Amazon Lambda Connector Example¶
Given below is a sample scenario that demonstrates how to create an Amazon Lambda function in the AWS Lambda Service using the ESB Amazon Lambda Connector.
What you'll build¶
To use the Amazon Lambda connector, add the
This example demonstrates how to use Amazon Lambda Connector to use createFunction operation.
Here we exposed the createFunction operation via an API. The API has one resource with the context /createFunction.
/createFunction: ThecreateFunctionoperation creates a Lambda function.
To create a function, you need a deployment package and an execution role. The deployment package contains your function code. The execution role grants the function permission to use AWS services.
The following diagram illustrates all the required functionality of the Amazon Lambda Service that you are going to build.
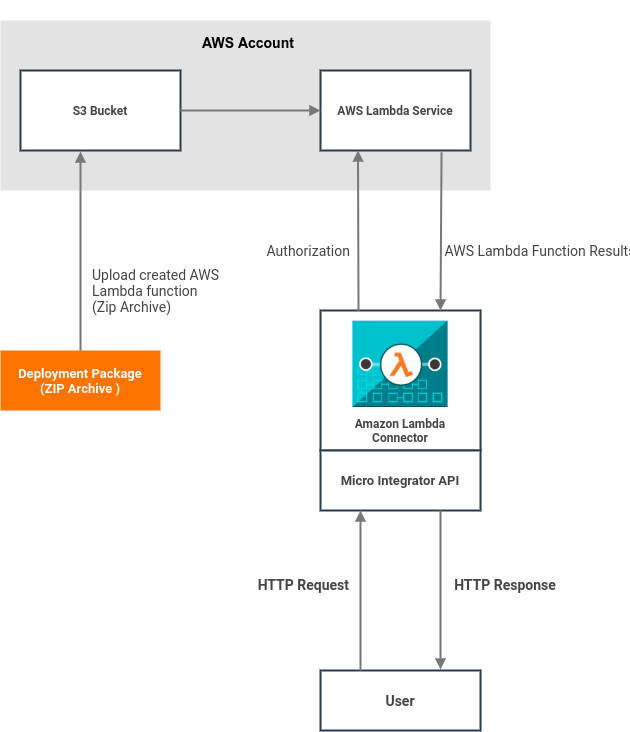
This example demonstrates, how to create an Amazon Lambda function easily using the ESB Amazon Lambda Connector. Before creating an Amazon Lambda function inside the AWS Lambda service, you need to implement the required deployment package (ZIP Archive) locally.
As a next step, simply create an AWS S3 bucket and the deployment package should be uploaded into that bucket. This sample API contains a service that can be invoked through an HTTP POST request. Once the service is invoked, it creates a Lambda function inside the AWS Lambda service. When the created Lambda function is invoked, it is able to run without provisioning or managing servers.
If you do not want to configure this yourself, you can simply get the project and run it.
Configure the connector in ESB Integration Studio¶
Follow these steps to set up the Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project.
-
Open ESB Integration Studio and create an Integration Project.
-
Right-click the project that you created and click on Add or Remove Connector -> Add Connector. You will get directed to the Connector Store.
-
Search for the specific connector required for your integration scenario and download it to the workspace.

-
Click Finish, and your Integration Project is ready. The downloaded connector is displayed on the side palette with its operations.
-
You can drag and drop the operations to the design canvas and build your integration logic.
-
Right click on the created Integration Project and select New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
-
Right click on the created Integration Project and select, -> New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
-
Specify the API name as
createFunctionand API context as/createFunction. You can go to the XML configuration of the API (source view) and copy the following configuration.
3. Now we can export the imported connector and the API into a single CAR application. The CAR application is what we are going to deploy during server runtime.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <api context="/createFunction" name="createFunction" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <resource methods="POST"> <inSequence> <property expression="json-eval($.secretAccessKey)" name="secretAccessKey" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.accessKeyId)" name="accessKeyId" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.region)" name="region" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.blocking)" name="blocking" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.functionName)" name="functionName" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.functionDescription)" name="functionDescription" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.apiVersionCreateFunction)" name="apiVersionCreateFunction" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.s3Bucket)" name="s3Bucket" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.s3Key)" name="s3Key" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.s3ObjectVersion)" name="s3ObjectVersion" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.zipFile)" name="zipFile" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.targetArn)" name="targetArn" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.environmentVariables)" name="environmentVariables" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.handler)" name="handler" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.kmsKeyArn)" name="kmsKeyArn" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.layers)" name="layers" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.memorySize)" name="memorySize" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.publish)" name="publish" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.role)" name="role" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.runtime)" name="runtime" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.tags)" name="tags" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.timeout)" name="timeout" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.mode)" name="mode" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.securityGroupIds)" name="securityGroupIds" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <property expression="json-eval($.subnetIds)" name="subnetIds" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <amazonlambda.init> <region>{$ctx:region}</region> <accessKeyId>{$ctx:accessKeyId}</accessKeyId> <secretAccessKey>{$ctx:secretAccessKey}</secretAccessKey> <blocking>{$ctx:blocking}</blocking> </amazonlambda.init> <amazonlambda.createFunction> <functionName>{$ctx:functionName}</functionName> <functionDescription>{$ctx:functionDescription}</functionDescription> <apiVersionCreateFunction>{$ctx:apiVersionCreateFunction}</apiVersionCreateFunction> <s3Bucket>{$ctx:s3Bucket}</s3Bucket> <s3Key>{$ctx:s3Key}</s3Key> <s3ObjectVersion>{$ctx:s3ObjectVersion}</s3ObjectVersion> <zipFile>{$ctx:zipFile}</zipFile> <targetArn>{$ctx:targetArn}</targetArn> <environmentVariables>{$ctx:environmentVariables}</environmentVariables> <handler>{$ctx:handler}</handler> <kmsKeyArn>{$ctx:kmsKeyArn}</kmsKeyArn> <layers>{$ctx:layers}</layers> <memorySize>{$ctx:memorySize}</memorySize> <publish>{$ctx:publish}</publish> <role>{$ctx:role}</role> <runtime>{$ctx:runtime}</runtime> <tags>{$ctx:tags}</tags> <timeout>{$ctx:timeout}</timeout> <mode>{$ctx:mode}</mode> <securityGroupIds>{$ctx:securityGroupIds}</securityGroupIds> <subnetIds>{$ctx:subnetIds}</subnetIds> </amazonlambda.createFunction> <respond/> </inSequence> <outSequence/> <faultSequence/> </resource> </api>
Exporting Integration Logic as a CApp¶
CApp (Carbon Application) is the deployable artifact on the integration runtime. Let us see how we can export integration logic we developed into a CApp along with the connector.
Creating Connector Exporter Project¶
To bundle a Connector into a CApp, a Connector Exporter Project is required.
-
Navigate to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Extensions -> Project Types -> Connector Exporter Project.
-
Enter a name for the Connector Exporter Project.
-
In the next screen select, Specify the parent from workspace and select the specific Integration Project you created from the dropdown.
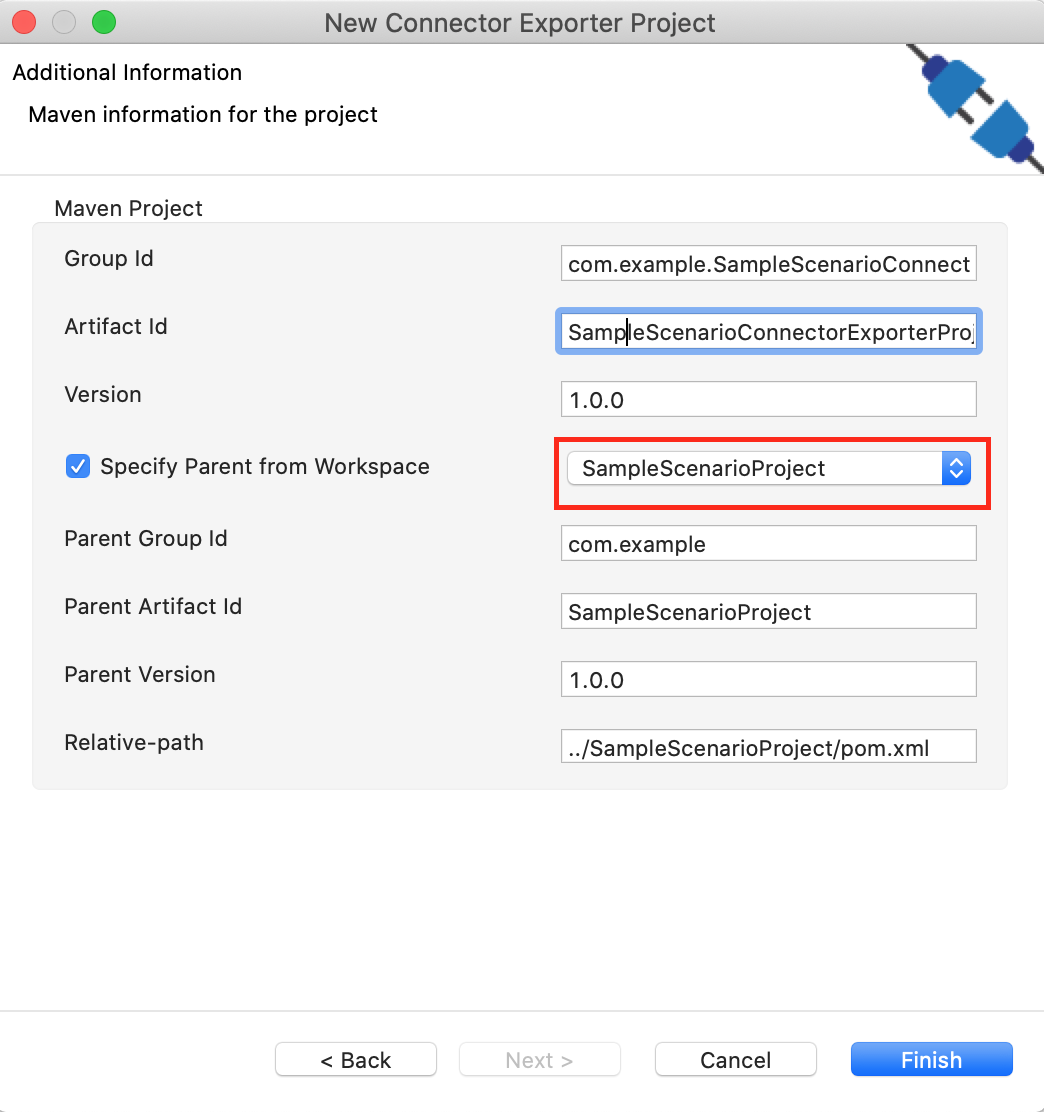
-
Now you need to add the Connector to Connector Exporter Project that you just created. Right-click the Connector Exporter Project and select, New -> Add Remove Connectors -> Add Connector -> Add from Workspace -> Connector
-
Once you are directed to the workspace, it displays all the connectors that exist in the workspace. You can select the relevant connector and click Ok.
Creating a Composite Application Project¶
To export the Integration Project as a CApp, a Composite Application Project needs to be created. Usually, when an Integration project is created, this project can be created as part of that project by Integration Studio. If not, you can specifically create it by navigating to File -> New -> Other -> WSO2 -> Distribution -> Composite Application Project.
Exporting the Composite Application Project¶
-
Right-click the Composite Application Project and click Export Composite Application Project.

-
Select an Export Destination where you want to save the .car file.
-
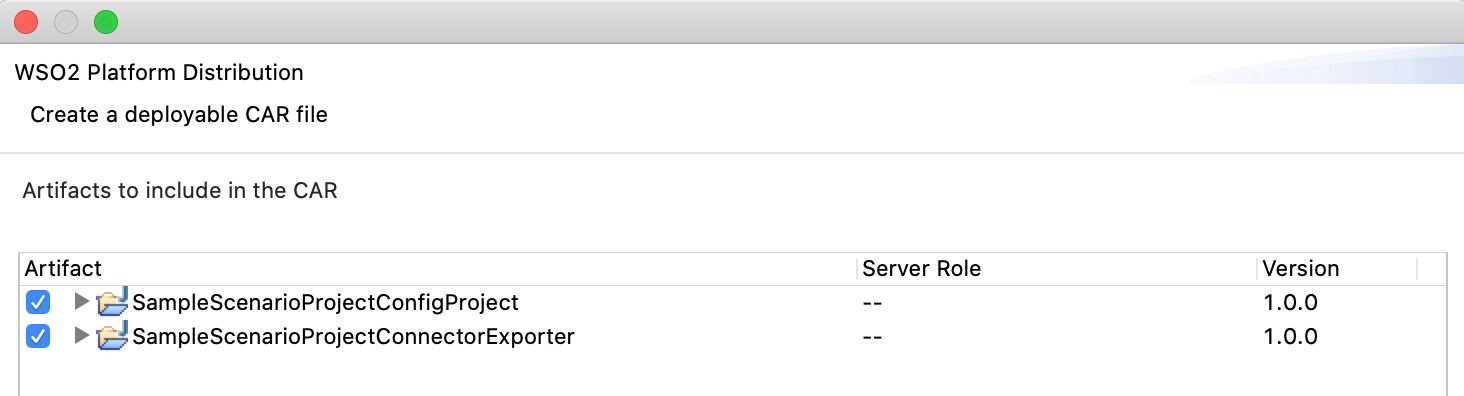
In the next Create a deployable CAR file screen, select both the created Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project to save and click Finish. The CApp is created at the specified location provided at the previous step.
Create Amazon Lambda Deployment Package (Lambda function)¶
In this scenario we created sample AWS Deployment Package (Lambda function) in Python.
-
Our sample Deployment Package would look similar to the following (source view : addingNumbers.py).
import json print('Loading function') def addingNumbers(event, context): #print("Received event: " + json.dumps(event, indent=2)) value1 = event['key1'] value2 = event['key2'] print("value1 = " + value1) print("value2 = " + value2) return float(value1) + float(value2) # Echo back the addition of two keys #raise Exception('Something went wrong') -
Create a ZIP archive.
Please use command line terminal or shell to run following commands. Commands are shown in listings preceded by a prompt symbol ($) and the name of the current directory, when appropriate:
~/Documents$ zip addingNumbers.zip addingNumbers.py
adding: addingNumbers.py.py (deflated 17%)Upload Amazon Lambda Deployment Package (ZIP archive) in to the AWS S3 bucket¶
- Log in to the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to the created S3 bucket (e.g., eiconnectortest).
- Click Upload.
- Select created Amazon Lambda Deployment Package (ZIP archive) and Upload.
Create Execution Role¶
You need to create an Execution Role by referring to the Setting up the Amazon Lambda Environment documentation.
Get the project¶
You can download the ZIP file and extract the contents to get the project code.
Tip
You may need to update the value of the access key and make other such changes before deploying and running this project.
Deployment¶
Follow these steps to deploy the exported CApp in the integration runtime.
Deploying on Micro Integrator
You can copy the composite application to the <PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps folder and start the server. Micro Integrator will be started and the composite application will be deployed.
You can further refer the application deployed through the CLI tool. See the instructions on managing integrations from the CLI.
Click here for instructions on deploying on ESB Enterprise Integrator 6
You can copy the composite application to the
<PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonappsfolder and start the server.ESB EI server starts and you can login to the Management Console https://localhost:9443/carbon/ URL. Provide login credentials. The default credentials will be admin/admin.
You can see that the API is deployed under the API section.
Testing¶
- Log in to the Micro Integrator CLI tool.
./mi remote login -
Provide default credentials admin for both username and password.
-
In order to view the proxy services deployed, execute the following command.
./mi api show - Send a POST request using a CURL command or sample client.
curl -v POST -d '{ "secretAccessKey":"xxxx", "accessKeyId":"xxxx", "region":"us-east-2", "blocking":"false", "s3Bucket":"eiconnectortest", "s3Key":"addingNumbers.zip", "s3ObjectVersion":"null", "functionName":"eiLambdaConnector", "handler":"addingNumbers.addingNumbers", "role":"arn:aws:iam::610968236798:role/EIConnectorTestRole", "runtime":"python3.7", "apiVersionCreateFunction":"2015-03-31" }' "http://localhost:8290/createFunction" -H "Content-Type:application/json" - See the following message content.
{ "Description": "", "TracingConfig": { "Mode": "PassThrough" }, { "VpcConfig": null, "RevisionId": "4b6e5fdd-cbfa-4ba2-9f6e-528cccdb333f", "LastModified": "2020-03-13T05:33:54.900+0000", "FunctionName": "eiLambdaConnector", "Runtime": "python3.7", "Version": "$LATEST", "LastUpdateStatus": "Successful", "Layers": null, "FunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-2:610968236798:function:eiLambdaConnector", "KMSKeyArn": null, "MemorySize": 128, "LastUpdateStatusReason": null, "DeadLetterConfig": null, "Timeout": 3, "Handler": "addingNumbers.addingNumbers", "CodeSha256": "VAISY9lY/a7DvxZNOSKCj+q/fsbfUaJjKhCsCVG3yzU=", "Role": "arn:aws:iam::610968236798:role/EIConnectorTestRole", "MasterArn": null, "CodeSize": 405, "State": "Active", "StateReason": null, "Environment": null, "StateReasonCode": null, "LastUpdateStatusReasonCode": null } -
Log in to the AWS Management Console.
-
Navigate to the AWS Lambda and Functions tab.
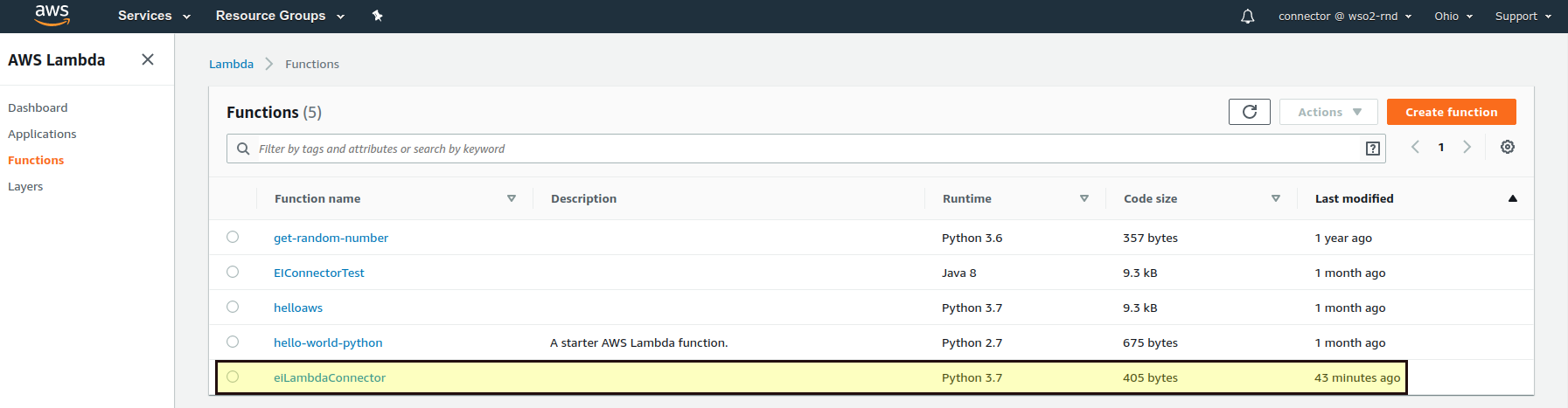
-
Next you need to execute the function. Navigate to Configure test events.
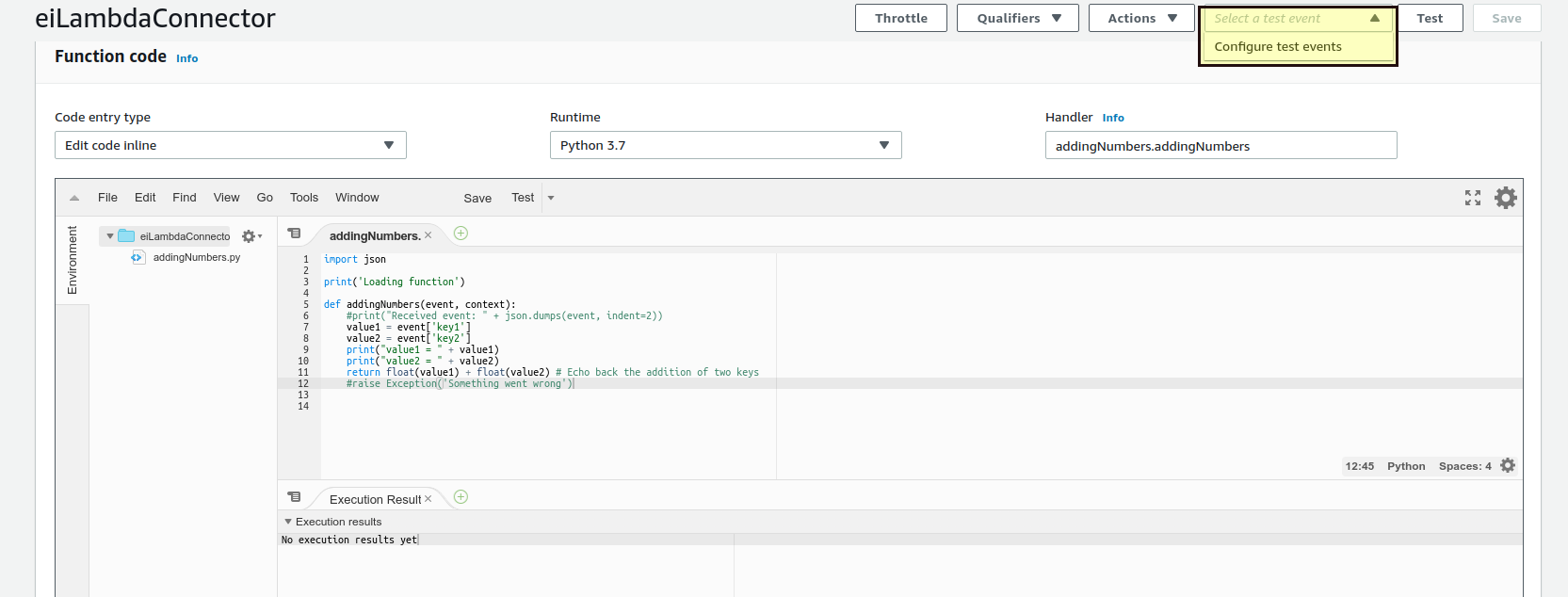
-
Click Create new test event.
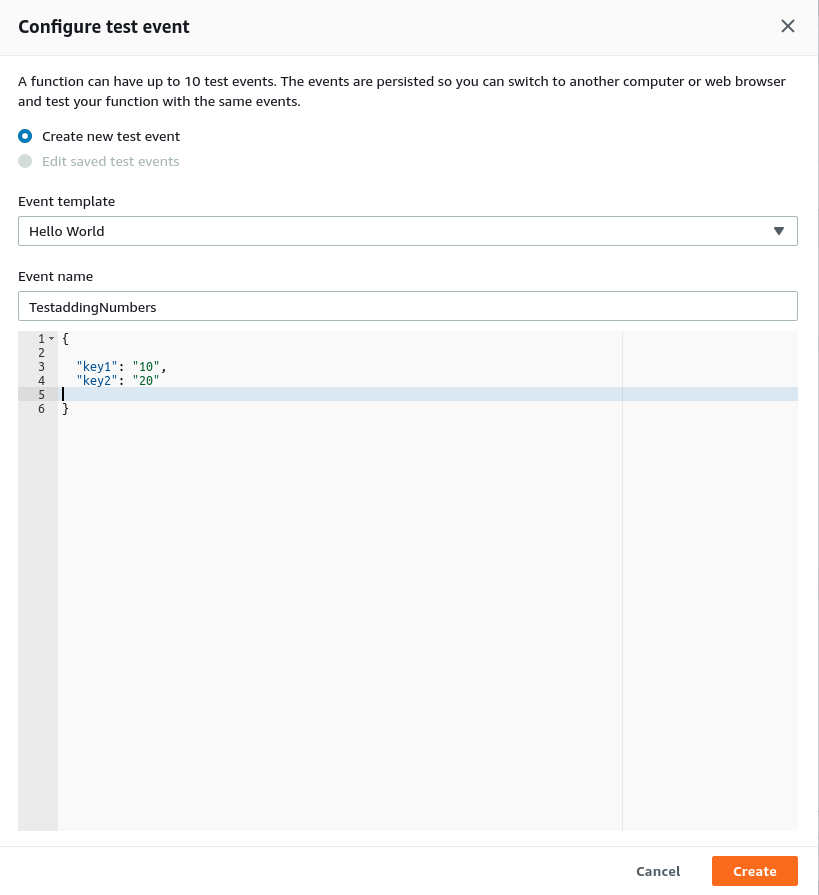
-
Navigate and select the created test event from the dropdown in the top right corner. Click the Test button and execute the test event.
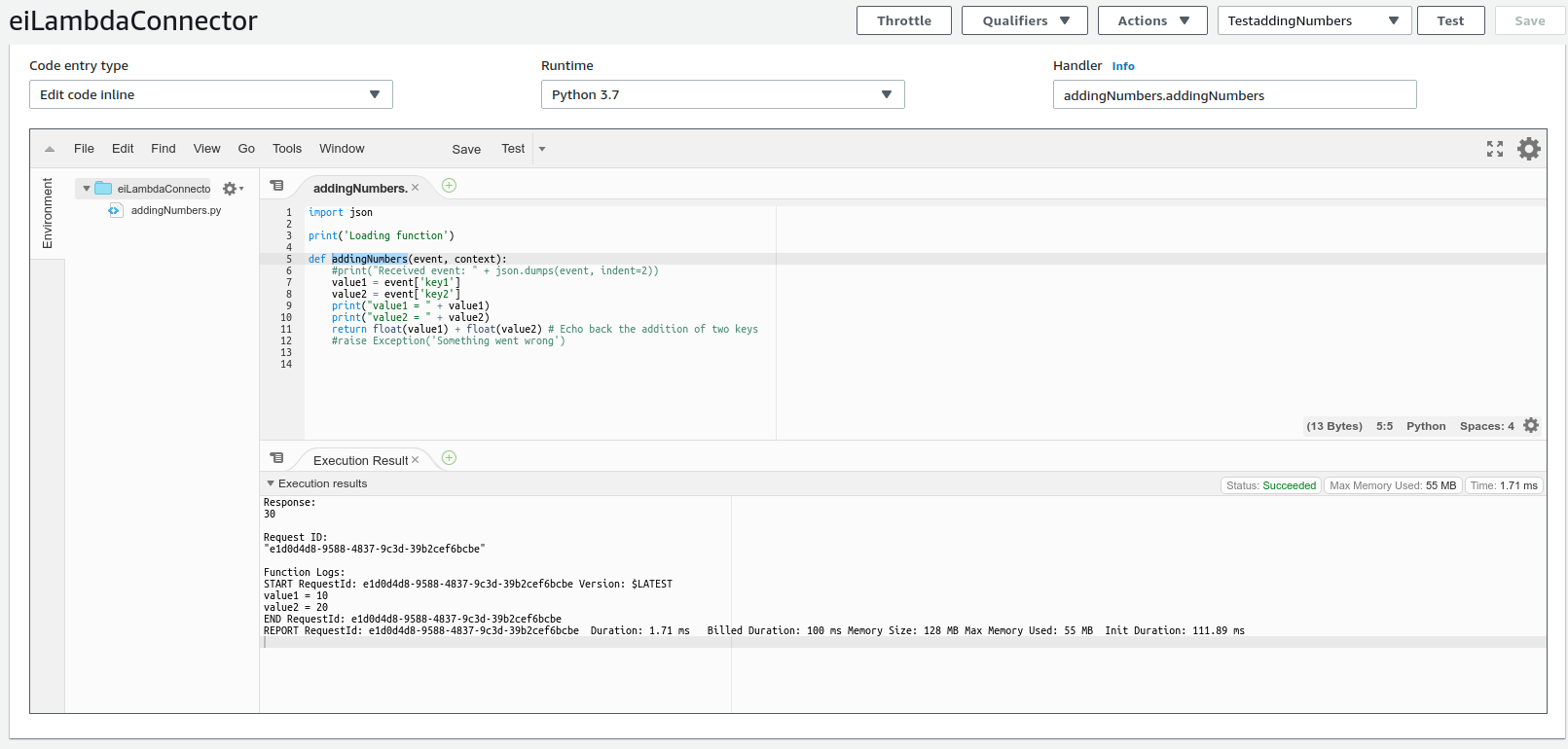
What's next¶
- To customize this example for your own scenario, see Amazon Lambda Connector Configuration documentation.