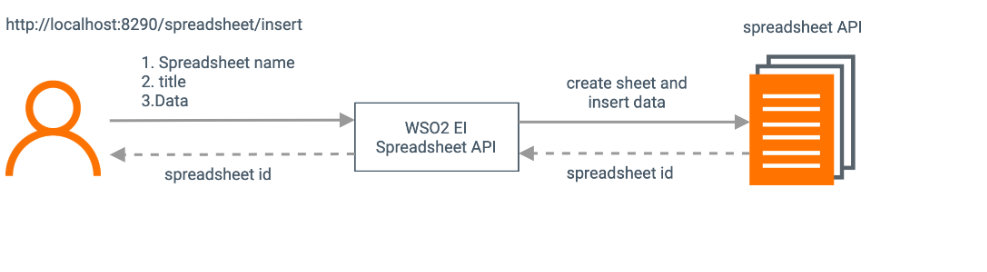
-
/read: The user sends the request payload, which includes the spreadsheet Id that should be obtained from calling theinsertAPI resource, and the range of the cell range to be read.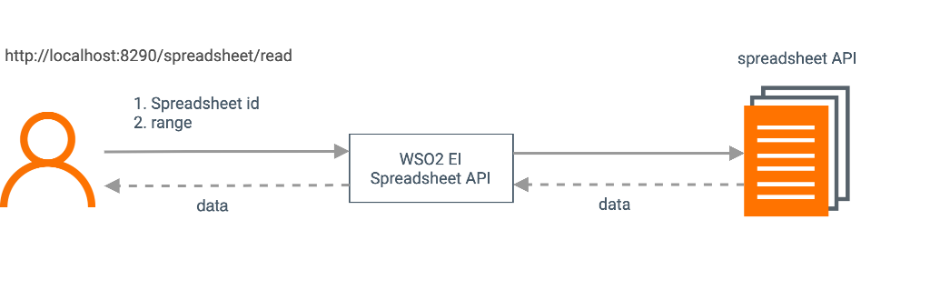
-
/edit: The user sends the request payload, which includes the spreadsheet Id that should be obtained from calling theinsertAPI resource, and the data to be edited that includes values and the range.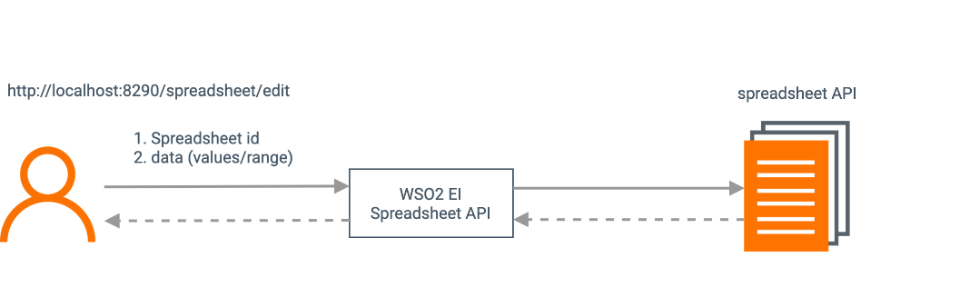
If you do not want to configure this yourself, you can simply get the project and run it.
Configure the connector in ESB Integration Studio¶
Follow these steps to set up the Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project.
-
Open ESB Integration Studio and create an Integration Project.
-
Right-click the project that you created and click on Add or Remove Connector -> Add Connector. You will get directed to the Connector Store.
-
Search for the specific connector required for your integration scenario and download it to the workspace.

-
Click Finish, and your Integration Project is ready. The downloaded connector is displayed on the side palette with its operations.
-
You can drag and drop the operations to the design canvas and build your integration logic.
-
Right click on the created Integration Project and select New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
Creating the Integration Logic¶
-
Follow these steps to Configure Google Sheets API and obtain the Client Id, Client Secret, Access Token, and Refresh Token.
-
Right click on the created Integration Project and select, -> New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
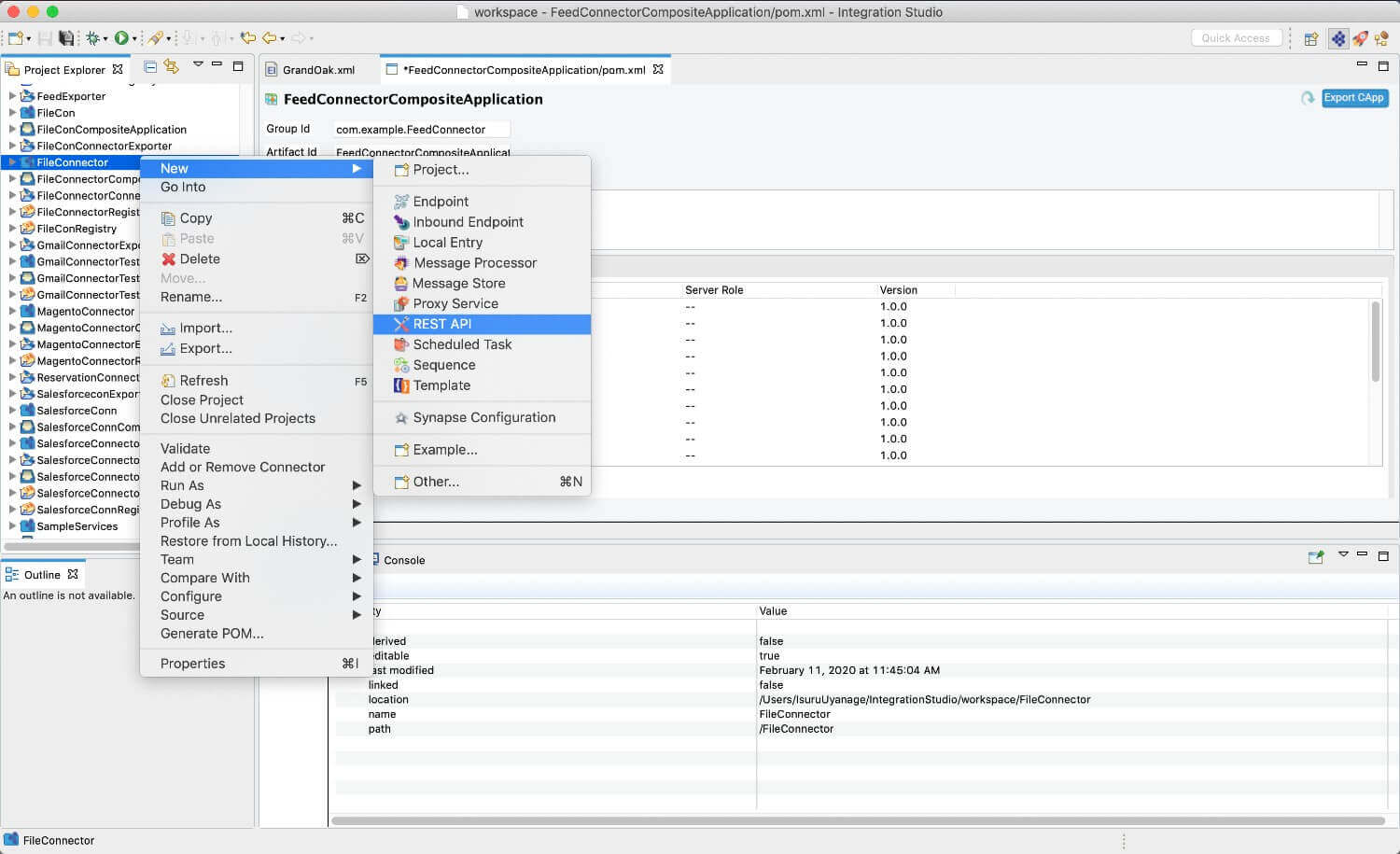
-
Provide the API name as
SpreadsheetAPIand the API context as/insert. -
First we will create the
/insertresource. Right click on the API Resource and go to Properties view. We use a URL template called/insertas we have two API resources inside single API. The method will bePost.
-
In this operation we are going to receive input from the user, which are
properties,sheets,rangeandvalues.- properties - It can provide the spreadsheet properties such as title of the spreadsheet.
- sheets - It can provide set of sheets to be created.
- range - It provides the sheet name and the range that data need to be inserted.
- values - Data to be inserted.
-
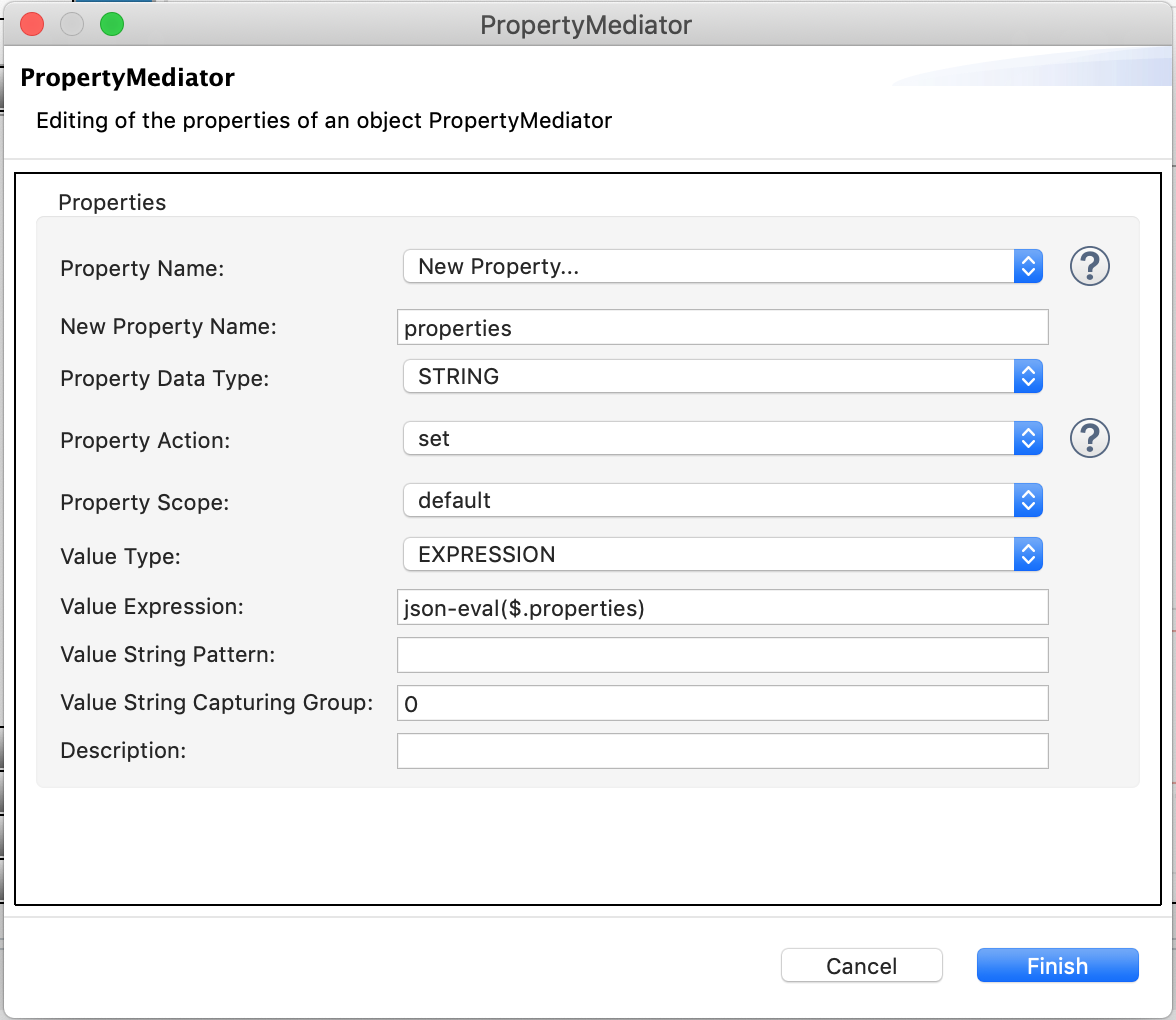
The above four parameters are saved to a property group. Drag and drop the Property Group mediator onto the canvas in the design view and do as shown below. For further reference, you can read about the Property Group mediator. You can add set of properties as below.
-
Once all the properties are added to the Property Group Mediator, it looks as below.
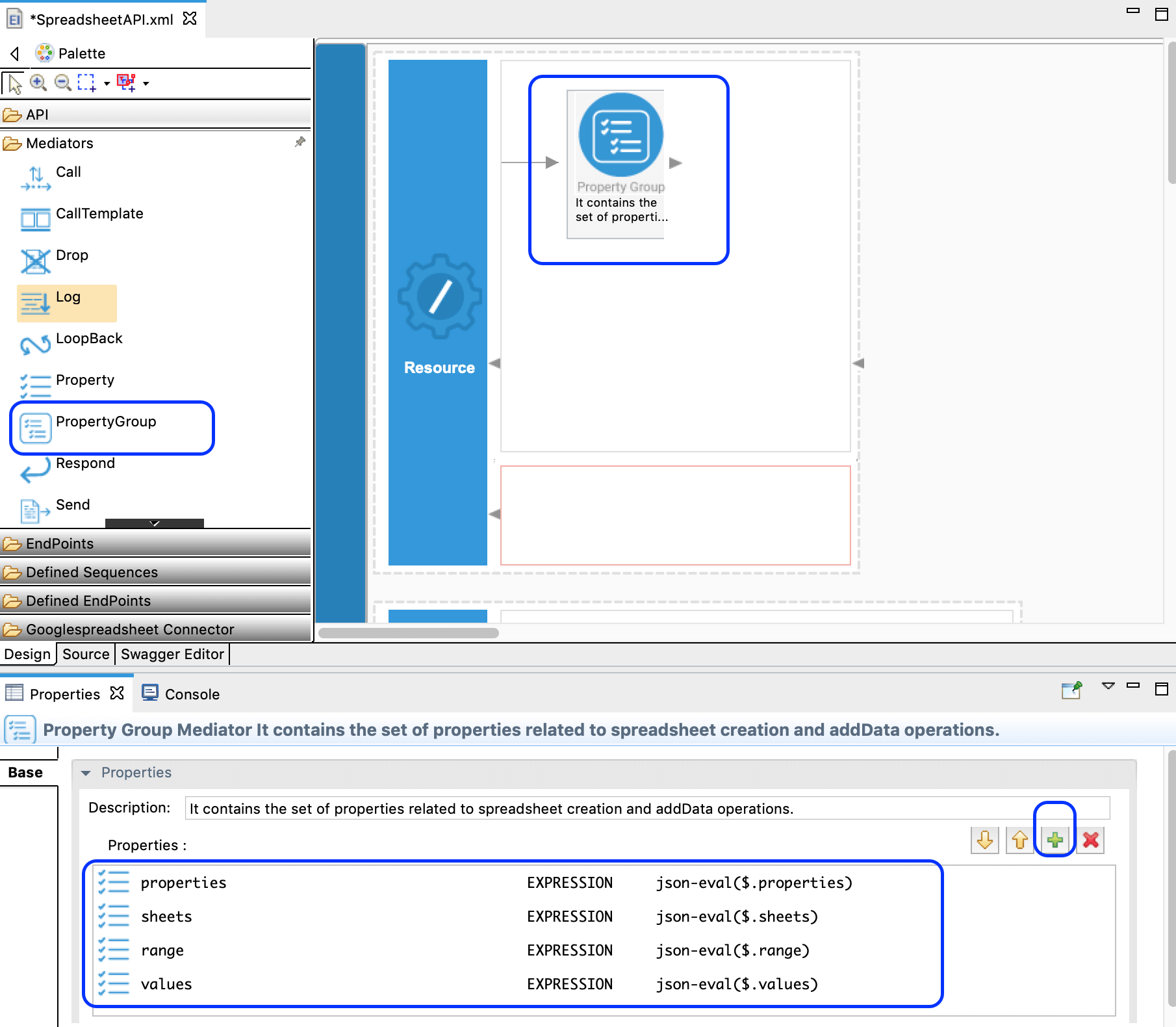
-
The
createSpreadsheetoperation is going to be added as a separate sequence. Right click on the created Integration Project and select, -> New -> Sequence to create thecreateSpreadsheetsequence. -
Drag and drop the init operation in the Googlespreadsheet Connector as below. Fill the following values that you obtained in the step 1.
- accessToken
- apiUrl: https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets
- clientId
- clientSecret
- refreshToken
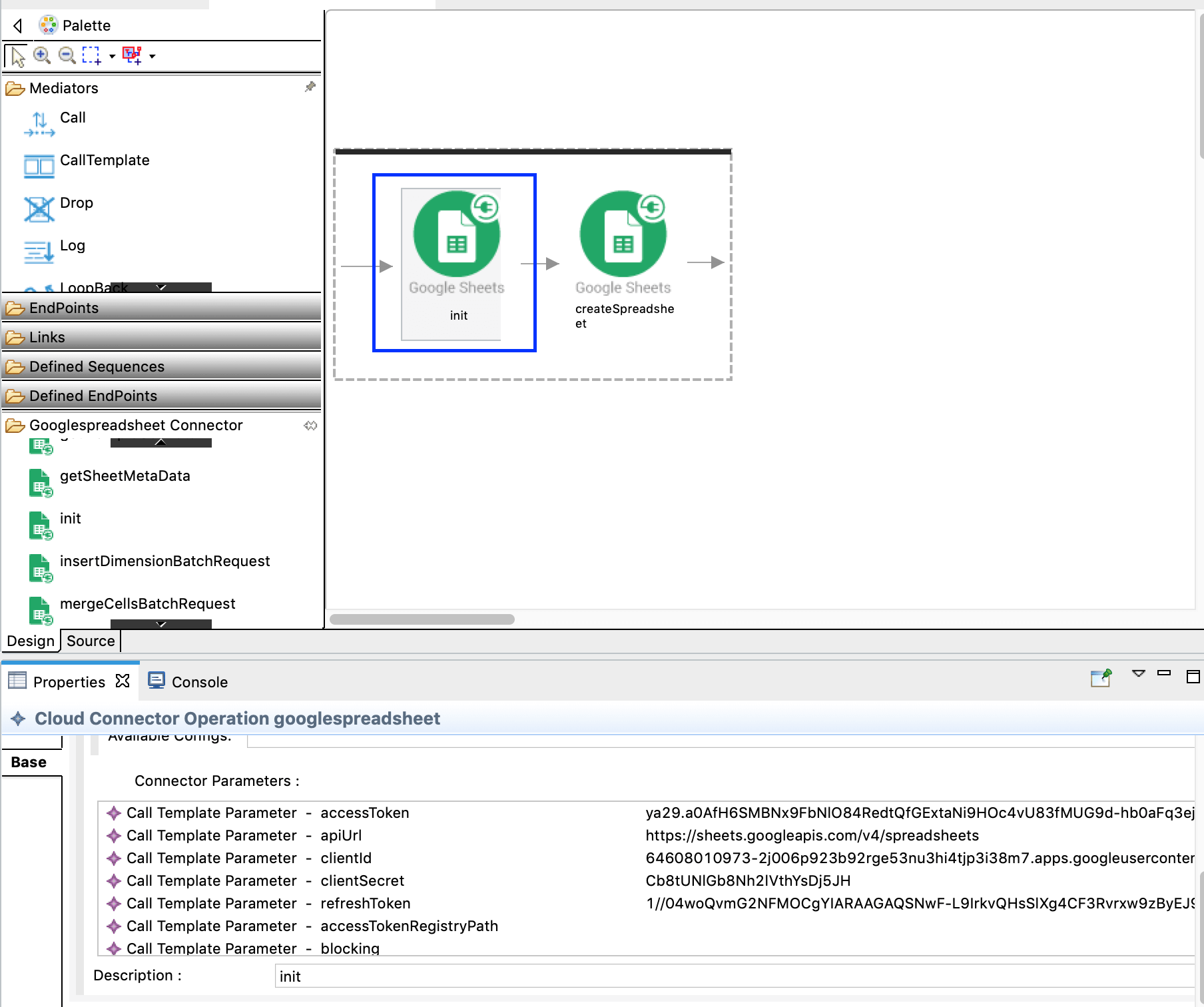
-
Drag and drop createSpreadsheet operation to the Canvas next. Parameter values are defined in step 6 and 7 in the property group.
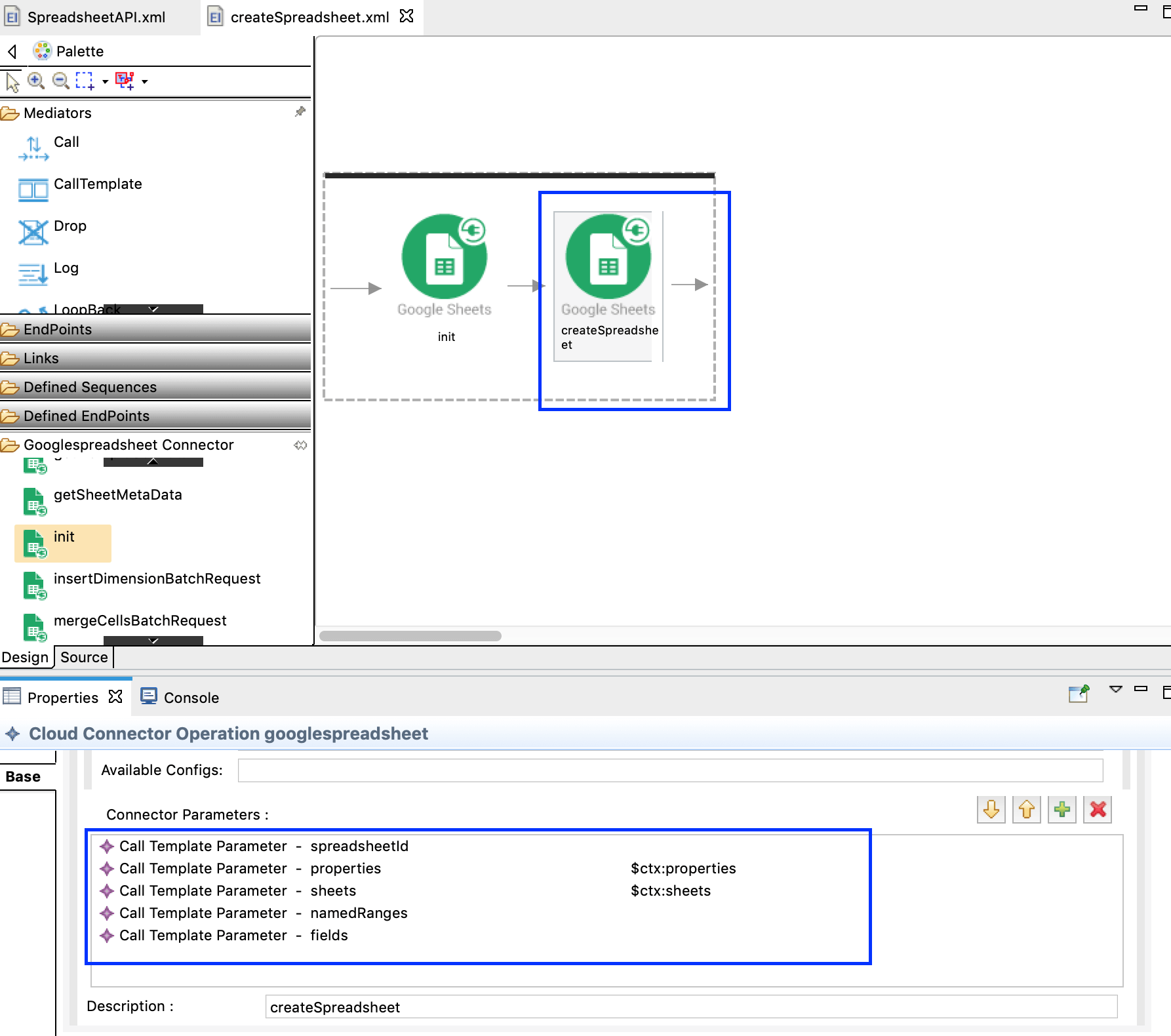
-
The complete XML configuration for the
createSpreadsheet.xmllooks as below.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <sequence name="createSpreadsheet" trace="disable" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <googlespreadsheet.init> <accessToken></accessToken> <apiUrl>https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets</apiUrl> <clientId></clientId> <clientSecret></clientSecret> <refreshToken></refreshToken> </googlespreadsheet.init> <googlespreadsheet.createSpreadsheet> <properties>{$ctx:properties}</properties> <sheets>{$ctx:sheets}</sheets> </googlespreadsheet.createSpreadsheet> </sequence> -
Next we need to create the
addData.xmlsequence as above. As explained in step 8, create a sequence by right clicking the Integration Project that has already been created. -
Below is the complete XML configuration for
addData.xmlfile.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <sequence name="addData" trace="disable" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <property expression="json-eval($.spreadsheetId)" name="spreadsheetId" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <googlespreadsheet.init> <accessToken></accessToken> <apiUrl>https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets</apiUrl> <clientId></clientId> <clientSecret></clientSecret> <refreshToken></refreshToken> </googlespreadsheet.init> <googlespreadsheet.addRowsColumnsData> <spreadsheetId>{$ctx:spreadsheetId}</spreadsheetId> <range>{$ctx:range}</range> <insertDataOption>INSERT_ROWS</insertDataOption> <valueInputOption>RAW</valueInputOption> <majorDimension>ROWS</majorDimension> <values>{$ctx:values}</values> </googlespreadsheet.addRowsColumnsData> </sequence> -
Now go back to
SpreadsheeetAPI.xmlfile, and from Defined Sequences drag and drop createSpreadsheet sequence, addData sequence and finally the Respond Mediator to the canvas. Now we are done with creating the first API resource, and it is displayed as shown below.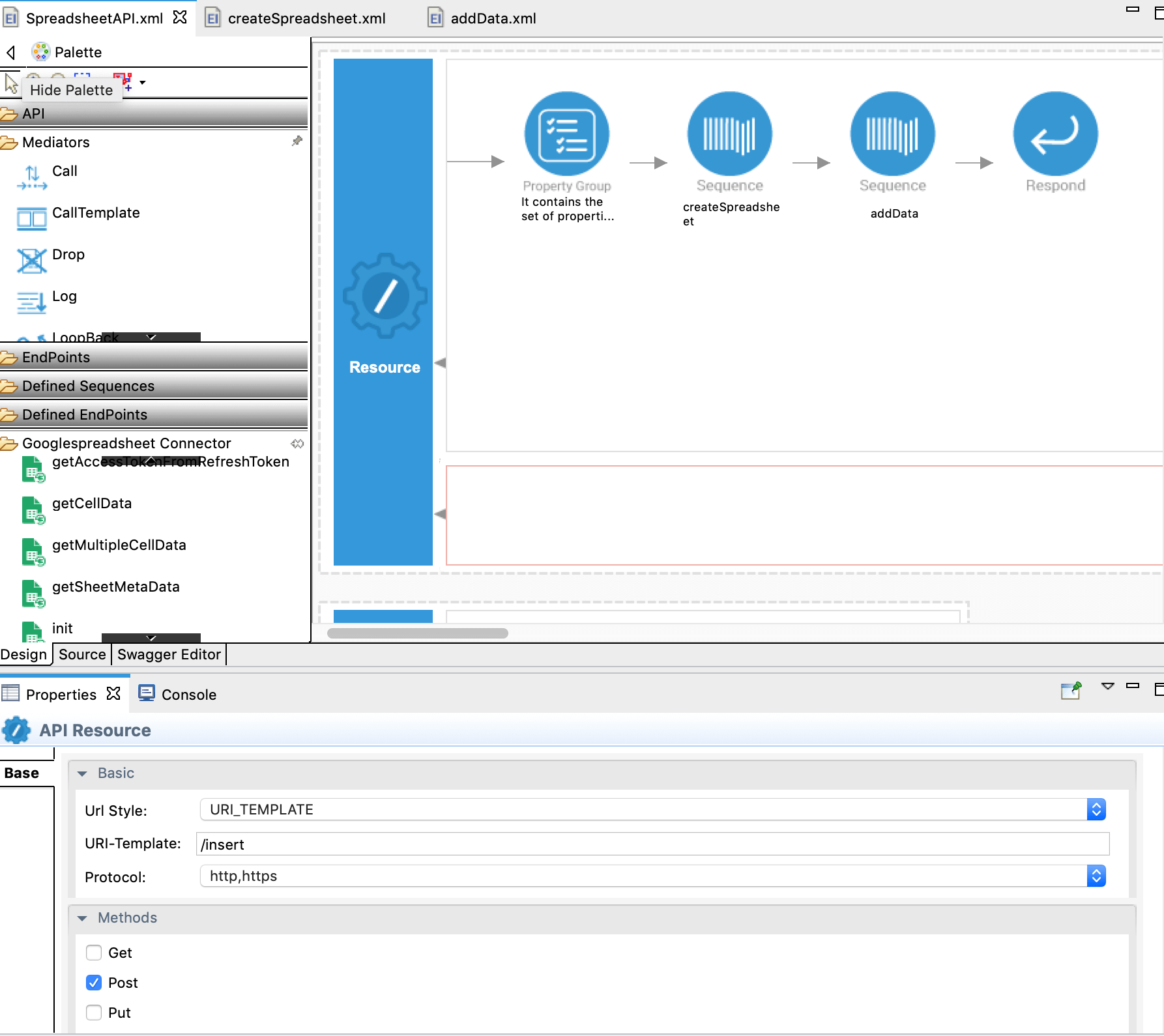
-
Create the next API resource, which is
/read. From this, we are going to read the specified spreadsheet data. Use the URL template as/read. The method will be POST.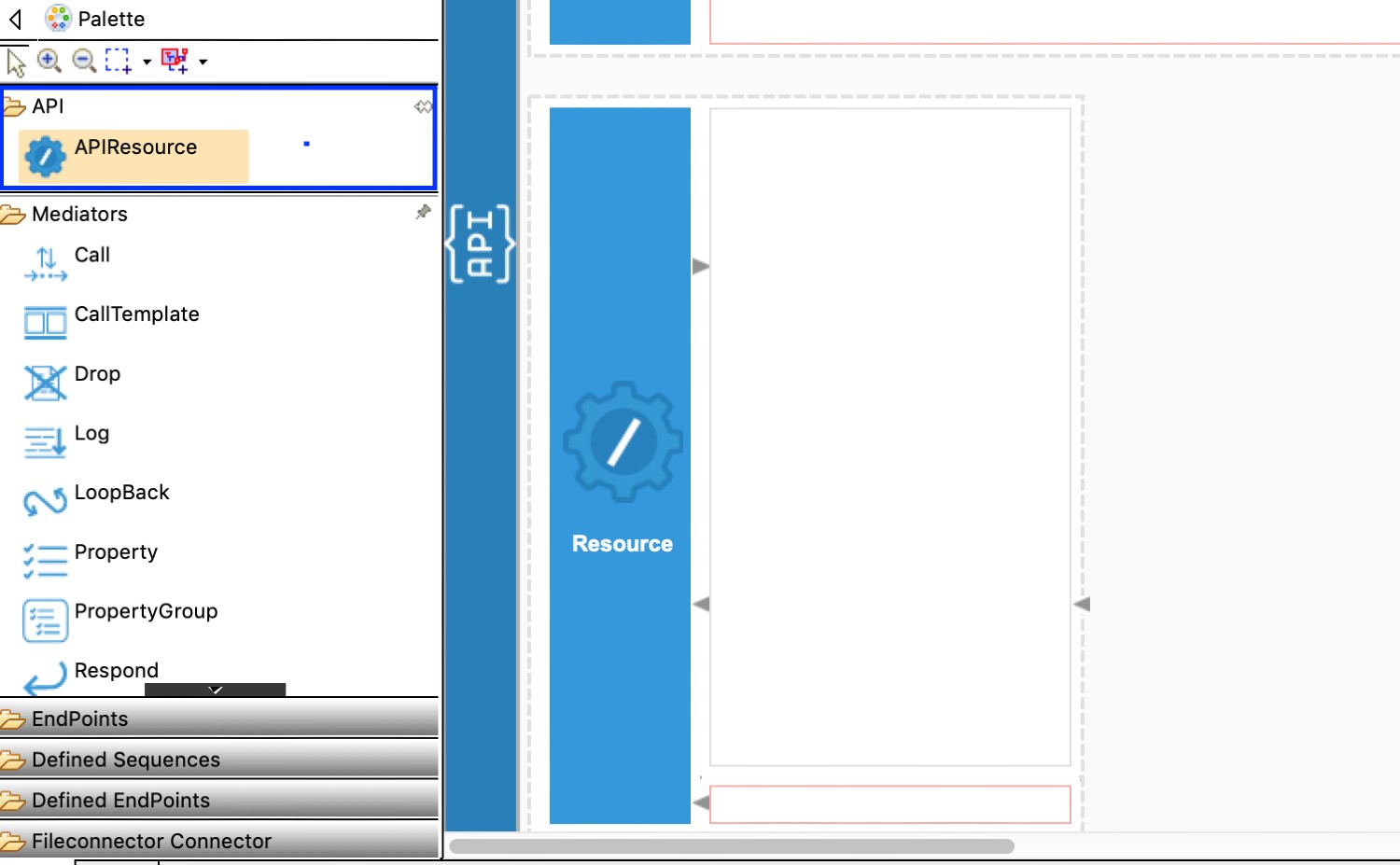
-
Let's create
readData.xmlsequence. The complete XML configuration looks as below.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <sequence name="readData" trace="disable" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <property expression="json-eval($.spreadsheetId)" name="spreadsheetId" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.range)" name="range" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <googlespreadsheet.init> <accessToken></accessToken> <apiUrl>https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets</apiUrl> <clientId></clientId> <clientSecret></clientSecret> <refreshToken></refreshToken> </googlespreadsheet.init> <googlespreadsheet.getCellData> <spreadsheetId>{$ctx:spreadsheetId}</spreadsheetId> <range>{$ctx:range}</range> <dateTimeRenderOption>SERIAL_NUMBER</dateTimeRenderOption> <majorDimension>ROWS</majorDimension> <valueRenderOption>UNFORMATTED_VALUE</valueRenderOption> </googlespreadsheet.getCellData> </sequence> -
In this operation, the user sends the spreadsheetId and range as the request payload. They will be written to properties as we did in step 10.
-
Go back to SpreadsheetAPI. Drag and drop
readDatasequence from the Defined Sequences to the canvas followed by a Respond mediator.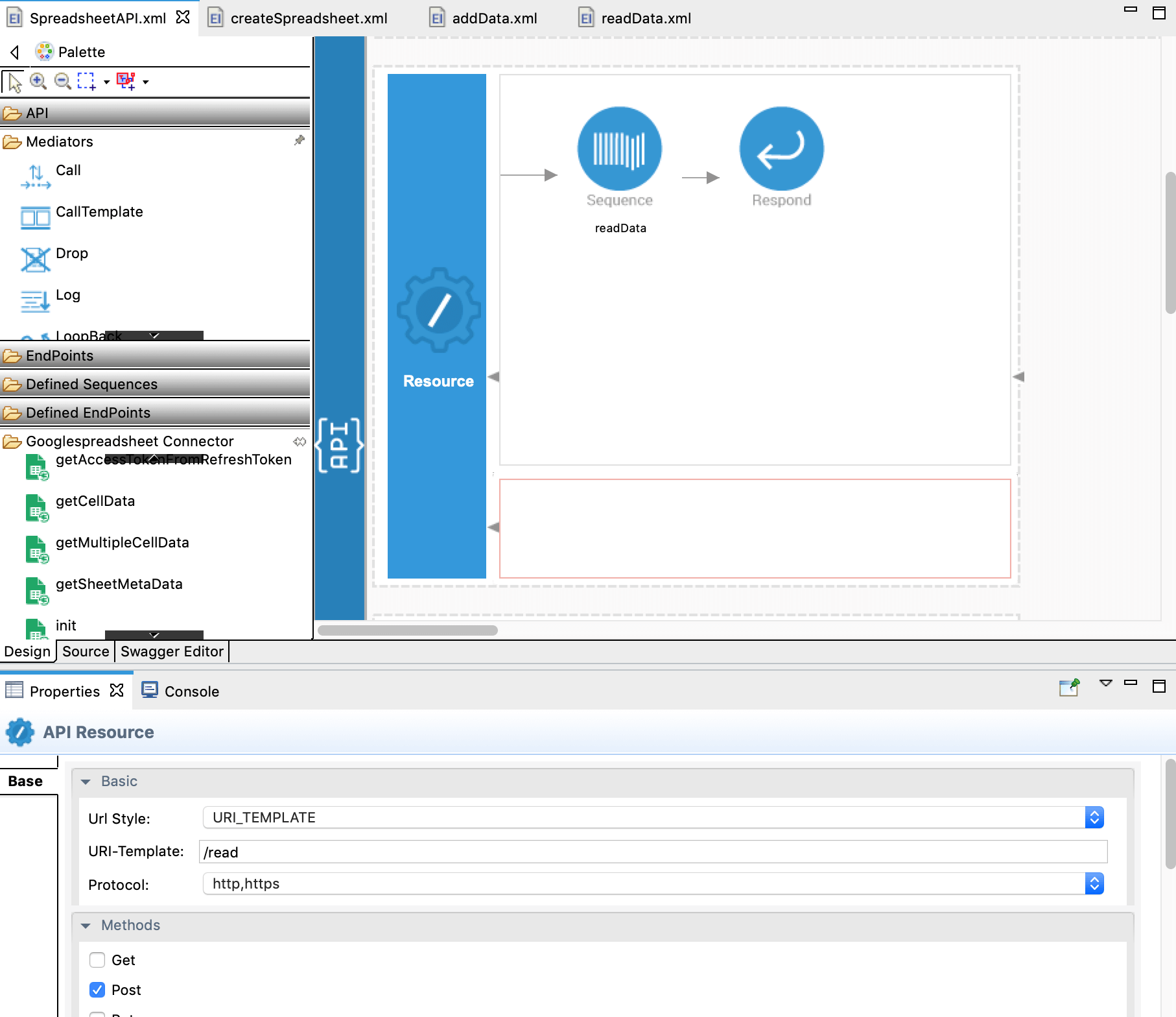
-
Next go to SpreadsheetAPI. To create the next API resource, drag and drop another API resource to the design view. Use the URL template as
/edit. The method will be POST. -
Create the sequence
editSpeadsheet.xmlwhich looks as below.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <sequence name="editSpreadsheet" trace="disable" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <property expression="json-eval($.spreadsheetId)" name="spreadsheetId" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.data)" name="data" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <googlespreadsheet.init> <accessToken></accessToken> <apiUrl>https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets</apiUrl> <clientId></clientId> <clientSecret></clientSecret> <refreshToken></refreshToken> </googlespreadsheet.init> <googlespreadsheet.editMultipleCell> <spreadsheetId>{$ctx:spreadsheetId}</spreadsheetId> <valueInputOption>RAW</valueInputOption> <data>{$ctx:data}</data> </googlespreadsheet.editMultipleCell> </sequence> -
Go back to SpreadsheetAPI. Drag and drop
editSpeadsheetsequence from the Defined Sequences to the canvas followed by a Respond mediator.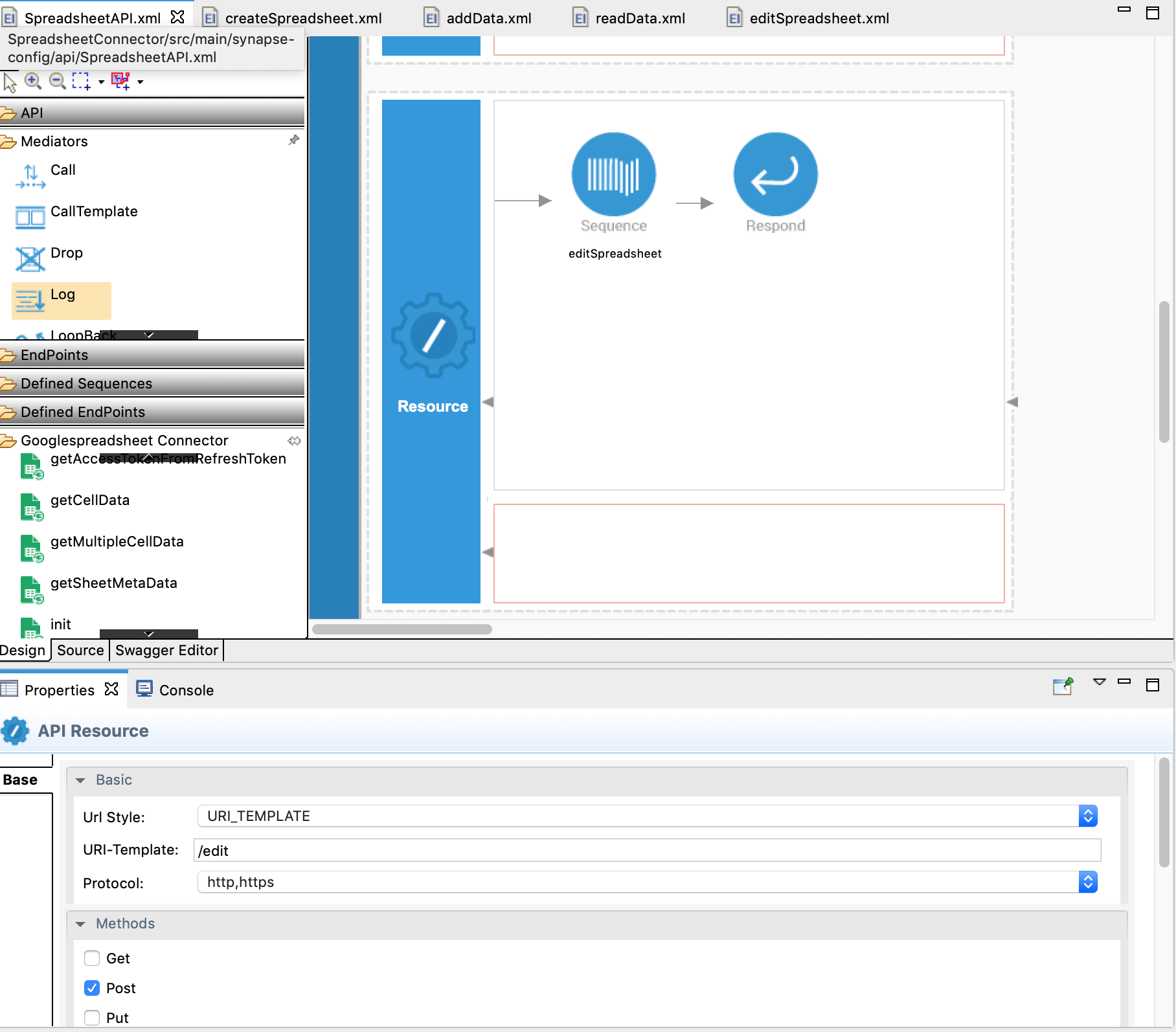
-
Below is the complete XML configuration of the SpreadsheetAPI.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <api context="/spreadsheet" name="SpreadsheetAPI" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <resource methods="POST" uri-template="/insert"> <inSequence> <propertyGroup description="It contains the set of properties related to spreadsheet creation and addData operations. "> <property expression="json-eval($.properties)" name="properties" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.sheets)" name="sheets" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.range)" name="range" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.values)" name="values" scope="default" type="STRING"/> </propertyGroup> <sequence description="This sequence will create a spreadsheet and outputs the spreadsheet url. " key="createSpreadsheet"/> <sequence description="This sequence will insert the data to the created spreadsheet. " key="addData"/> <respond/> </inSequence> <outSequence/> <faultSequence/> </resource> <resource methods="POST" uri-template="/read"> <inSequence> <sequence description="This sequence will read data of the spreadsheet. " key="readData"/> <respond/> </inSequence> <outSequence/> <faultSequence/> </resource> <resource methods="POST" uri-template="/edit"> <inSequence> <sequence key="editSpreadsheet"/> <respond/> </inSequence> <outSequence/> <faultSequence/> </resource> </api>
Exporting Integration Logic as a CApp¶
CApp (Carbon Application) is the deployable artifact on the integration runtime. Let us see how we can export integration logic we developed into a CApp along with the connector.
Creating Connector Exporter Project¶
To bundle a Connector into a CApp, a Connector Exporter Project is required.
-
Navigate to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Extensions -> Project Types -> Connector Exporter Project.
-
Enter a name for the Connector Exporter Project.
-
In the next screen select, Specify the parent from workspace and select the specific Integration Project you created from the dropdown.
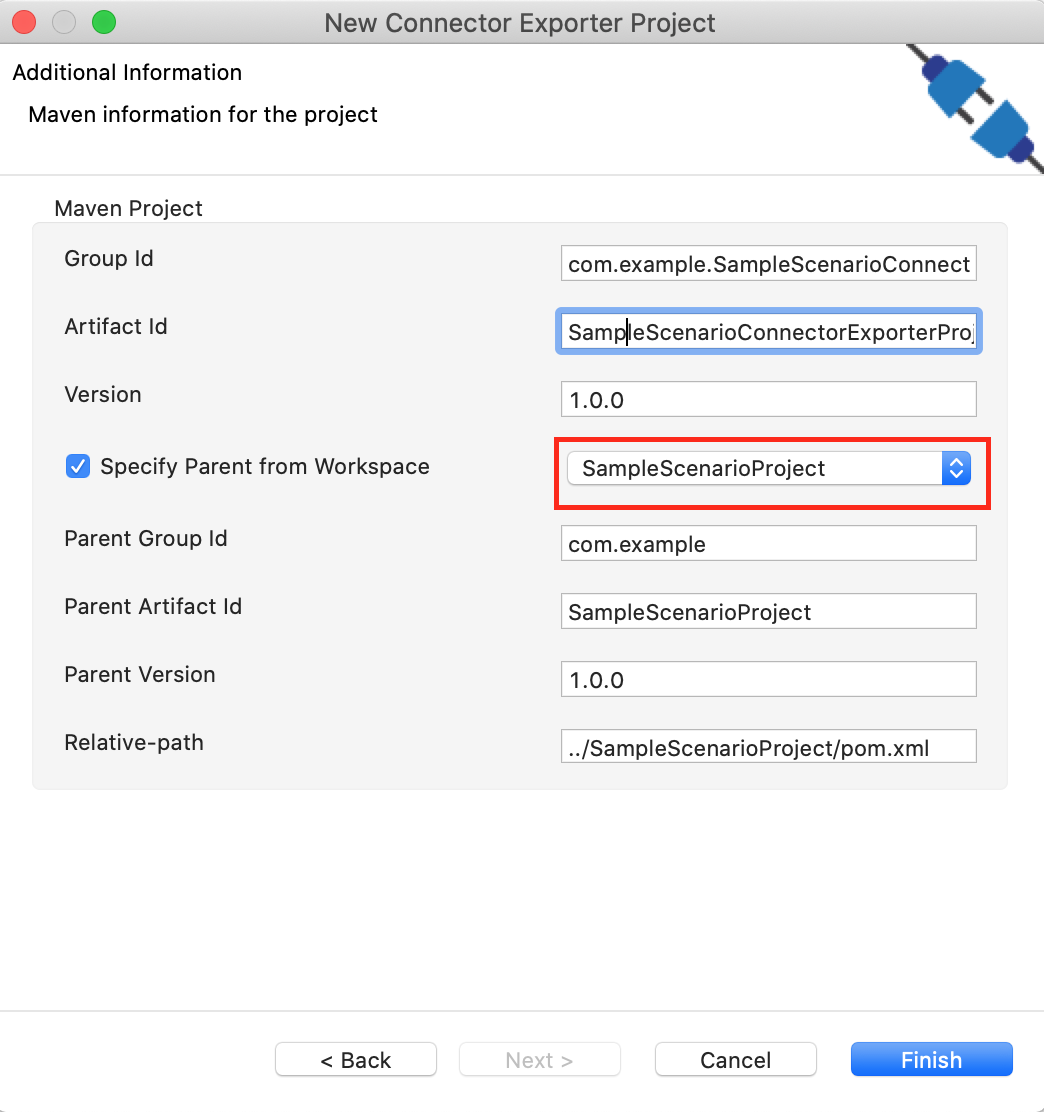
-
Now you need to add the Connector to Connector Exporter Project that you just created. Right-click the Connector Exporter Project and select, New -> Add Remove Connectors -> Add Connector -> Add from Workspace -> Connector
-
Once you are directed to the workspace, it displays all the connectors that exist in the workspace. You can select the relevant connector and click Ok.
Creating a Composite Application Project¶
To export the Integration Project as a CApp, a Composite Application Project needs to be created. Usually, when an Integration project is created, this project can be created as part of that project by Integration Studio. If not, you can specifically create it by navigating to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Distribution -> Composite Application Project.
Exporting the Composite Application Project¶
-
Right-click the Composite Application Project and click Export Composite Application Project.

-
Select an Export Destination where you want to save the .car file.
-
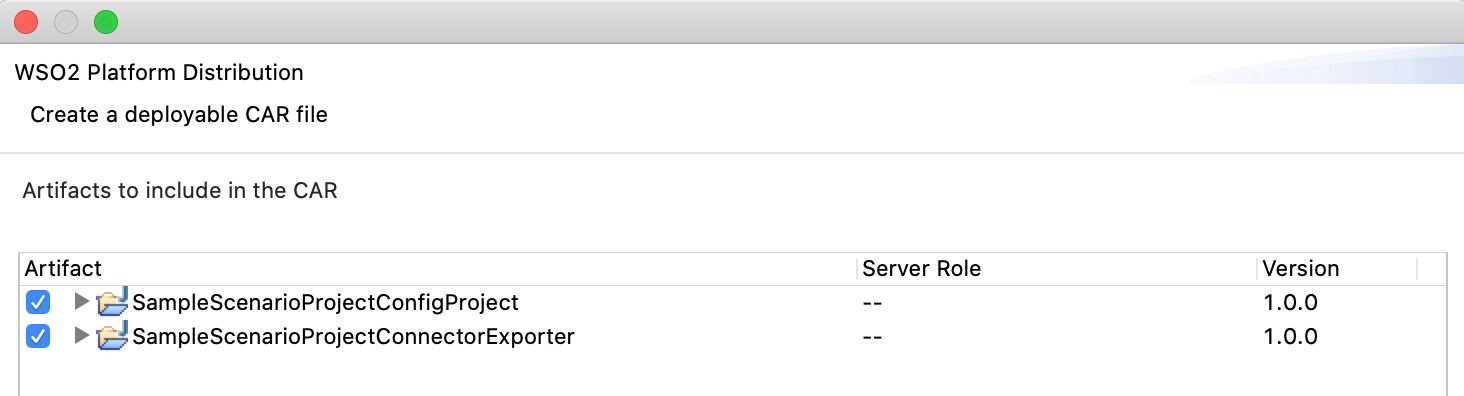
In the next Create a deployable CAR file screen, select both the created Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project to save and click Finish. The CApp is created at the specified location provided at the previous step.
Get the project¶
You can download the ZIP file and extract the contents to get the project code.
Tip
You may need to update the value of the access token and make other such changes before deploying and running this project.
Deployment¶
Follow these steps to deploy the exported CApp in the integration runtime.
Deploying on Micro Integrator
You can copy the composite application to the <PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps folder and start the server. Micro Integrator will be started and the composite application will be deployed.
You can further refer the application deployed through the CLI tool. See the instructions on managing integrations from the CLI.
Click here for instructions on deploying on ESB Enterprise Integrator 6
You can copy the composite application to the
<PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonappsfolder and start the server.ESB EI server starts and you can login to the Management Console https://localhost:9443/carbon/ URL. Provide login credentials. The default credentials will be admin/admin.
You can see that the API is deployed under the API section.
Testing¶
Spreadsheet insert Operation¶
Invoke the SpreadsheetAPI with the following URL. An application such as Postman can be used to invoke the API.
Resource method: POST
URL: http://localhost:8290/spreadsheet/insert {
"properties":{
"title": "Company"
},
"sheets":[
{
"properties":
{
"title": "Employees"
}
},
{
"properties":
{
"title": "Hector"
}
}
],
"range":"Employees!A1:C3",
"values":[
[
"First Name",
"Last Name",
"Gender"
],
[
"John",
"Doe",
"Male"
],
[
"Leon",
"Wins",
"Female"
]
]
}
{
"spreadsheetId": "1ddnO00fcjuLvEMCUORVjYQ4C0VLeAPNGmcvSvELHbPU",
"updates": {
"spreadsheetId": "1ddnO00fcjuLvEMCUORVjYQ4C0VLeAPNGmcvSvELHbPU",
"updatedRange": "Employees!A1:C3",
"updatedRows": 3,
"updatedColumns": 3,
"updatedCells": 9
}
}Spreadsheet Read Operation¶
Invoke the SpreadsheetAPI with the following URL. An application such as Postman can be used to invoke the API. Obtain the Spreadsheet ID from step 1.
Resource method: POST
URL: http://localhost:8290/spreadsheet/read {
"spreadsheetId":"1Ht0FWeKtKqBb1pEEzLcRMM8s5mktJdhivX3iaFXo-qQ",
"range":"Employees!A1:C3"
}Expected Response: You should get the following response returned.
{
"range": "Employees!A1:C3",
"majorDimension": "ROWS",
"values": [
[
"First Name",
"Last Name",
"Gender"
],
[
"John",
"Doe",
"Male"
],
[
"Leon",
"Wins",
"Female"
]
]
}
Spreadsheet Edit Operation¶
- Invoke the SpreadsheetAPI with the following URL. Application such as Postman can be used to invoke the API. Obtain the Spreadsheet ID from the step 1.
Resource method: POST URL: http://localhost:8290/spreadsheet/edit
{
"spreadsheetId":"1Ht0FWeKtKqBb1pEEzLcRMM8s5mktJdhivX3iaFXo-qQ",
"data": [
{
"values": [["Isuru","Uyanage","Female"],["Supun","Silva","Male"]],
"range": "Employees!A6"
}
]
}Expected Response: You should get the following response returned.
{
"spreadsheetId": "1Ht0FWeKtKqBb1pEEzLcRMM8s5mktJdhivX3iaFXo-qQ",
"totalUpdatedRows": 2,
"totalUpdatedColumns": 3,
"totalUpdatedCells": 6,
"totalUpdatedSheets": 1,
"responses": [
{
"spreadsheetId": "1Ht0FWeKtKqBb1pEEzLcRMM8s5mktJdhivX3iaFXo-qQ",
"updatedRange": "Employees!A6:C7",
"updatedRows": 2,
"updatedColumns": 3,
"updatedCells": 6
}
]
}What's Next¶
- To customize this example for your own scenario, see Google Spreadsheet Connector Configuration documentation for all operation details of the connector.