Amazon S3 Connector Example¶
The AmazonS3 Connector allows you to access the REST API of Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3).
What you'll build¶
This example depicts how to use AmazonS3 connector to:
- Create a S3 bucket (a location for storing your data) in Amazon cloud.
- Upload a message into the created bucket as a text file.
- Retrieve created text file back and convert into a message in the integration runtime.
All three operations are exposed via an API. The API with the context /s3connector has three resources:
/createbucket- Once invoked, it will create a bucket in Amazon with the specified name/addobject- The incoming message will be stored into the specified bucket with the specified name/info- Once invoked, it will read the specified file from the specified bucket and respond with the content of the file
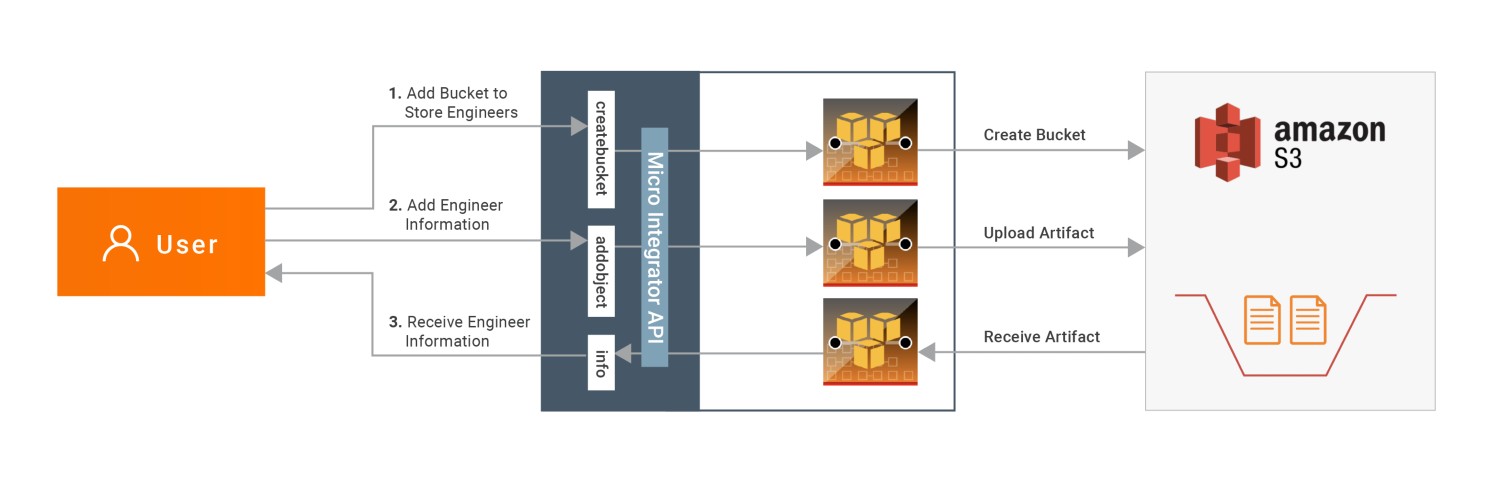
Following diagram shows the overall solution. The user creates a bucket, stores some message into the bucket, and then receives it back.
To invoke each operation, the user uses the same API.
If you do not want to configure this yourself, you can simply get the project and run it.
Setting up the environment¶
Please follow the steps mentioned at Setting up Amazon S3 document in order to create a Amazon S3 account and obtain credentials you need to access the Amazon APIs. Keep them saved to be used in the next steps.
Configure the connector in ESB Integration Studio¶
Follow these steps to set up the Integration Project and import AmazonS3 connector into it.
-
Open ESB Integration Studio and create an Integration Project.
-
Right-click the project that you created and click on Add or Remove Connector -> Add Connector. You will get directed to the Connector Store.
-
Search for the specific connector required for your integration scenario and download it to the workspace.

-
Click Finish, and your Integration Project is ready. The downloaded connector is displayed on the side palette with its operations.
-
You can drag and drop the operations to the design canvas and build your integration logic.
-
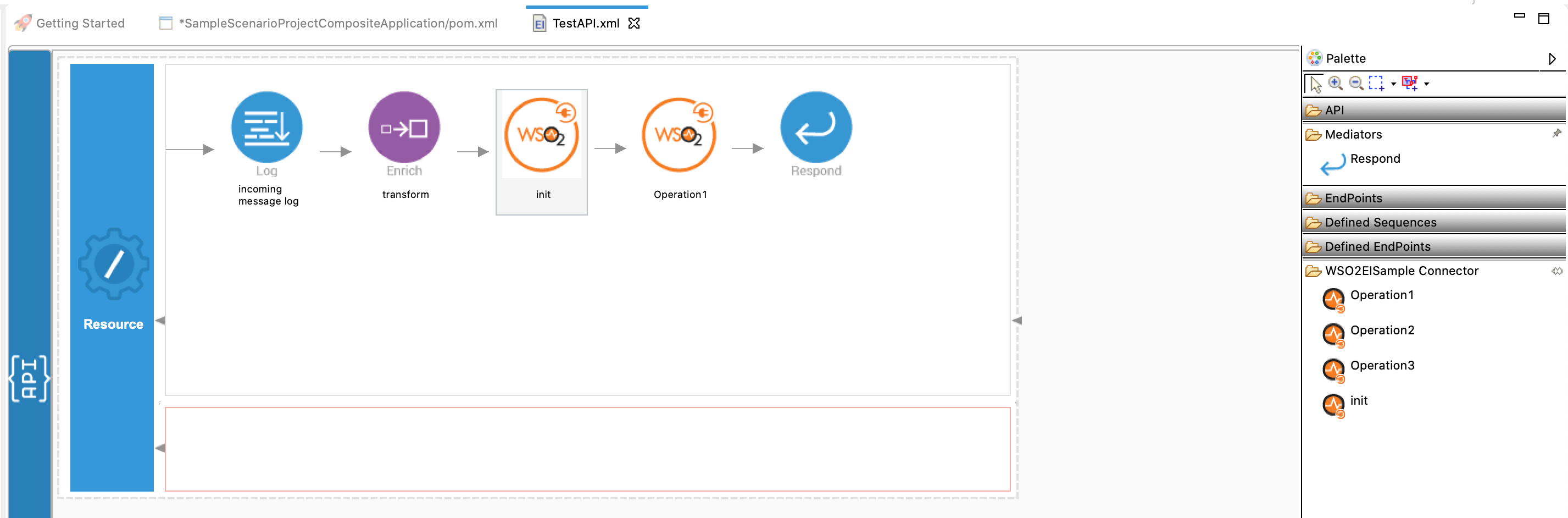
Right click on the created Integration Project and select New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
-
Right click on the created Integration Project and select, -> New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
-
Specify the API name as
S3ConnectorTestAPIand API context as/s3connector. You can go to the source view of the XML configuration file of the API and copy the following configuration.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<api context="/s3connector" name="S3ConnectorTestAPI" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<resource methods="PUT" uri-template="/createbucket">
<inSequence>
<log description="identifier log" level="custom">
<property name="message" value="Create bucket if not exists"/>
</log>
<propertyGroup description="message inputs">
<property expression="//bucketName" name="bucketName" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="fn:concat('http://s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/',get-property('bucketName'))" name="bucketUrl" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="//bucketRegion" name="bucketRegion" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
</propertyGroup>
<amazons3.init>
<accessKeyId>AKICJA4J6GE6D6JSVB7B</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>H/P/H6Tey2fQODHAU1JBbl/NhL/WpSaEkebvLlp4</secretAccessKey>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<methodType>{$ctx:REST_METHOD}</methodType>
<addCharset>false</addCharset>
<host>s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com</host>
<isXAmzDate>true</isXAmzDate>
<bucketName>{$ctx:bucketName}</bucketName>
<expect>100-continue</expect>
<xAmzAcl>public-read</xAmzAcl>
</amazons3.init>
<amazons3.createBucket>
<bucketUrl>{$ctx:bucketUrl}</bucketUrl>
<bucketRegion>{$ctx:bucketRegion}</bucketRegion>
</amazons3.createBucket>
<respond/>
</inSequence>
<outSequence/>
<faultSequence/>
</resource>
<resource methods="POST PUT" uri-template="/addobject">
<inSequence>
<log description="identifier log" level="custom">
<property name="message" value="Store into S3 bucket"/>
</log>
<propertyGroup description="message properties">
<property expression="//bucketName/text()" name="targetBucketName" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="//message/text()" name="msgContent" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="//objectName" name="objectName" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
</propertyGroup>
<propertyGroup description="init properties">
<property name="accessKeyId" scope="default" type="STRING" value="AKIAJA3J6GE646JSVA7A"/>
<property name="secretAccessKey" scope="default" type="STRING" value="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"/>
<property expression="fn:concat(get-property('targetBucketName'),'.','s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com')" name="host" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="fn:concat('http://',get-property('targetBucketName'),'.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com')" name="bucketUrl" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property name="region" scope="default" type="STRING" value="us-east-2"/>
<property name="ContentType" scope="axis2" type="STRING" value="application/xml"/>
<property name="addCharset" scope="default" type="STRING" value="false"/>
<property name="isXAmzDate" scope="default" type="STRING" value="true"/>
</propertyGroup>
<!-- initialize multiPart upload -->
<property name="methodType" scope="default" type="STRING" value="POST"/>
<amazons3.init>
<accessKeyId>{$ctx:accessKeyId}</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>{$ctx:secretAccessKey}</secretAccessKey>
<region>{$ctx:region}</region>
<methodType>{$ctx:methodType}</methodType>
<contentType>{$ctx:ContentType}</contentType>
<addCharset>{$ctx:addCharset}</addCharset>
<host>{$ctx:host}</host>
<isXAmzDate>{$ctx:isXAmzDate}</isXAmzDate>
<expect>100-continue</expect>
</amazons3.init>
<amazons3.initMultipartUpload>
<bucketUrl>{$ctx:bucketUrl}</bucketUrl>
<objectName>{$ctx:objectName}</objectName>
</amazons3.initMultipartUpload>
<!-- We need to interpret the response as application/xml-->
<property name="ContentType" scope="axis2" type="STRING" value="application/xml"/>
<log level="full"/>
<!-- Extract generated uploadId -->
<property expression="$body//m0:UploadId" name="uploadId" scope="default" type="STRING" xmlns:m0="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/"/>
<log level="custom">
<property expression="$ctx:uploadId" name="uploadId"/>
</log>
<!-- execute multiPart upload -->
<property name="methodType" scope="default" type="STRING" value="PUT"/>
<amazons3.init>
<accessKeyId>{$ctx:accessKeyId}</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>{$ctx:secretAccessKey}</secretAccessKey>
<region>{$ctx:region}</region>
<methodType>{$ctx:methodType}</methodType>
<contentType>{$ctx:ContentType}</contentType>
<addCharset>{$ctx:addCharset}</addCharset>
<host>{$ctx:host}</host>
<isXAmzDate>{$ctx:isXAmzDate}</isXAmzDate>
<expect>100-continue</expect>
</amazons3.init>
<!--Create body of the message to upload-->
<payloadFactory media-type="text">
<format>$1</format>
<args>
<arg evaluator="xml" expression="$ctx:msgContent"/>
</args>
</payloadFactory>
<property name="partNumber" scope="default" type="STRING" value="1"/>
<amazons3.uploadPart>
<bucketUrl>{$ctx:bucketUrl}</bucketUrl>
<objectName>{$ctx:objectName}</objectName>
<uploadId>{$ctx:uploadId}</uploadId>
<partNumber>{$ctx:partNumber}</partNumber>
</amazons3.uploadPart>
<property expression="$trp:ETag" name="eTag" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<log level="custom">
<property expression="$trp:ETag" name="eTag"/>
</log>
<payloadFactory media-type="xml">
<format>
<partDetails xmlns="">
<Part>
<PartNumber>1</PartNumber>
<ETag>$1</ETag>
</Part>
</partDetails>
</format>
<args>
<arg evaluator="xml" expression="$ctx:eTag"/>
</args>
</payloadFactory>
<!--complete multiPart upload-->
<property name="methodType" scope="default" type="STRING" value="POST"/>
<amazons3.init>
<accessKeyId>{$ctx:accessKeyId}</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>{$ctx:secretAccessKey}</secretAccessKey>
<methodType>{$ctx:methodType}</methodType>
<contentType>{$ctx:contentType}</contentType>
<addCharset>{$ctx:addCharset}</addCharset>
<isXAmzDate>{$ctx:isXAmzDate}</isXAmzDate>
<bucketName>{$ctx:bucketName}</bucketName>
</amazons3.init>
<amazons3.completeMultipartUpload>
<bucketUrl>{$ctx:bucketUrl}</bucketUrl>
<objectName>{$ctx:objectName}</objectName>
<uploadId>{$ctx:uploadId}</uploadId>
<partDetails>{//partDetails/*}</partDetails>
</amazons3.completeMultipartUpload>
<respond/>
</inSequence>
<outSequence/>
<faultSequence/>
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" uri-template="/info">
<inSequence>
<log description="identifier log" level="custom">
<property name="message" value="getting information from amazon S3"/>
</log>
<property name="contentType" scope="default" type="STRING" expression="$axis2:ContentType"/>
<property expression="//bucketName/text()" name="targetBucketName" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="//objectName/text()" name="objectName" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="fn:concat('http://',get-property('targetBucketName'),'.s3-us-east-2.amazonaws.com')" name="bucketUrl" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<property expression="fn:concat(get-property('targetBucketName'),'.s3-us-east-2.amazonaws.com')" name="host" scope="default" type="STRING"/>
<amazons3.init>
<accessKeyId>AKIAJA3J6GE646JSVA7A</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<methodType>GET</methodType>
<contentType>{$ctx:contentType}</contentType>
<addCharset>false</addCharset>
<host>{$ctx:host}</host>
<isXAmzDate>true</isXAmzDate>
</amazons3.init>
<amazons3.getObject>
<bucketUrl>{$ctx:bucketUrl}</bucketUrl>
<objectName>{$ctx:objectName}</objectName>
</amazons3.getObject>
<respond/>
</inSequence>
<outSequence/>
<faultSequence/>
</resource>
</api>Note:
- As
accessKeyIduse the access key obtained from Amazon S3 setup and update the above API configuration. - As
secretAccessKeyuse the secret key obtained from Amazon S3 setup and update the above API configuration. - Note that When you configure the
addobjectresource, there are three parts to it. You need to use three operations of the connector in order.- initMultipartUpload - initialize the upload to the bucket. In the response of this operation you will receive generated
uploadIdby amazon S3 - uploadPart - upload message part. There can be multiple parts to the same object. When you invoke the operation, feed
uploadIdand the correctpartNumber. - completeMultipartUpload - once all parts are done uploading, call this operation. It will add up all the parts and create the object in the requested bucket.
- initMultipartUpload - initialize the upload to the bucket. In the response of this operation you will receive generated
- Note that
regionathostandbucketUrlproperties are hard coded. Please change them as per the requirement. - For more information please refer the reference guide for Amazon S3 connector.
Now we can export the imported connector and the API into a single CAR application. CAR application is the one we are going to deploy to server runtime.
Exporting Integration Logic as a CApp¶
CApp (Carbon Application) is the deployable artifact on the integration runtime. Let us see how we can export integration logic we developed into a CApp along with the connector.
Creating Connector Exporter Project¶
To bundle a Connector into a CApp, a Connector Exporter Project is required.
-
Navigate to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Extensions -> Project Types -> Connector Exporter Project.
-
Enter a name for the Connector Exporter Project.
-
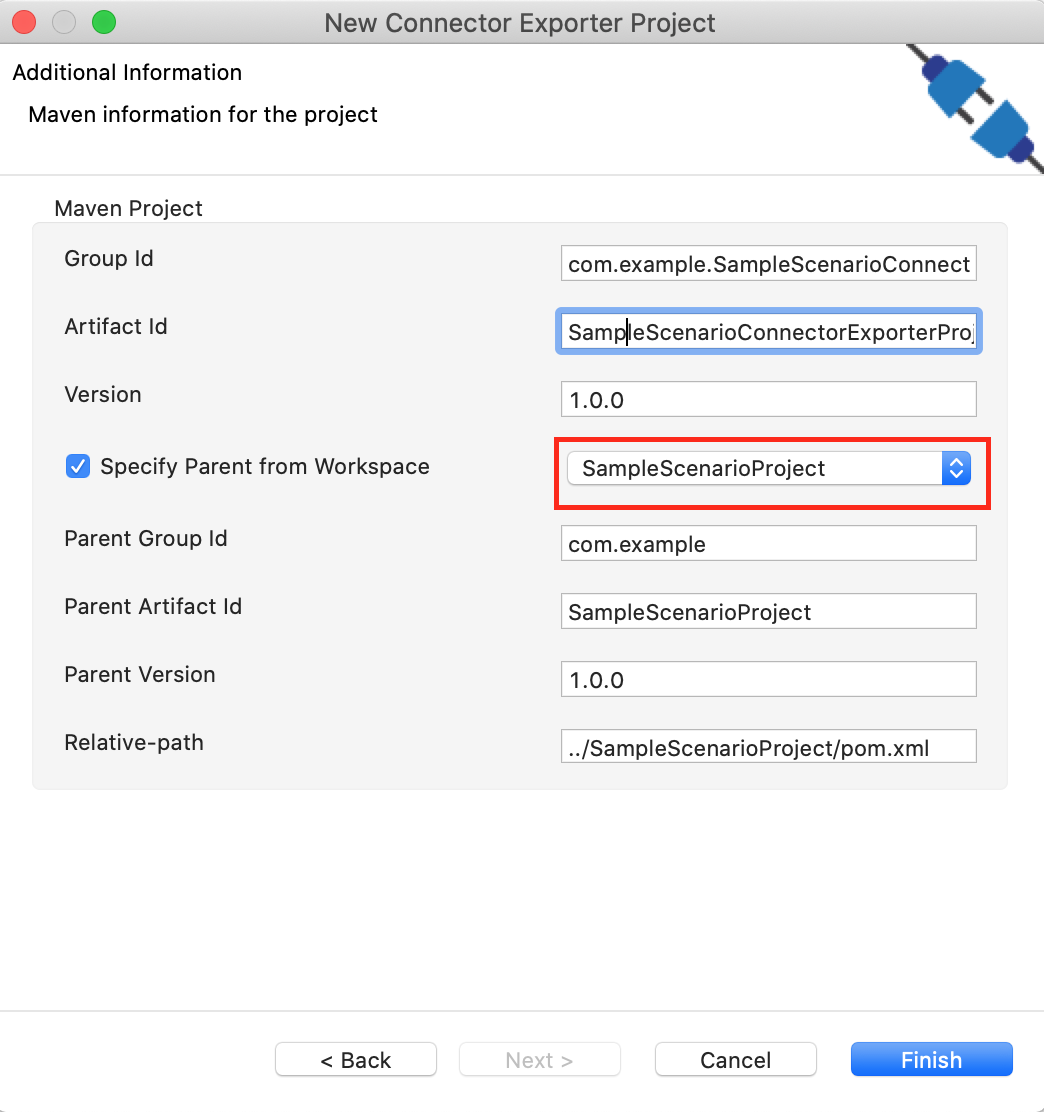
In the next screen select, Specify the parent from workspace and select the specific Integration Project you created from the dropdown.
-
Now you need to add the Connector to Connector Exporter Project that you just created. Right-click the Connector Exporter Project and select, New -> Add Remove Connectors -> Add Connector -> Add from Workspace -> Connector
-
Once you are directed to the workspace, it displays all the connectors that exist in the workspace. You can select the relevant connector and click Ok.
Creating a Composite Application Project¶
To export the Integration Project as a CApp, a Composite Application Project needs to be created. Usually, when an Integration project is created, this project can be created as part of that project by Integration Studio. If not, you can specifically create it by navigating to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Distribution -> Composite Application Project.
Exporting the Composite Application Project¶
-
Right-click the Composite Application Project and click Export Composite Application Project.

-
Select an Export Destination where you want to save the .car file.
-
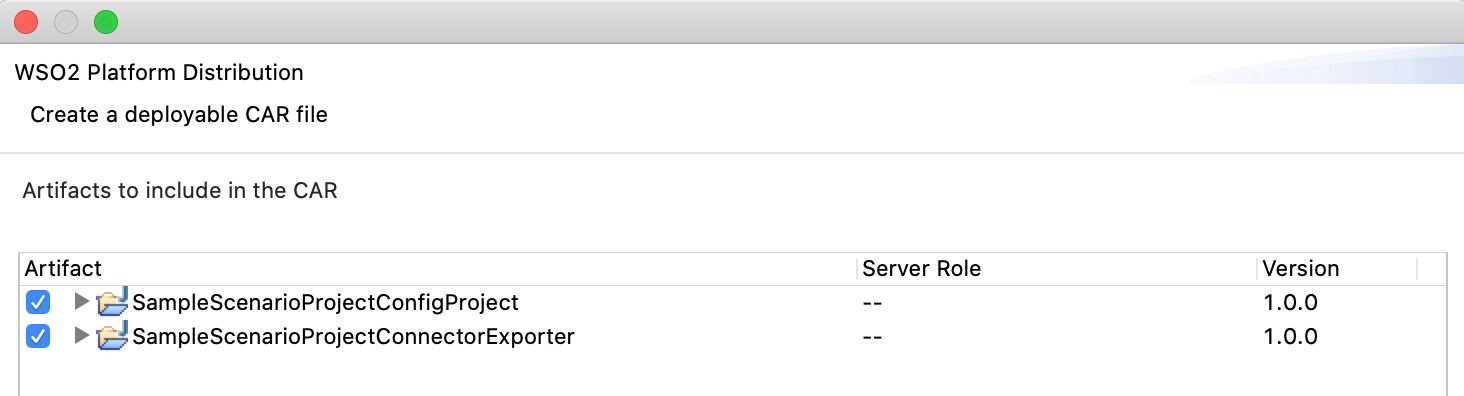
In the next Create a deployable CAR file screen, select both the created Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project to save and click Finish. The CApp is created at the specified location provided at the previous step.
Now the exported CApp can be deployed in the integration runtime so that we can run it and test.
Get the project¶
You can download the ZIP file and extract the contents to get the project code.
Tip
You may need to update the value of the access key and make other such changes before deploying and running this project.
Deployment¶
Follow these steps to deploy the exported CApp in the integration runtime.
Deploying on Micro Integrator
You can copy the composite application to the <PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps folder and start the server. Micro Integrator will be started and the composite application will be deployed.
You can further refer the application deployed through the CLI tool. See the instructions on managing integrations from the CLI.
Click here for instructions on deploying on ESB Enterprise Integrator 6
You can copy the composite application to the
<PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonappsfolder and start the server.ESB EI server starts and you can login to the Management Console https://localhost:9443/carbon/ URL. Provide login credentials. The default credentials will be admin/admin.
You can see that the API is deployed under the API section.
Testing¶
We can use Curl or Postman to try the API. The testing steps are provided for curl. Steps for Postman should be straightforward and can be derived from the curl requests.
Creating a bucket in Amazon S3¶
- Create a file called data.xml with the following content. Note that the bucket region is
us-east-2. If you need to create the bucket in a different region, modify the hard coded region of the API configuration accordingly.<createBucket> <bucketName>wso2engineers</bucketName> <bucketRegion>us-east-2</bucketRegion> </createBucket> -
Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command. Curl Application can be downloaded from here.
Expected Response:curl -H "Content-Type: application/xml" --request PUT --data @data.xml http://127.0.0.1:8290/s3connector/createbucketYou should receive 200OK response. Please navigate to Amazon AWS S3 console[s3.console.aws.amazon.com] and see if a bucket called
wso2engineersis created. If you tried to create a bucket with a name that already exists, it will reply back with a message indicating the conflict.
Post a message into Amazon S3 bucket¶
- Create a file called data.xml with the following content.
<addMessage> <objectName>Julian.txt</objectName> <bucketName>wso2engineers</bucketName> <message>Julian Garfield, Software Engineer, Integration Group</message> </addMessage> - Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command. Curl Application can be downloaded from here.
Expected Response: You will receive a response like below containing the details of the object created.curl -H "Content-Type: application/xml" --request POST --data @data.xml http://127.0.0.1:8290/s3connector/addobject
Navigate to AWS S3 console and click on the bucket<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <CompleteMultipartUploadResult xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/"> <Location>http://wso2engineers.s3.amazonaws.com/Julian.txt</Location> <Bucket>wso2engineers</Bucket> <Key>Julian.txt</Key> <ETag>"2b492c33895569c5c06cd7942f42914f-1"</ETag> </CompleteMultipartUploadResult>wso2engineers. You will note that a file has been created with the nameJulian.txt.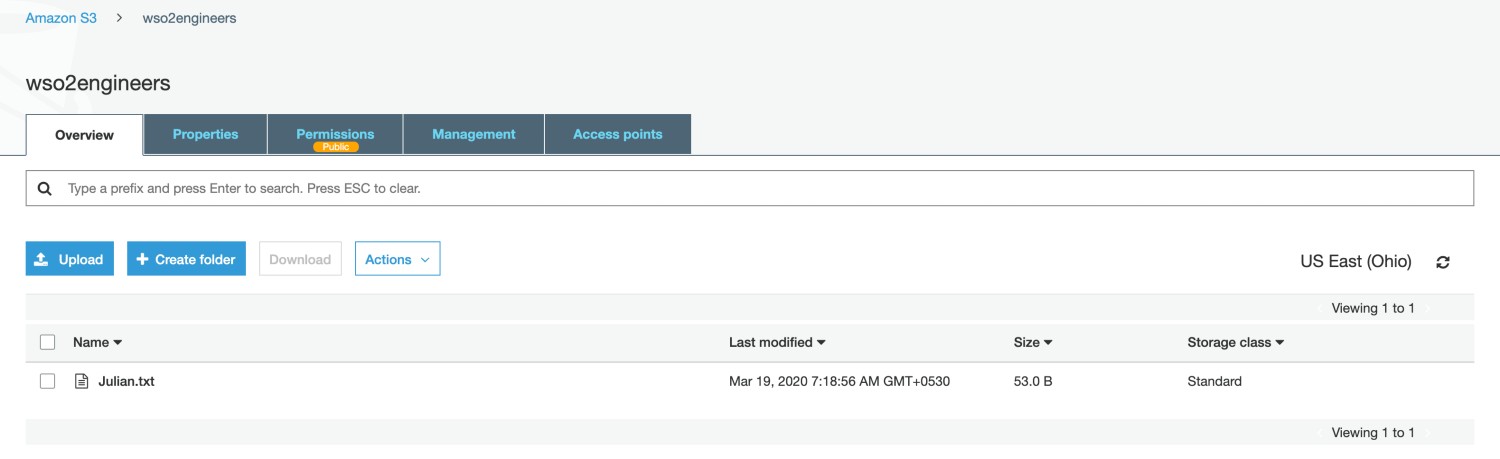
Read objects from Amazon S3 bucket¶
Now let us read the information on wso2engineers that we stored in the Amazon S3 bucket.
- Create a file called data.xml with the following content. It specifies which bucket to read from and what the filename is. This example assumes that the object is stored at root level inside the bucket. You can also read a object stored in a folder inside the bucket.
<getObject> <objectName>Julian.txt</objectName> <bucketName>wso2engineers</bucketName> </getObject> -
Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
Expected Response: You will receive a response like below containing the details of the engineer requested.curl -H "Content-Type: application/xml" --request POST --data @data.xml http://127.0.0.1:8290/s3connector/infoJulian Garfield, Software Engineer, Integration Group
In this example Amazon S3 connector is used to perform operations with Amazon S3 storage. You can receive details of the errors that occur when invoking S3 operations using the S3 responses itself. Please read the Amazon S3 connector reference guide to learn more about the operations you can perform with the Amazon S3 connector.
Top