Amazon DynamoDB Connector Example¶
Amazon DynamoDB Connector allows you to access the Amazon DynamoDB REST API from an integration sequence.
What you'll build¶
Given below is a sample scenario that demonstrates how to work with the Amazon DynamoDB Connector and how to perform various table and items operations with Amazon DynamoDB.
This example explains how to use Amazon DynamoDB Connector to:
- Create a table (a location for storing employee details) in Amazon DynamoDB.
- Insert employee details (items) in to the created table.
- Update employee details table.
- Retrieve information about the inserted employee details (items).
- Remove inserted employee details (items).
- Retrieve list of tables.
- Remove created employee details table.
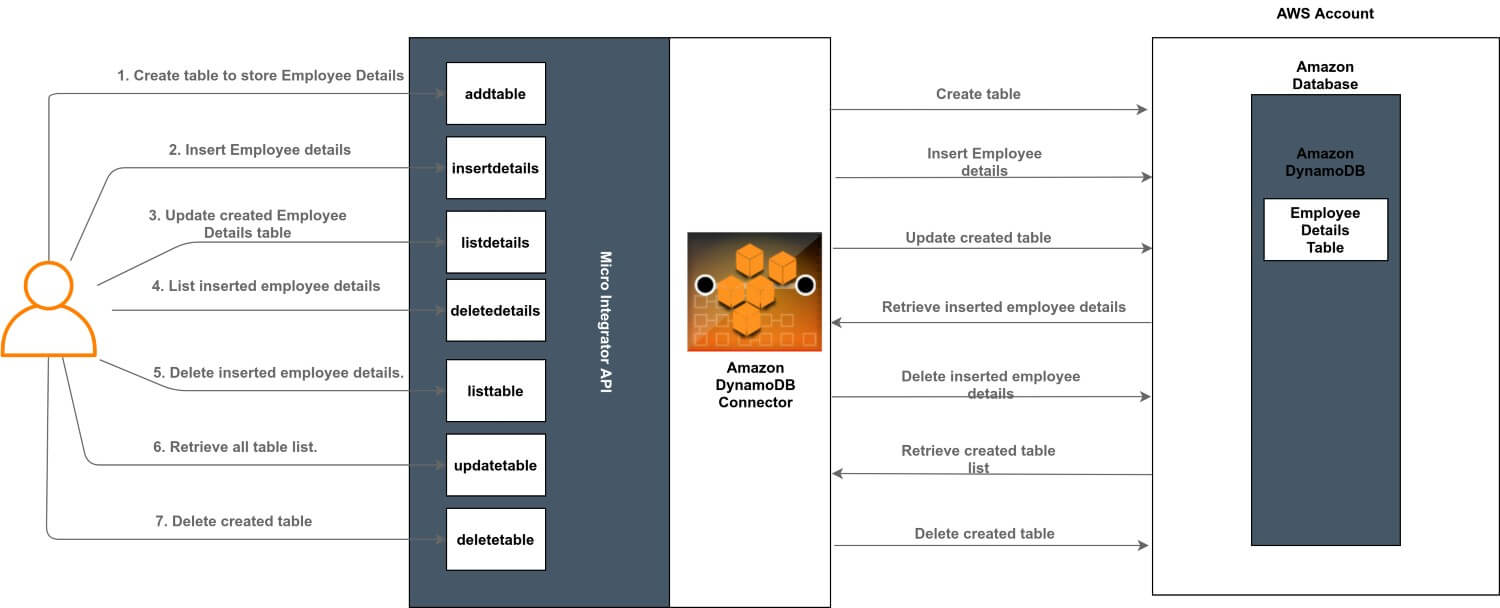
All seven operations are exposed via an API. The API with the context /resources has seven resources
/addtable: Creates a new table in the Amazon DynamoDB with the specified table name to store employee details./insertdetails: Insert employee data (items) and store in the specified table./updatetable: Update specified table (provisioned throughput settings, global secondary indexes, or DynamoDB Streams settings for a specified table)./listdetails: Retrieve information about the added employee details (items)./deletedetails: Remove added employee details from the specified table (items)./listtable: Retrieve information about the created tables./deletetable: Remove created table in the Amazon DynamoDB.
For more information about these operations, please refer to the Amazon DynamoDB connector reference guide.
Note: Before invoking the API, you need to configure message builders/formatters in deployment.toml. See Setting up the Amazon DynamoDB Connector documentation for more information.
The following diagram shows the overall solution. The user creates a table, stores some employee details (items) into the table, and then receives it back. To invoke each operation, the user uses the same API.
If you do not want to configure this yourself, you can simply get the project and run it.
Configure the connector in ESB Integration Studio¶
Connectors can be added to integration flows in ESB Integration Studio. Once added, the operations of the connector can be dragged onto your canvas and added to your resources.
Import the connector¶
Follow these steps to set up the Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project.
-
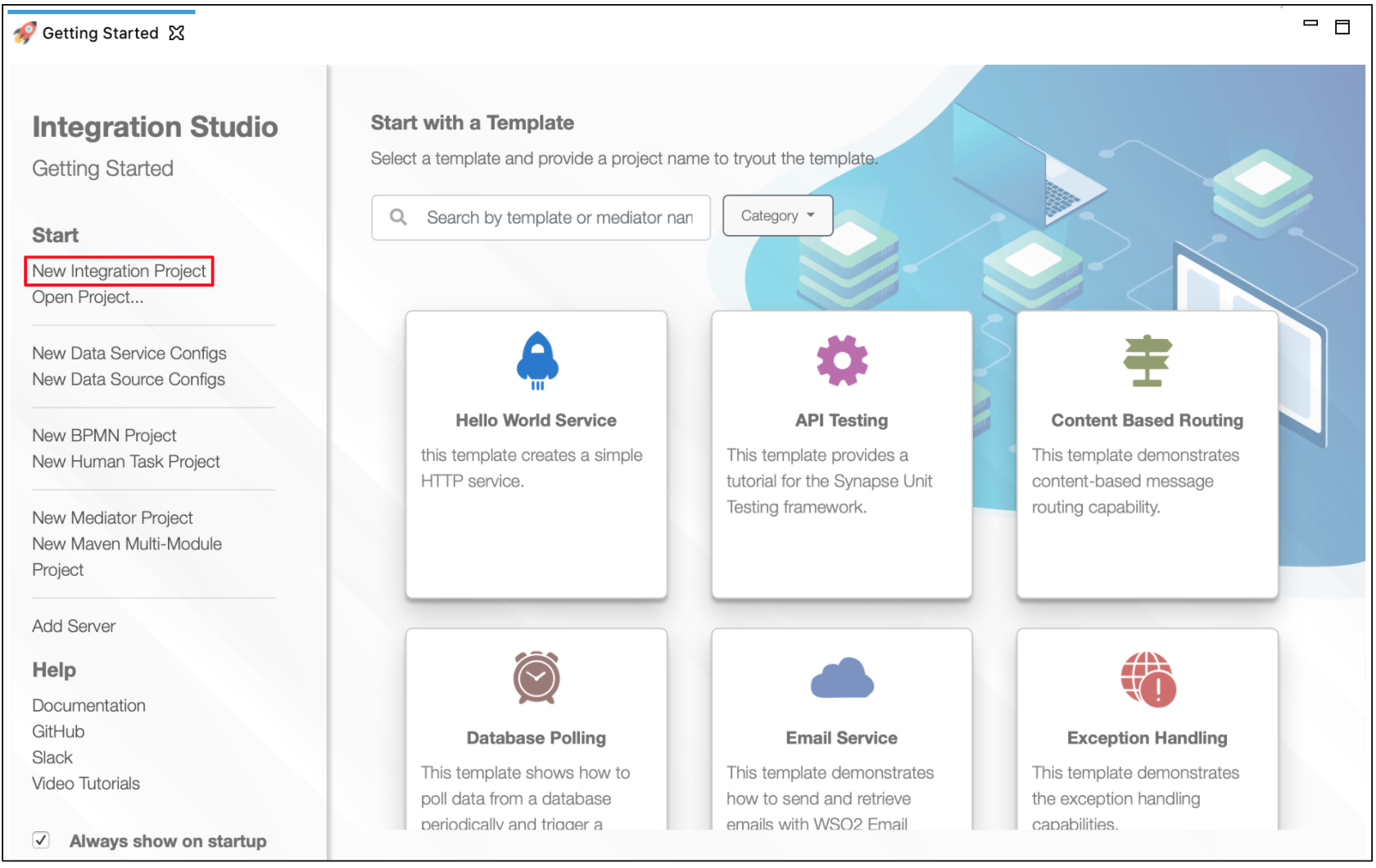
Open ESB Integration Studio and create an Integration Project.
-
Right-click the project that you created and click on Add or Remove Connector -> Add Connector. You will get directed to the Connector Store.
-
Search for the specific connector required for your integration scenario and download it to the workspace.

-
Click Finish, and your Integration Project is ready. The downloaded connector is displayed on the side palette with its operations.
-
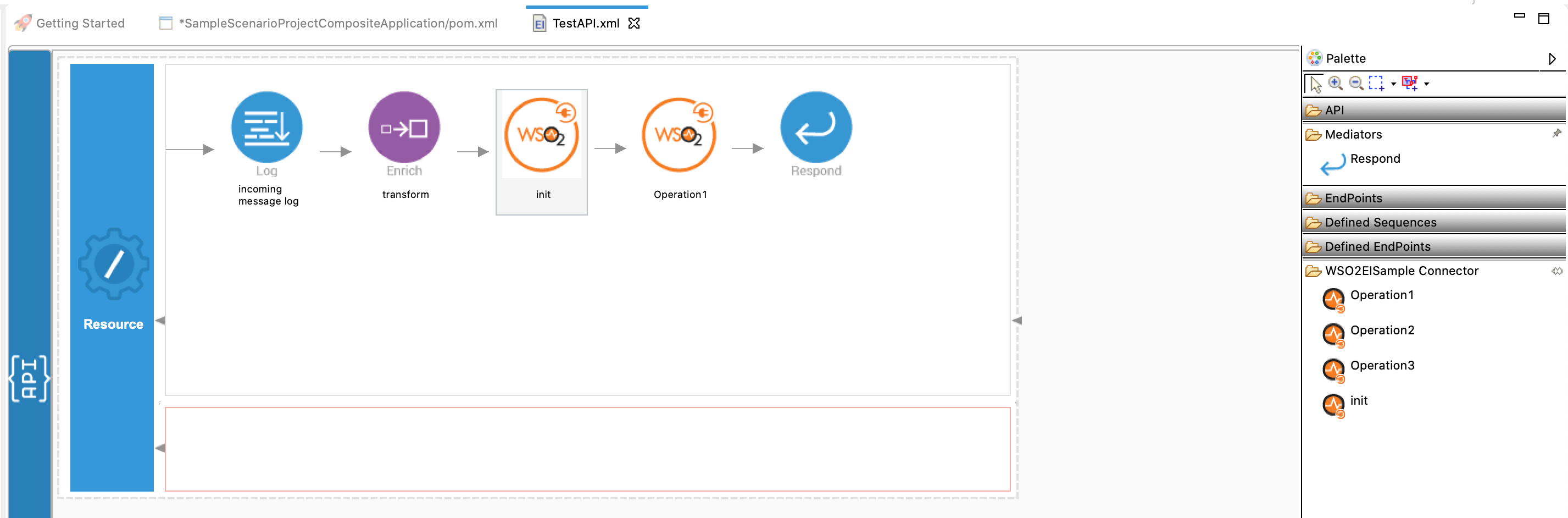
You can drag and drop the operations to the design canvas and build your integration logic.
-
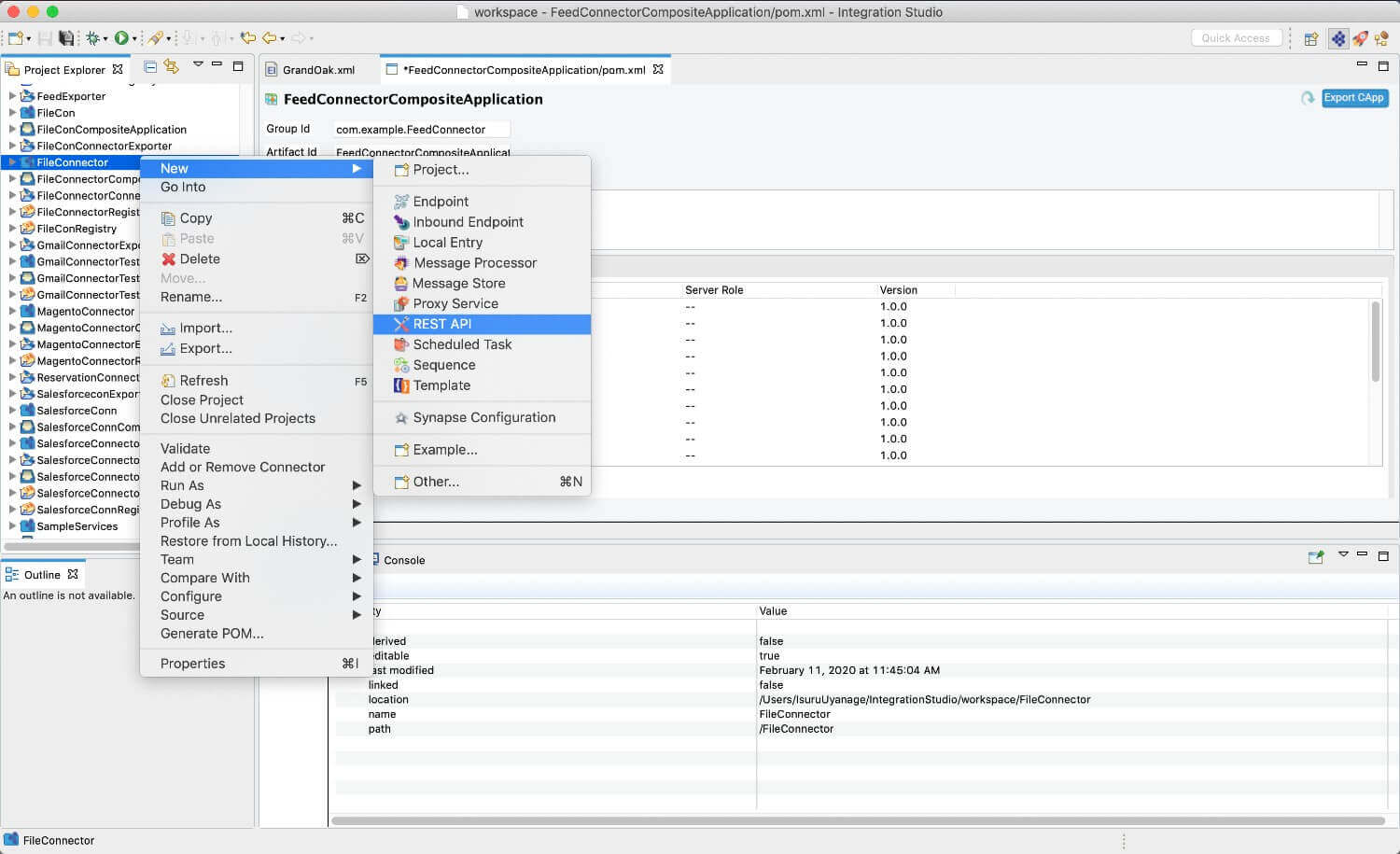
Right click on the created Integration Project and select New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
Add integration logic¶
First create an API, which will be where we configure the integration logic. Right click on the created Integration Project and select, New -> Rest API to create the REST API. Specify the API name as amazonDynamoDBAPI and API context as /resources.
Configuring the API¶
Now follow the steps below to add resources to the API.
Configure a resource for the addtable operation¶
-
Initialize the connector.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
initoperation into the Design pane.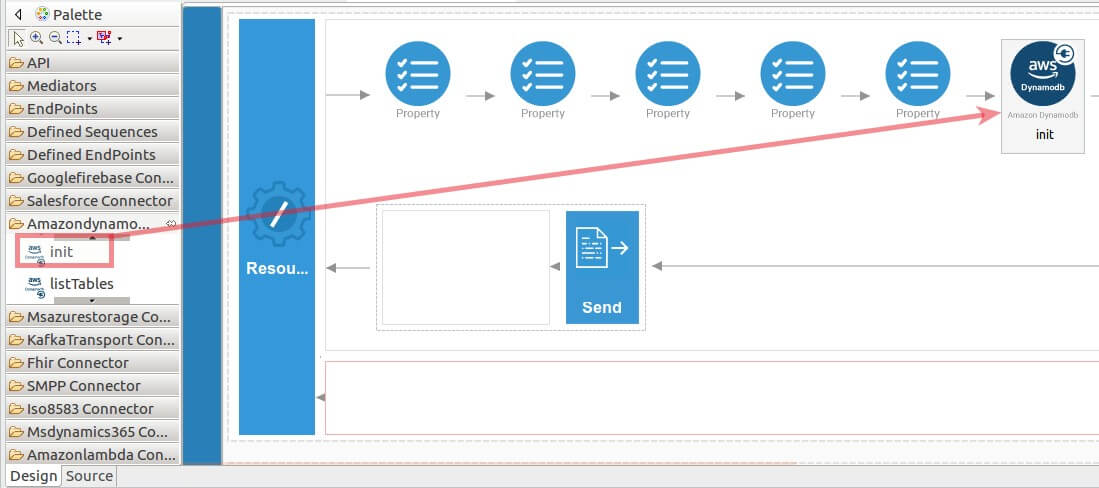
-
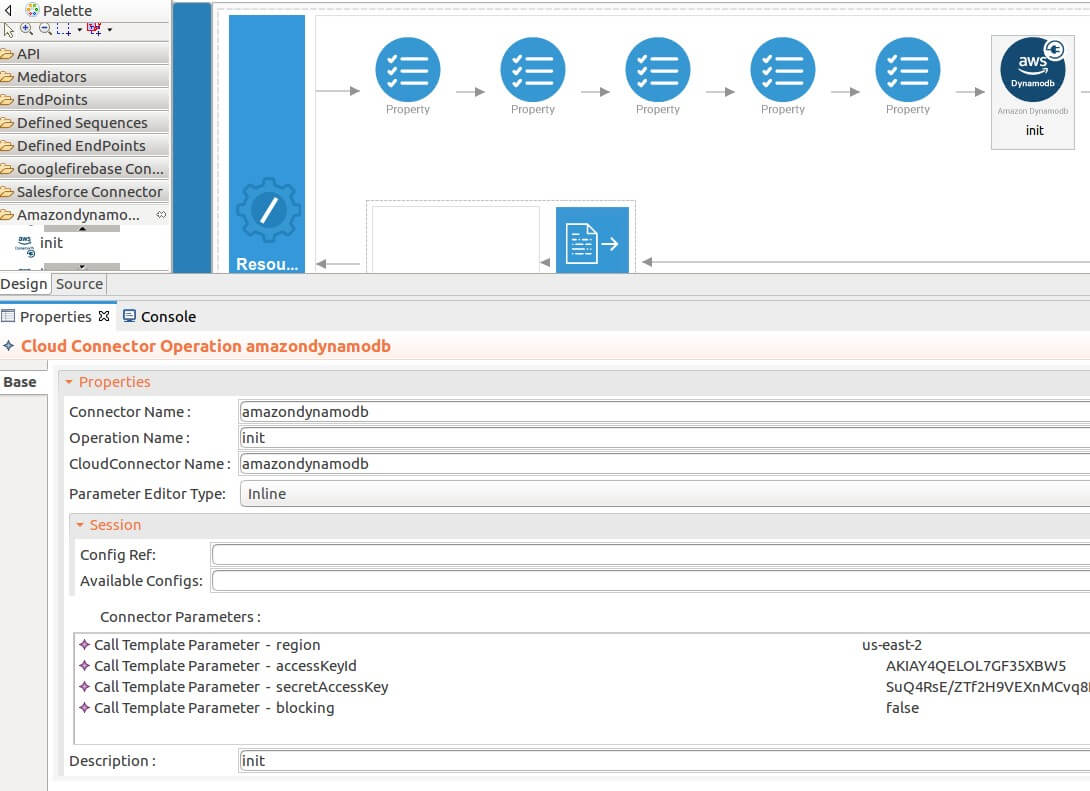
Add the property values into the
initoperation as shown below. Replace theregion,accessKeyId,secretAccessKey,blockingwith your values. -
region : The region of the application access.
- accessKeyId : The AWS secret access key.
- secretAccessKey : The AWS accessKeyId of the user account to generate the signature.
-
blocking : Boolean type, this property helps the connector perform blocking invocations to AmazonDynamoDB.
-
-
Set up the createTable operation.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
createTableoperation into the Design pane.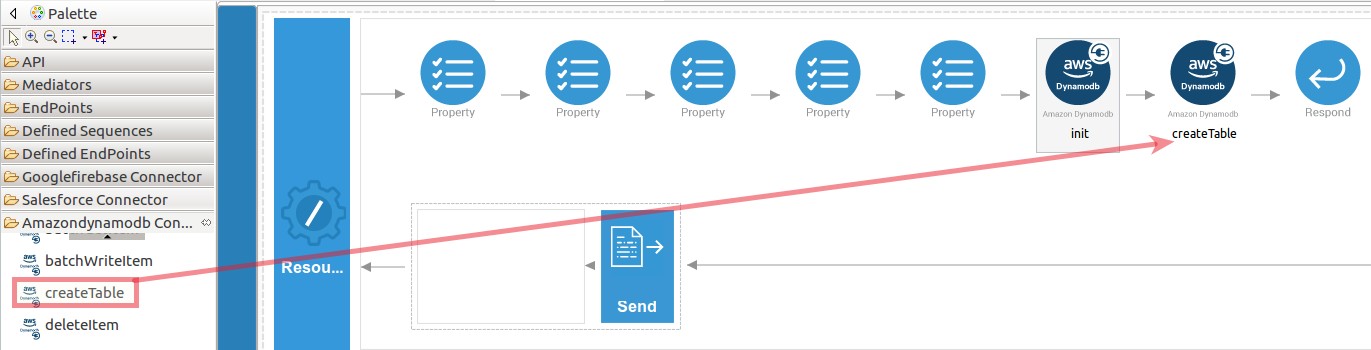
-
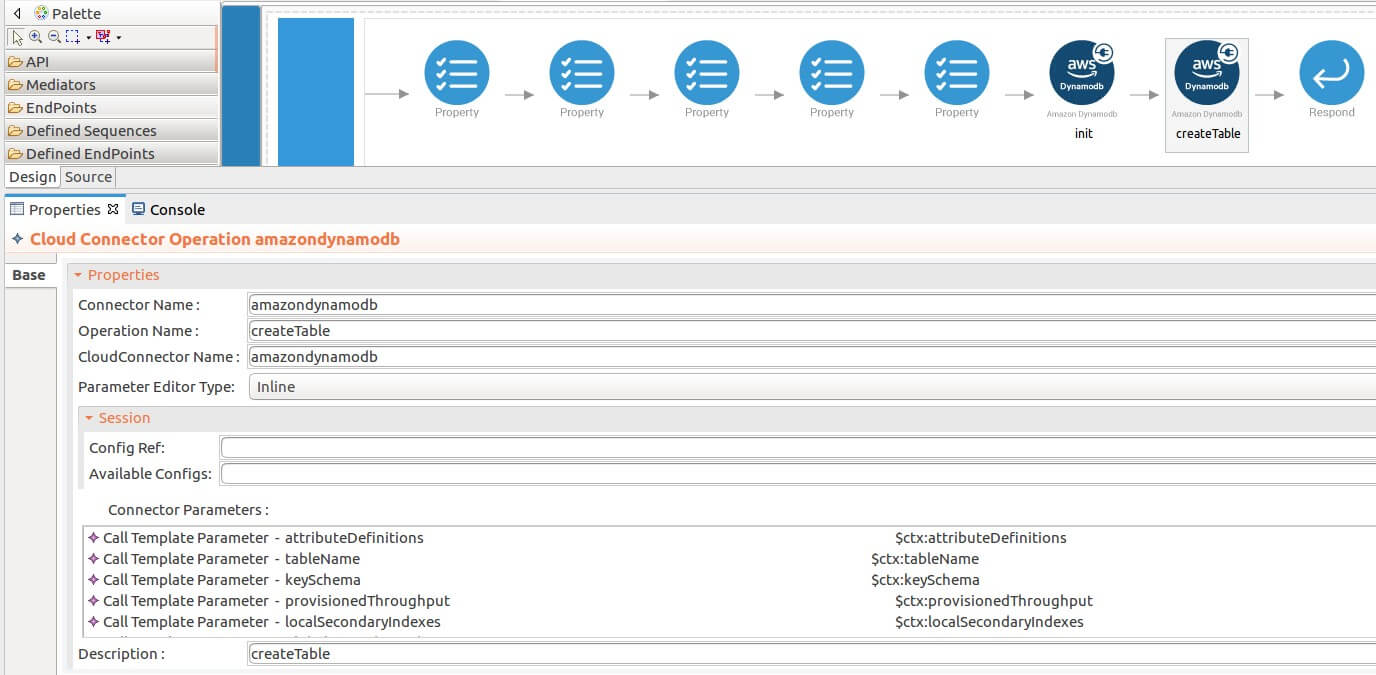
The createTable operation creates a new table. Table names must be unique within each region. The
createTableoperation parameters are listed here. -
attributeDefinitions : A list of attributes that describe the key schema for the table and indexes. If you are adding a new global secondary index to the table, AttributeDefinitions should include the key element(s) of the new index.
- tableName : The name of the table to create.
- keySchema : Specifies the attributes that make up the primary key for a table or an index. The attributes in keySchema must also be defined in attributeDefinitions.
- localSecondaryIndexes : One or more local secondary indexes (the maximum is five) to be created on the table. Each index is scoped to a given partition key value. There is a 10 GB size limit per partition key value. Alternately, the size of a local secondary index is unconstrained.
-
provisionedThroughput : Represents the provisioned throughput setting for a specified table or index.
While invoking the API, the above five parameter values come as a user inputs.
-
To get the input values in to the API we can use the property mediator. Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical mediators icons listed under the Mediators section. Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as shown below.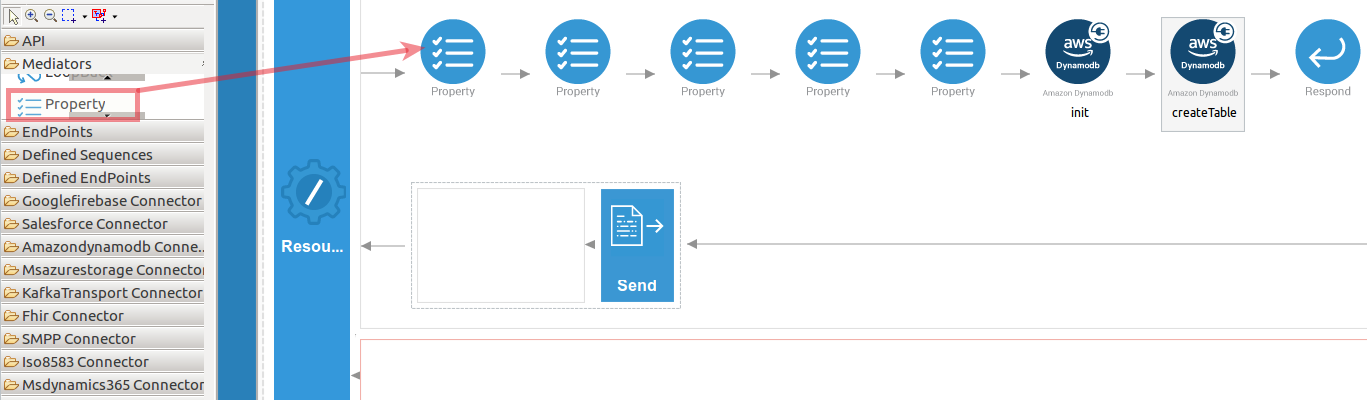
The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows:
Note: That the properties should be add to the pallet before create the operation.
-
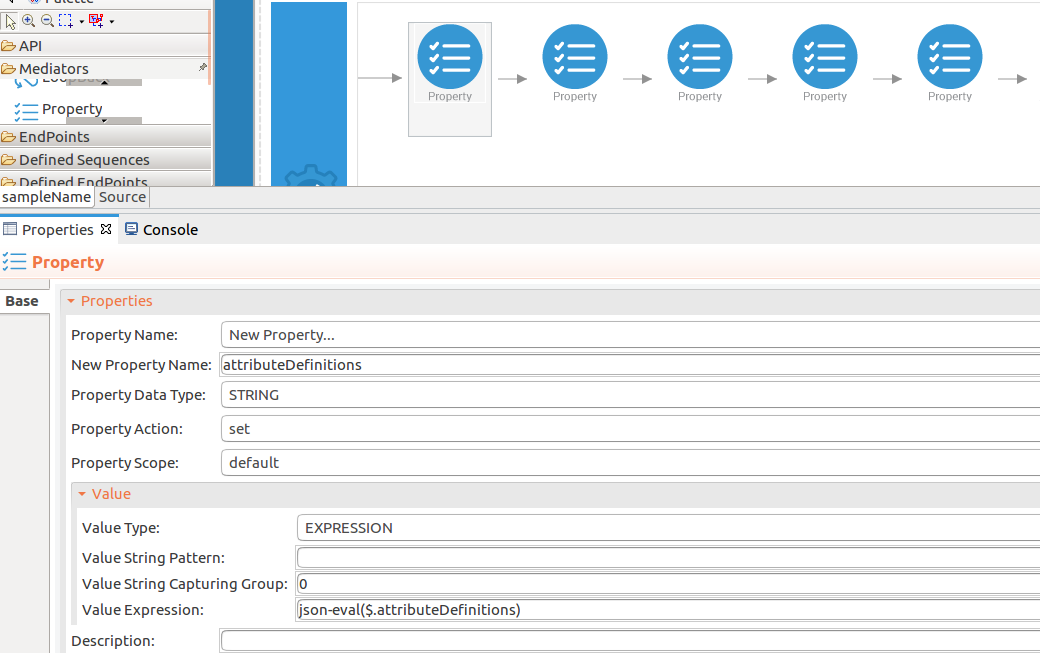
Add the property mediator to capture the
attributeDefinitionsvalue. -
name : attributeDefinitions
-
expression : json-eval($.attributeDefinitions)
-
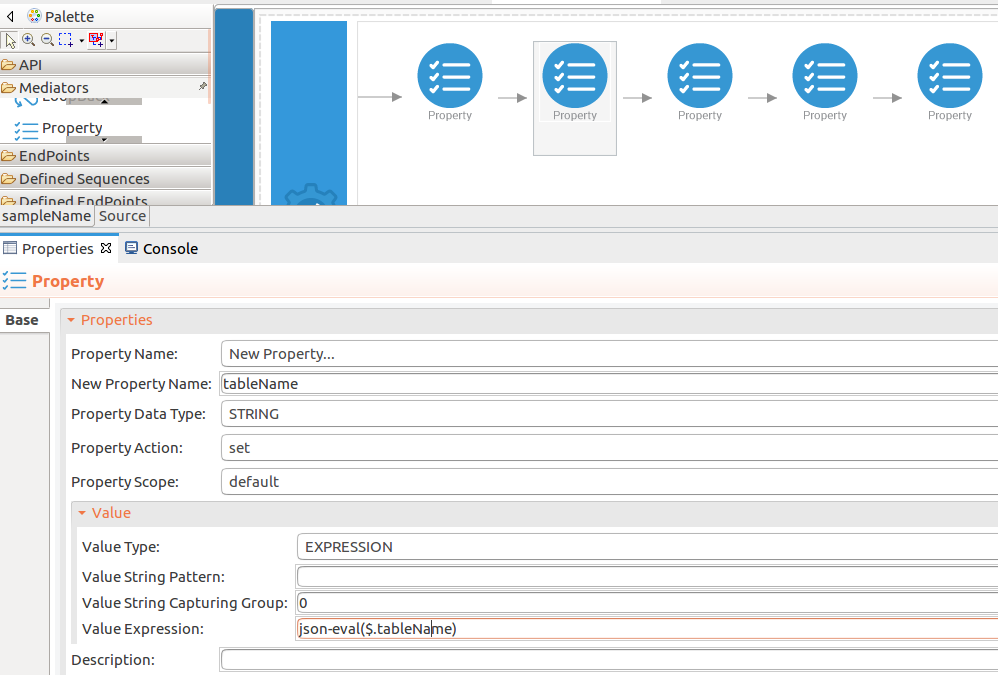
Add the property mediator to capture the
tableNamevalues. -
name : tableName
-
expression : json-eval($.tableName)
-
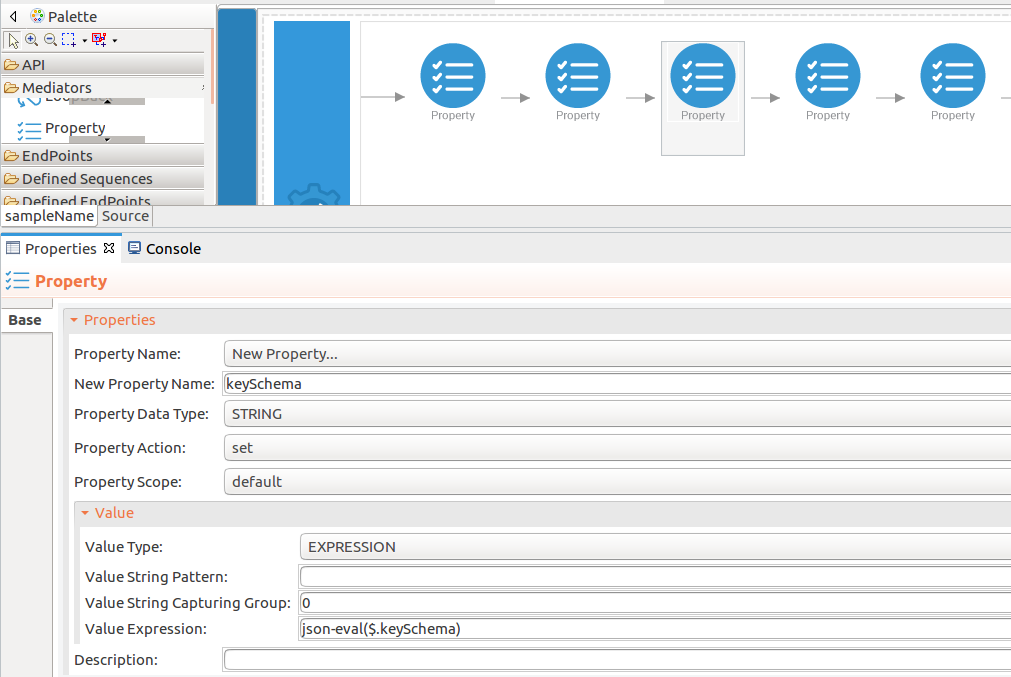
Add the property mediator to capture the
keySchemavalues. -
name : keySchema
-
expression : json-eval($.keySchema)
-
Add the property mediator to capture the
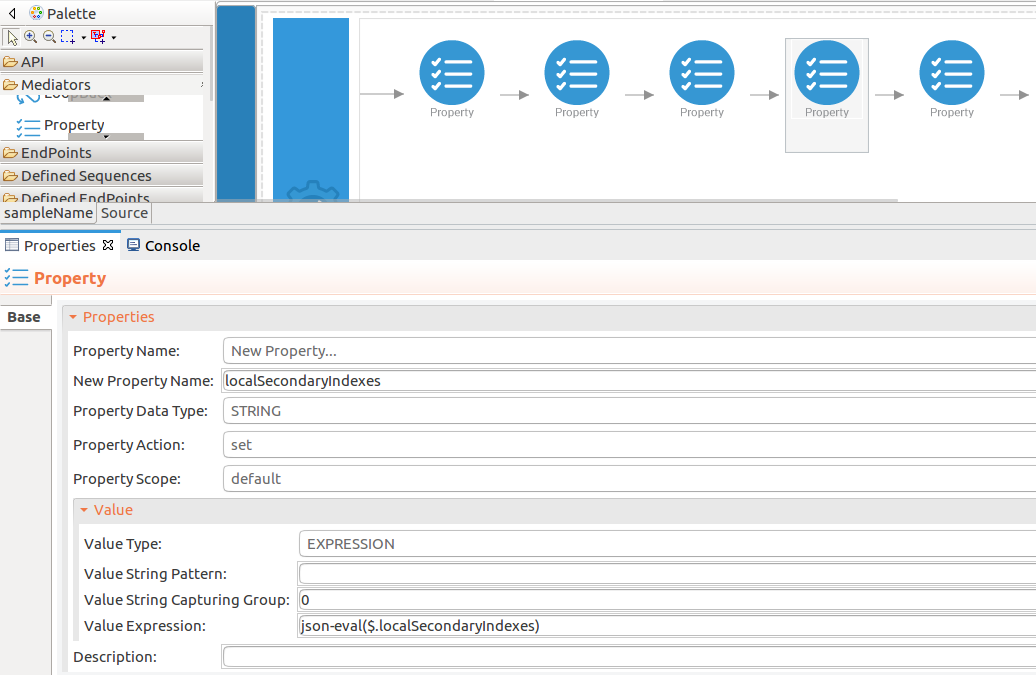
localSecondaryIndexesvalues. -
name : localSecondaryIndexes
-
expression : json-eval($.localSecondaryIndexes)
-
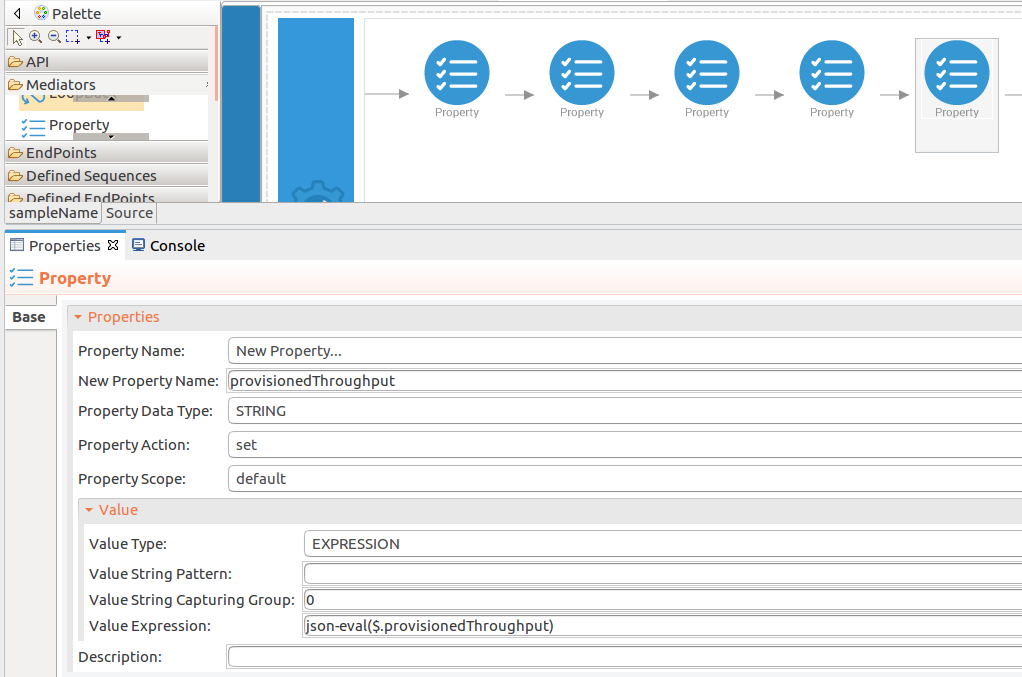
Add the property mediator to capture the
provisionedThroughputvalues. -
name : provisionedThroughput
-
expression : json-eval($.provisionedThroughput)
-
Configure a resource for the insertdetails operation¶
- Initialize the connector.
You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in 1.1 for setting up the init operation to the addtable operation.
-
Set up the putItem operation.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
putItemoperation into the Design pane.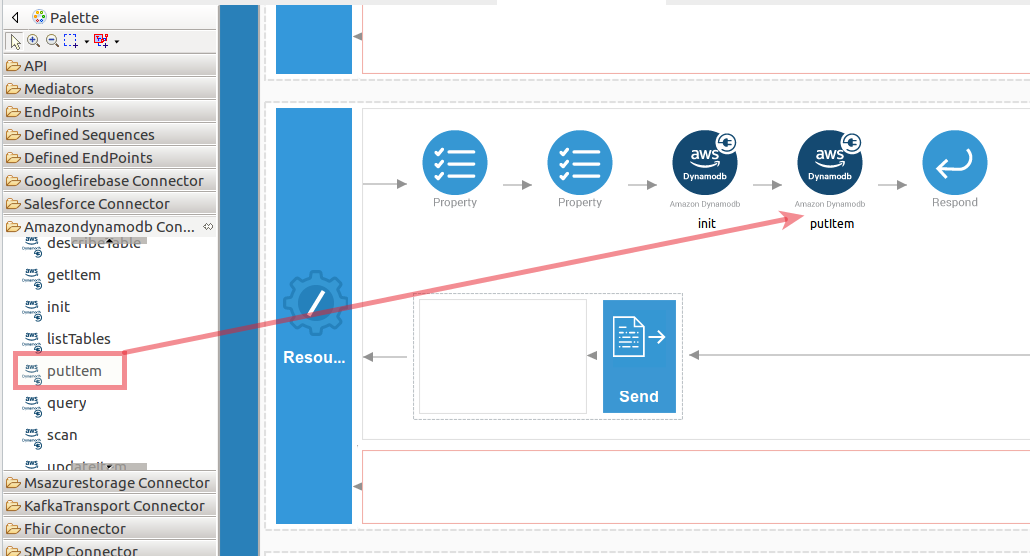
-
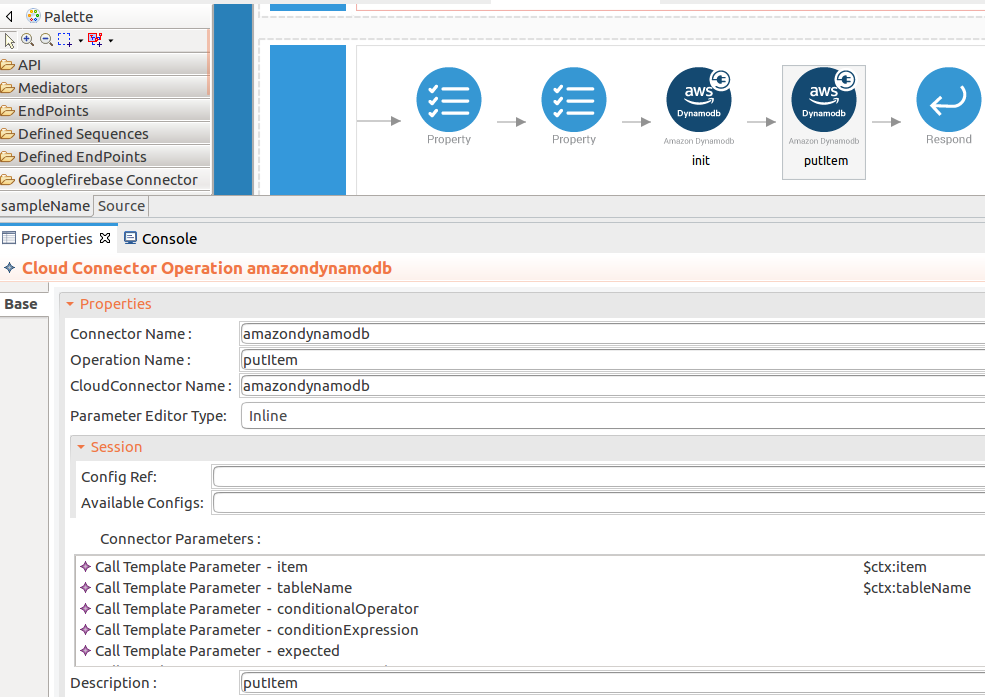
The putItem operation use to insert new items to the tables.
putItemoperation parameters listed here. -
item : A map of attribute name/value pairs, one for each attribute. Only the primary key attributes are required, but you can optionally provide other attribute name-value pairs for the item
-
tableName : The name of the table to contain the item.
While invoking the API, the above two parameter values come as a user inputs.
-
Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as mentioned inaddtableoperation. The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows.
Add the property mediator to capture the
itemvalue.- name : item
-
expression : json-eval($.item)
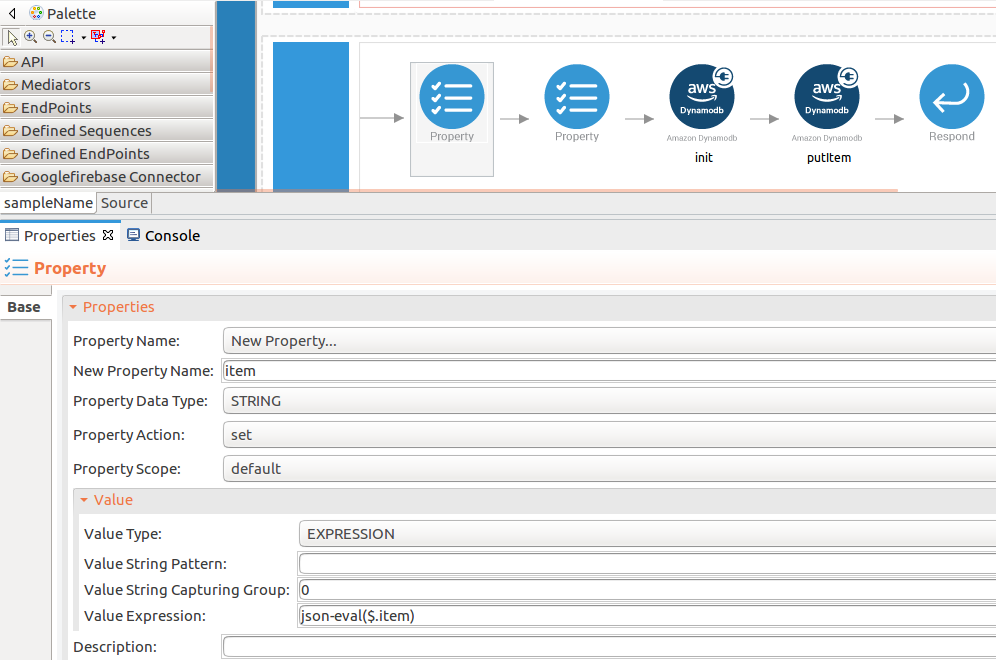
-
Add the property mediator to capture the
tableNamevalues. Please follow the steps given inaddtableoperation. -
name : tableName
- expression : json-eval($.tableName)
-
Configure a resource for the updatetable operation¶
- Initialize the connector.
You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in 1.1 for setting up the init operation to the addtable operation.
-
Set up the updateTable operation.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
updateTableoperation into the Design pane.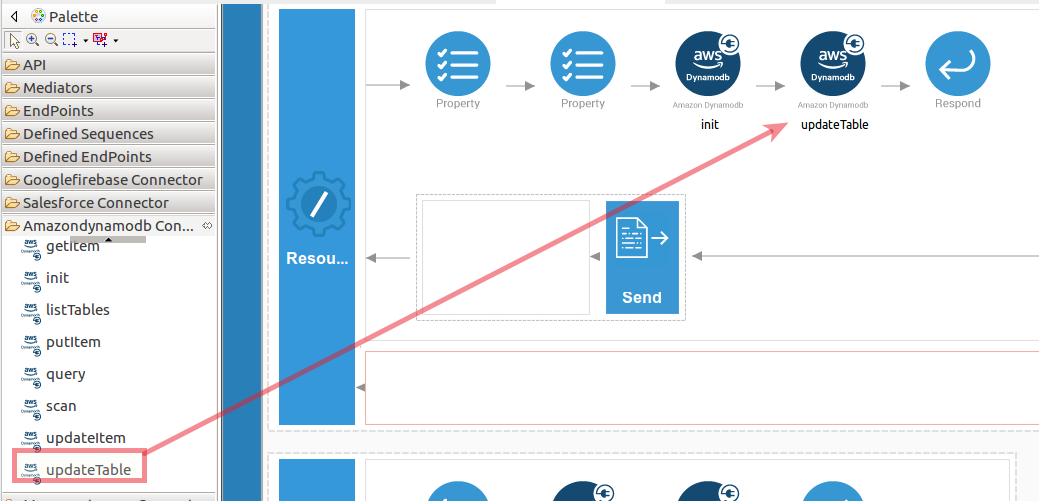
-
The updateTable operation is used to update the created tables. The
updateTableoperation parameters are listed here. -
provisionedThroughput : The new provisioned throughput setting for the specified table or index.
-
tableName : The name of the table to contain the item.
While invoking the API, the above two parameter values come as a user inputs.
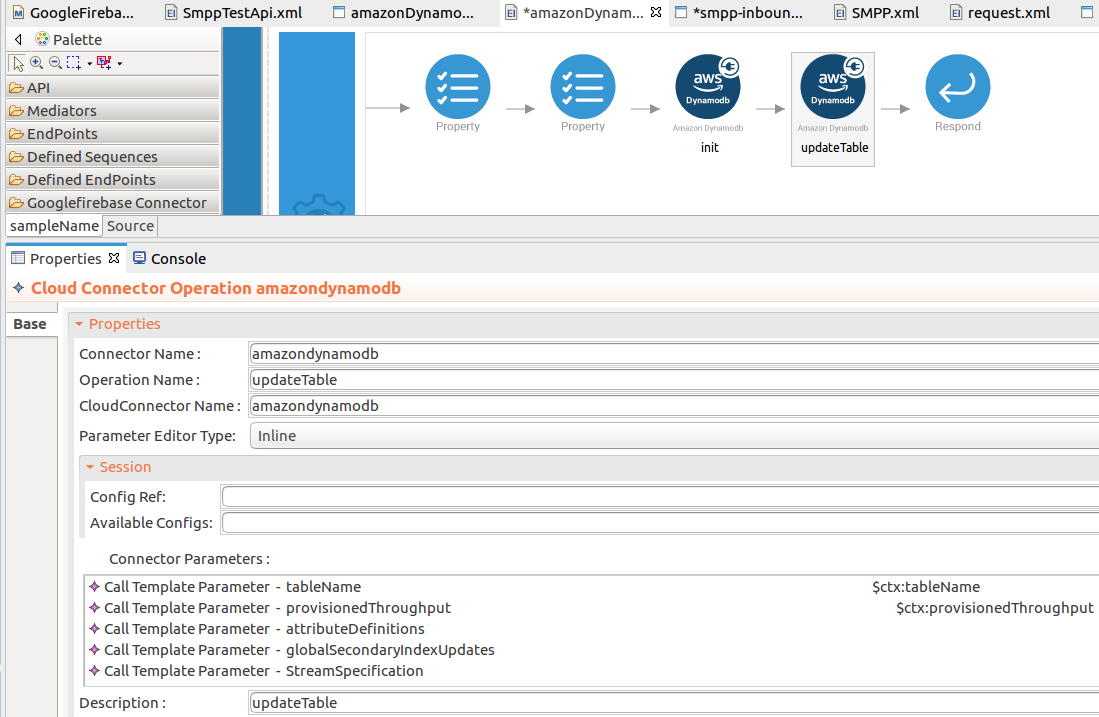
-
Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as mentioned in theaddtableoperation. The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows.
Add the property mediator to capture the
provisionedThroughputvalue.- name : provisionedThroughput
-
expression : json-eval($.provisionedThroughput)
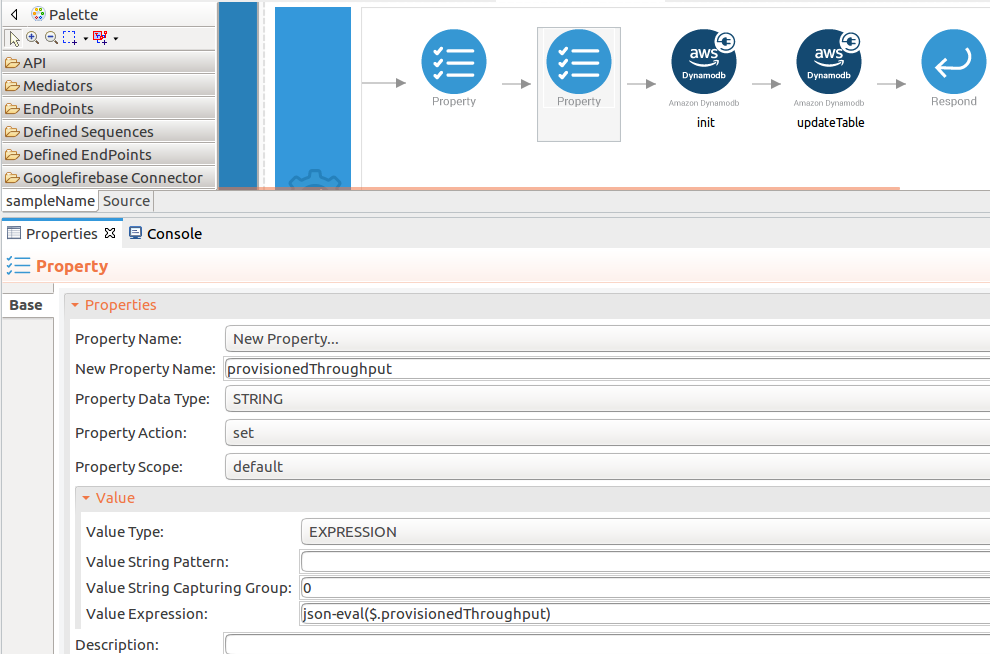
-
Add the property mediator to capture the
tableNamevalues. Please follow the steps given inaddtableoperation. -
name : tableName
- expression : json-eval($.tableName)
-
Configure a resource for the listdetails operation¶
- Initialize the connector.
You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in 1.1 for setting up the init operation to the addtable operation.
-
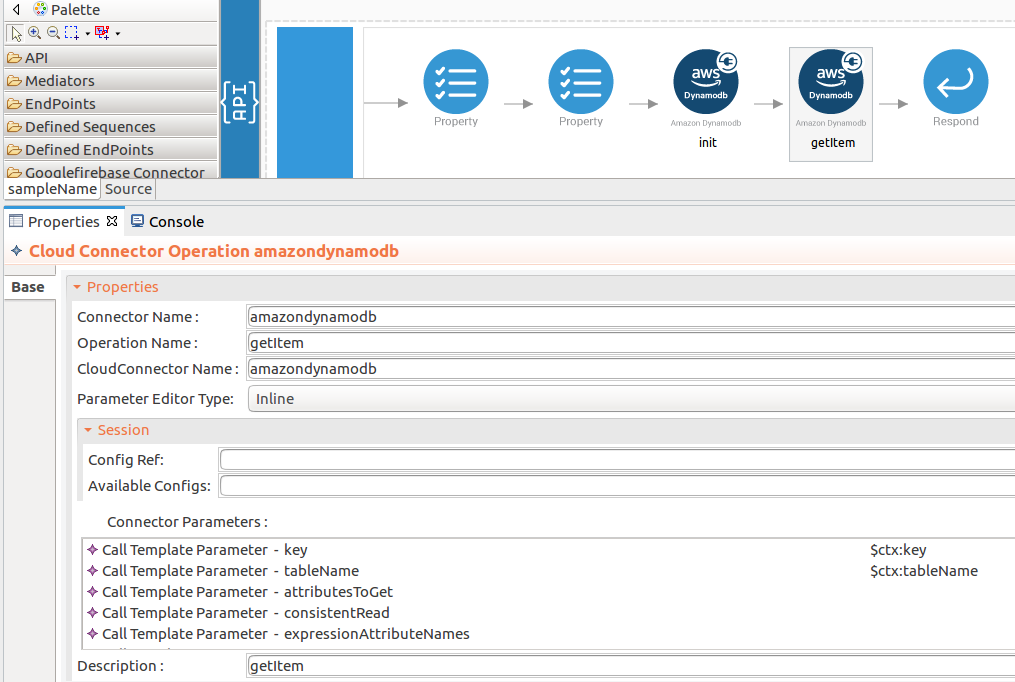
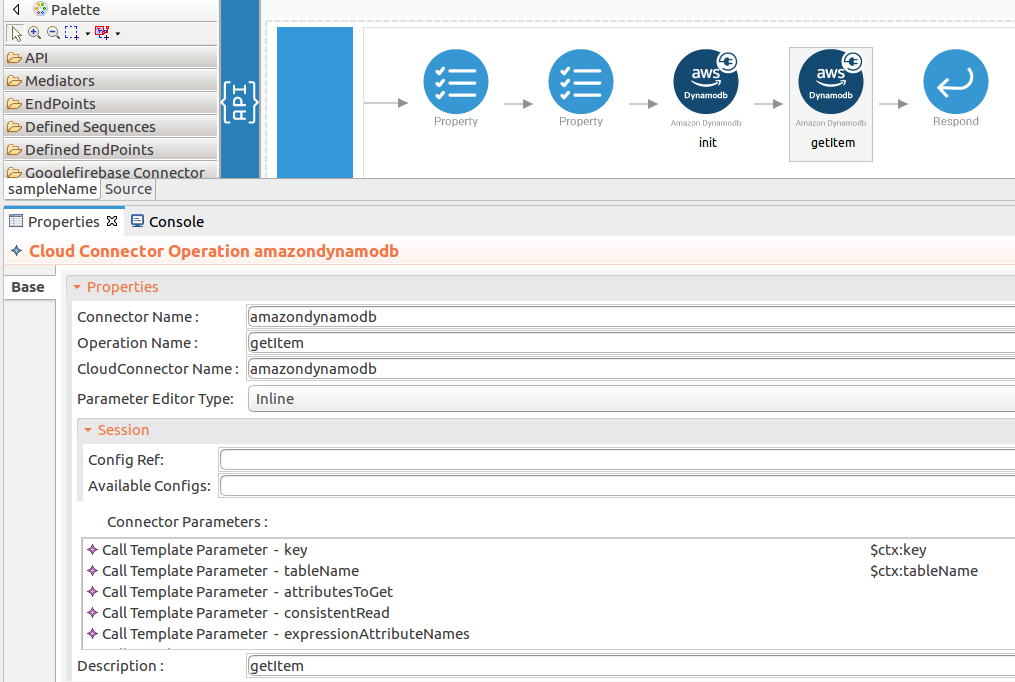
Set up the getItem operation.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
getItemoperation into the Design pane.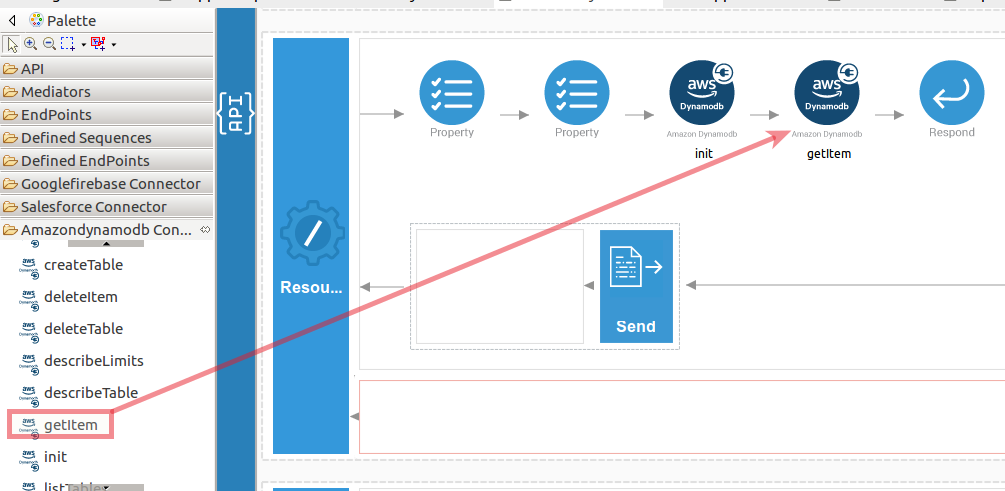
-
The getItem operation is used to retrieve inserted items to the tables. The
getItemoperation parameters are listed here. -
key : An array of primary key attribute values that define specific items in the table. For each primary key, you must provide all of the key attributes.
-
tableName : The name of the table to contain the item.
While invoking the API, the above two parameter values come as a user inputs.
-
Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as mentioned inaddtableoperation. The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows.
Add the property mediator to capture the
keyvalue.- name : key
-
expression : json-eval($.key)
-
Add the property mediator to capture the
tableNamevalues. Please follow the steps given inaddtableoperation. -
name : tableName
- expression : json-eval($.tableName)
-
Configure a resource for the deletedetails operation¶
- Initialize the connector.
You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in 1.1 for setting up the init operation to the addtable operation.
-
Set up the deleteItem operation.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
deleteItemoperation into the Design pane.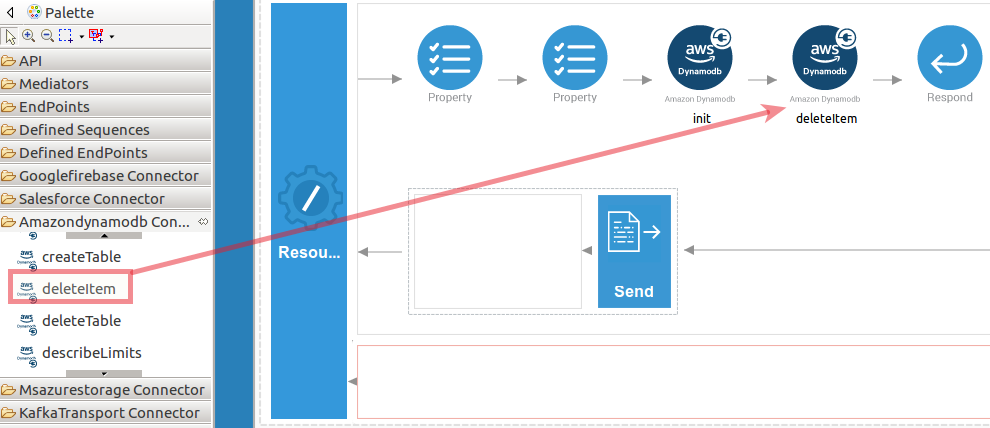
-
The deleteItem operation is used to remove inserted items from the table. The
deleteItemoperation parameters are listed here. -
key : An array of primary key attribute values that define specific items in the table. For each primary key, you must provide all of the key attributes.
- tableName : The name of the table to contain the item.
- returnConsumedCapacity : Determines the level of detail about provisioned throughput consumption that is returned in the response.
-
returnValues : Use returnValues if you want to get the item attributes as they appeared before they were deleted.
While invoking the API, the above two parameter values (key, tableName) come as a user inputs.
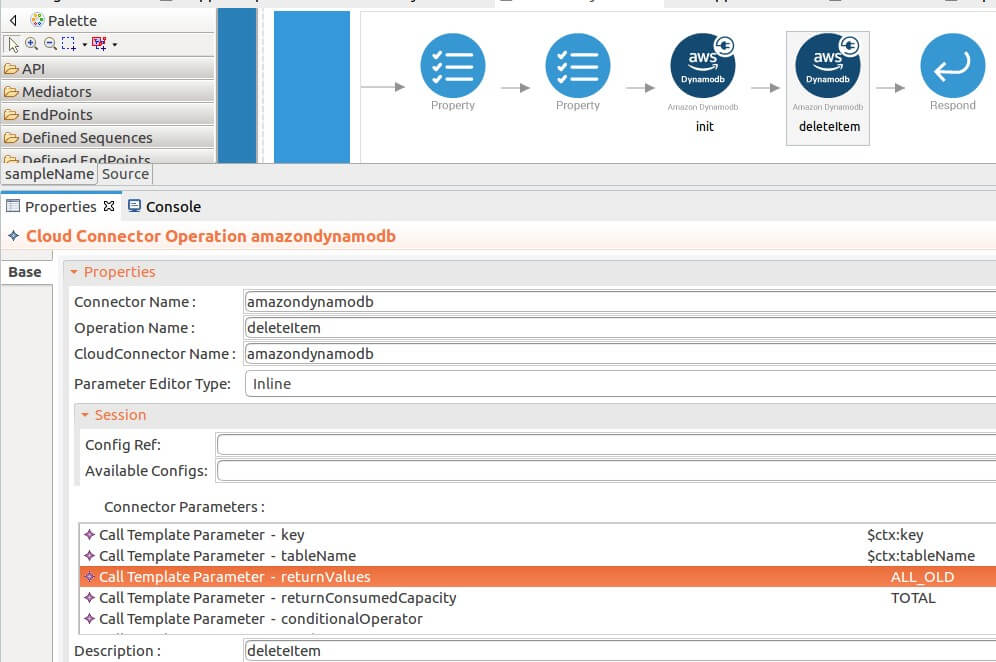
-
Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as mentioned in theaddtableoperation. The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows.
Add the property mediator to capture the
keyvalue. Please follow the steps given inlistdetailsoperation.- name : key
-
expression : json-eval($.key)
-
Add the property mediator to capture the
tableNamevalues. Please follow the steps given inlistdetailsoperation. -
name : tableName
- expression : json-eval($.tableName)
-
Configure a resource for the listtable operation¶
- Initialize the connector.
You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in 1.1 for setting up the init operation to the addtable operation.
-
Set up the listTables operation.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
listTablesoperation into the Design pane.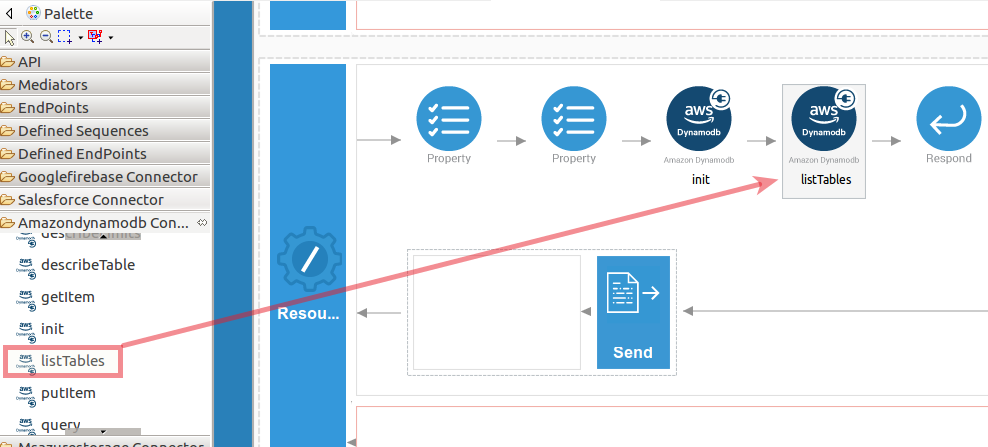
-
The listTables operation use to retrieve information about the created tables.
listTablesoperation parameters listed here. -
exclusiveStartTableName : The first table name that the listTables operation evaluates. Use the value returned for LastEvaluatedTableName.
-
limit : The maximum number of table names to retrieve. If this parameter is not specified, the limit is 100.
While invoking the API, the above two parameter values come as a user inputs.
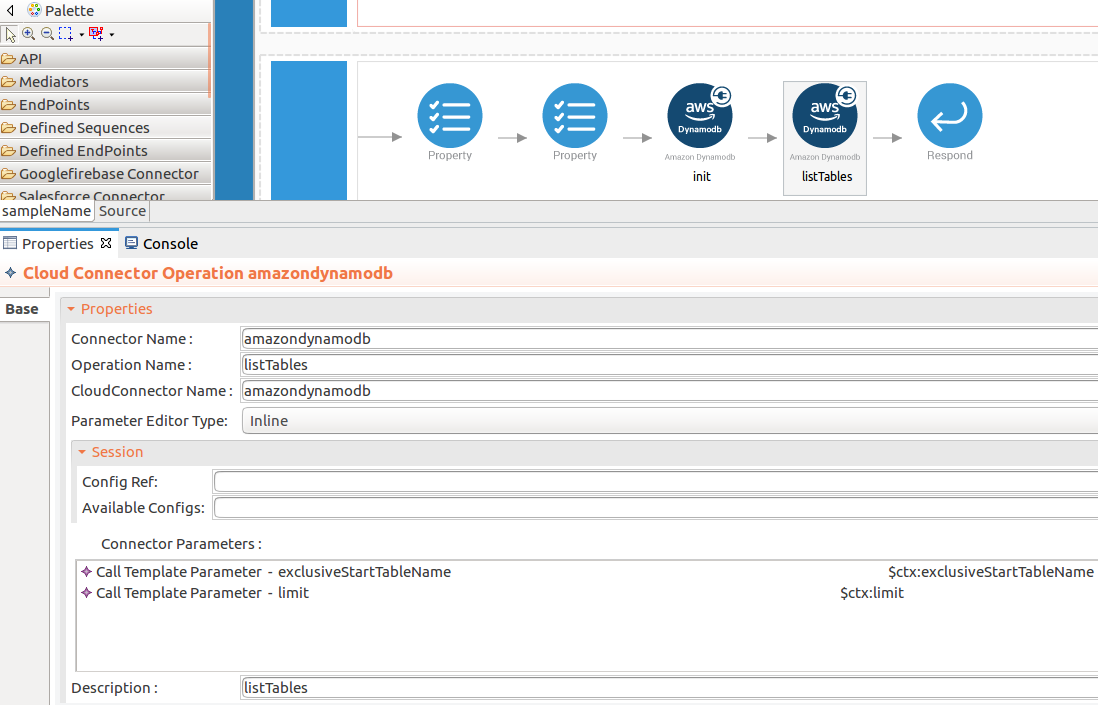
-
Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as mentioned inaddtableoperation. The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows.
Add the property mediator to capture the
exclusiveStartTableNamevalue. Please follow the steps given in thelistTablesoperation.- name : exclusiveStartTableName
-
expression : json-eval($.exclusiveStartTableName)
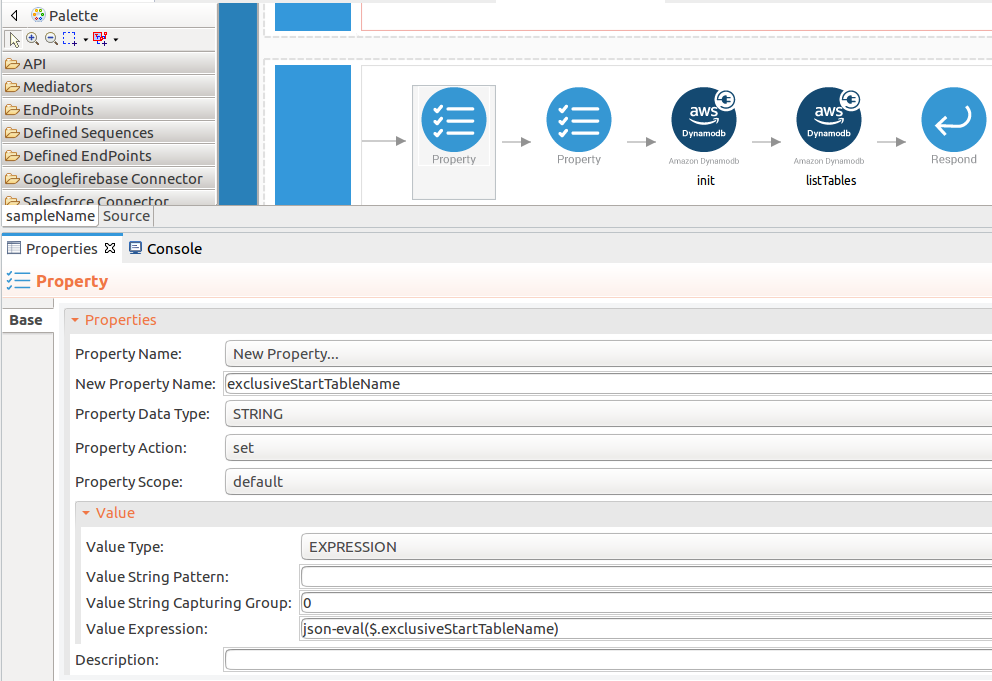
-
Add the property mediator to capture the
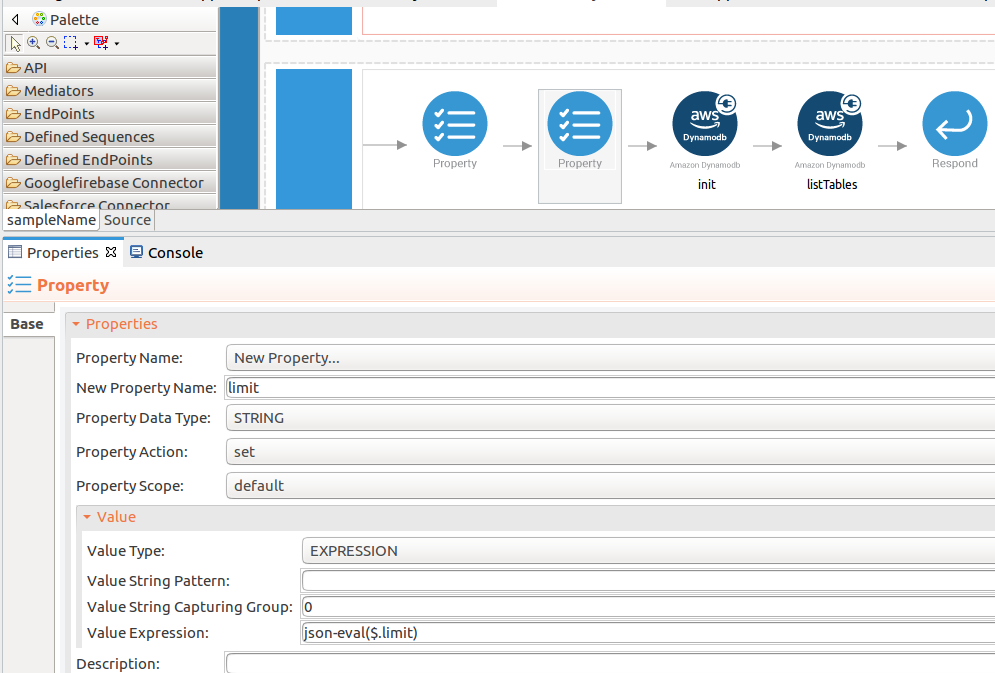
limitvalues. Please follow the steps given in thelistTablesoperation. -
name : limit
-
expression : json-eval($.limit)
-
Configure a resource for the deletetable operation¶
- Initialize the connector.
You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in 1.1 for setting up the init operation to the addtable operation.
-
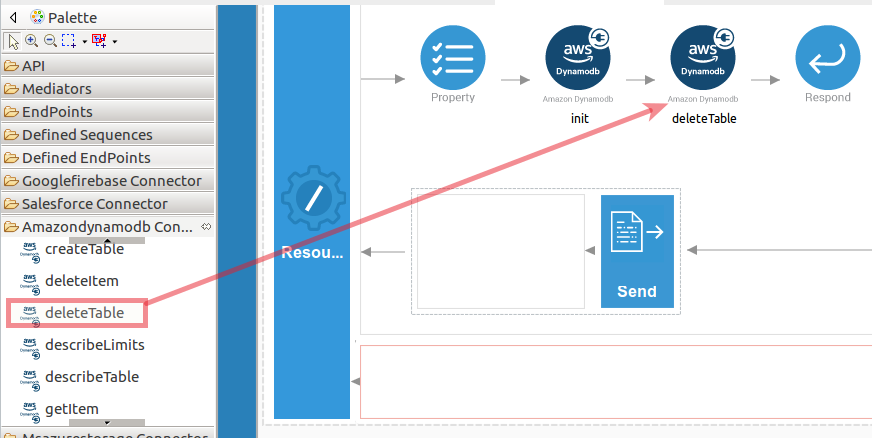
Set up the deleteTable operation.
- Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
deleteTableoperation into the Design pane.
-
The listTables operation is used to retrieve information about the created tables. The
deleteTableoperation parameters are listed here. -
exclusiveStartTableName : The first table name that the listTables operation evaluates. Use the value returned for LastEvaluatedTableName.
-
limit : The maximum number of table names to retrieve. If this parameter is not specified, the limit is 100.
While invoking the API, the above two parameter values come as user inputs.
-
Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as mentioned inaddtableoperation. The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows:
Add the property mediator to capture the
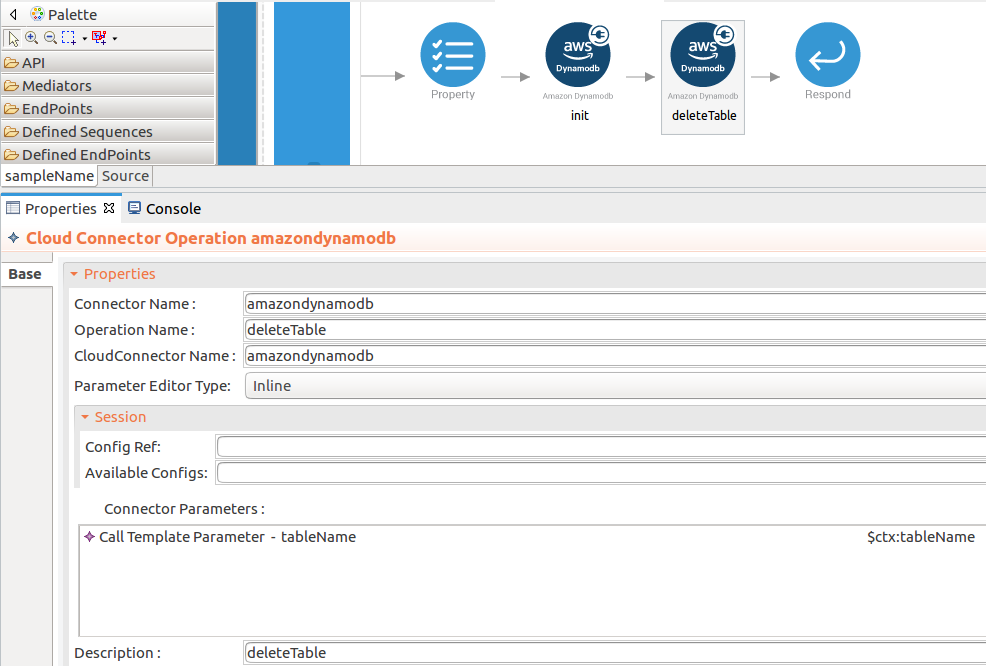
tableNamevalue. Please follow the steps given in thedeleteTableandlistdetailsoperations.- name : tableName
- expression : json-eval($.tableName)
- Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Amazondynamodb Connector section. Then drag and drop the
Get a response.¶
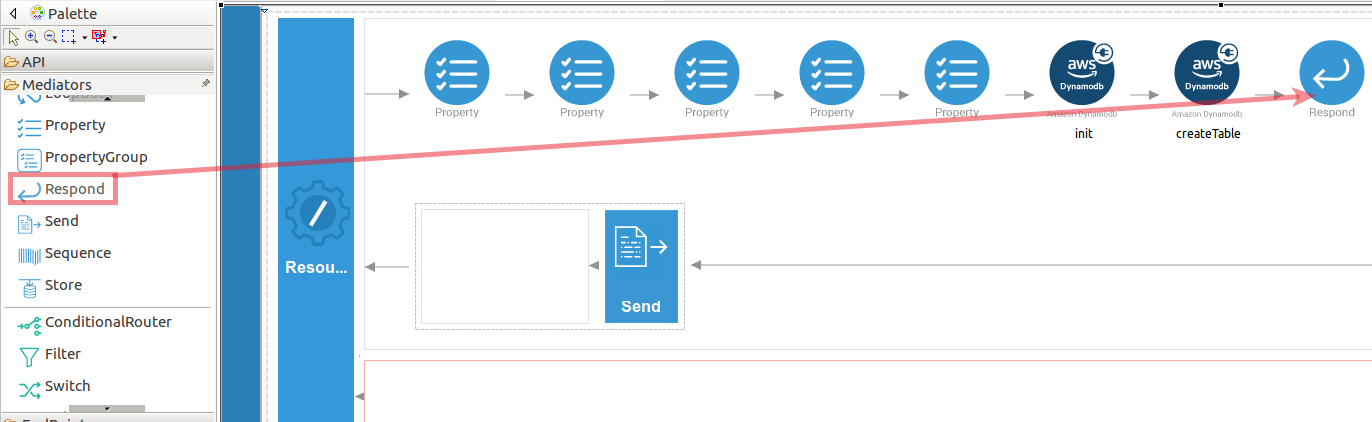
When you are invoking the created API, the request of the message is going through the each resource. Finally, it is passed to the Respond mediator. The Respond Mediator stops the processing on the current message and sends the message back to the client as a response.
Drag and drop respond mediator to the Design view.
Now you can switch into the Source view and check the XML configuration files of the created API.
amazonDynamoDBAPI.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<api xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" context="/resources" name="amazonDynamoDBAPI">
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/addtable">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.attributeDefinitions)" name="attributeDefinitions" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.tableName)" name="tableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.keySchema)" name="keySchema" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.localSecondaryIndexes)" name="localSecondaryIndexes" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.provisionedThroughput)" name="provisionedThroughput" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.createTable>
<attributeDefinitions>{$ctx:attributeDefinitions}</attributeDefinitions>
<tableName>{$ctx:tableName}</tableName>
<keySchema>{$ctx:keySchema}</keySchema>
<localSecondaryIndexes>{$ctx:localSecondaryIndexes}</localSecondaryIndexes>
<provisionedThroughput>{$ctx:provisionedThroughput}</provisionedThroughput>
</amazondynamodb.createTable>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/insertdetails">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.item)" name="item" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.tableName)" name="tableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.putItem>
<item>{$ctx:item}</item>
<tableName>{$ctx:tableName}</tableName>
</amazondynamodb.putItem>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/deletedetails">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.key)" name="key" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.tableName)" name="tableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.deleteItem>
<key>{$ctx:key}</key>
<tableName>{$ctx:tableName}</tableName>
<returnConsumedCapacity>TOTAL</returnConsumedCapacity>
<returnValues>ALL_OLD</returnValues>
</amazondynamodb.deleteItem>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/listdetails">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.key)" name="key" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.tableName)" name="tableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.getItem>
<key>{$ctx:key}</key>
<tableName>{$ctx:tableName}</tableName>
</amazondynamodb.getItem>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/listtable">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.exclusiveStartTableName)" name="exclusiveStartTableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.limit)" name="limit" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.listTables>
<exclusiveStartTableName>{$ctx:exclusiveStartTableName}</exclusiveStartTableName>
<limit>{$ctx:limit}</limit>
</amazondynamodb.listTables>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/updatetable">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.tableName)" name="tableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<property expression="json-eval($.provisionedThroughput)" name="provisionedThroughput" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.updateTable>
<tableName>{$ctx:tableName}</tableName>
<provisionedThroughput>{$ctx:provisionedThroughput}</provisionedThroughput>
</amazondynamodb.updateTable>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
<resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/deletetable">
<inSequence>
<property expression="json-eval($.tableName)" name="tableName" scope="default" type="STRING" />
<amazondynamodb.init>
<region>us-east-2</region>
<accessKeyId>AKIAY4QELOL7GF35XBW5</accessKeyId>
<secretAccessKey>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</secretAccessKey>
<blocking>false</blocking>
</amazondynamodb.init>
<amazondynamodb.deleteTable>
<tableName>{$ctx:tableName}</tableName>
</amazondynamodb.deleteTable>
<respond />
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
<faultSequence />
</resource>
</api>Get the project¶
You can download the ZIP file and extract the contents to get the project code.
Deployment¶
Follow these steps to deploy the exported CApp in the integration runtime.
Deploying on Micro Integrator
You can copy the composite application to the <PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps folder and start the server. Micro Integrator will be started and the composite application will be deployed.
You can further refer the application deployed through the CLI tool. See the instructions on managing integrations from the CLI.
Click here for instructions on deploying on ESB Enterprise Integrator 6
You can copy the composite application to the
<PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonappsfolder and start the server.ESB EI server starts and you can login to the Management Console https://localhost:9443/carbon/ URL. Provide login credentials. The default credentials will be admin/admin.
You can see that the API is deployed under the API section.
Testing¶
Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command. Curl Application can be downloaded from here.
- Creating a new table in the Amazon DynamoDB with the specified table name for store employee details.
Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"attributeDefinitions":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"AttributeType":"S"
},
{
"AttributeName":"name",
"AttributeType":"S"
},
{
"AttributeName":"department",
"AttributeType":"S"
}
],
"tableName":"Employee_Details",
"keySchema":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"KeyType":"HASH"
},
{
"AttributeName":"name",
"KeyType":"RANGE"
}
],
"localSecondaryIndexes":[
{
"IndexName":"department",
"KeySchema":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"KeyType":"HASH"
},
{
"AttributeName":"department",
"KeyType":"RANGE"
}
],
"Projection":{
"ProjectionType":"KEYS_ONLY"
}
}
],
"provisionedThroughput":{
"ReadCapacityUnits":5,
"WriteCapacityUnits":5
}
} Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json "http://localhost:8290/resources/addtable" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{
"TableDescription":{
"AttributeDefinitions":[
{
"AttributeName":"department",
"AttributeType":"S"
},
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"AttributeType":"S"
},
{
"AttributeName":"name",
"AttributeType":"S"
}
],
"CreationDateTime":1590068547.564,
"ItemCount":0,
"KeySchema":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"KeyType":"HASH"
},
{
"AttributeName":"name",
"KeyType":"RANGE"
}
],
"LocalSecondaryIndexes":[
{
"IndexArn":"arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-2:610968236798:table/Employee_Details/index/department",
"IndexName":"department",
"IndexSizeBytes":0,
"ItemCount":0,
"KeySchema":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"KeyType":"HASH"
},
{
"AttributeName":"department",
"KeyType":"RANGE"
}
],
"Projection":{
"ProjectionType":"KEYS_ONLY"
}
}
],
"ProvisionedThroughput":{
"NumberOfDecreasesToday":0,
"ReadCapacityUnits":5,
"WriteCapacityUnits":5
},
"TableArn":"arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-2:610968236798:table/Employee_Details",
"TableId":"10520308-ae1e-4742-b9d4-fc6aae67191e",
"TableName":"Employee_Details",
"TableSizeBytes":0,
"TableStatus":"CREATING"
}
}
- Insert employee details (items) and stored into the specified table.
Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"tableName":"Employee_Details",
"item":{
"employee_id":{
"S":"001"
},
"name":{
"S":"Jhone Fedrick"
},
"department":{
"S":"Engineering"
}
}
}Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json "http://localhost:8290/resources/insertdetails" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{}Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"tableName":"Employee_Details",
"provisionedThroughput":{
"ReadCapacityUnits":12,
"WriteCapacityUnits":12
}
}Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json "http://localhost:8290/resources/updatetable" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{
"TableDescription":{
"AttributeDefinitions":[
{
"AttributeName":"department",
"AttributeType":"S"
},
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"AttributeType":"S"
},
{
"AttributeName":"name",
"AttributeType":"S"
}
],
"CreationDateTime":1590068547.564,
"ItemCount":0,
"KeySchema":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"KeyType":"HASH"
},
{
"AttributeName":"name",
"KeyType":"RANGE"
}
],
"LocalSecondaryIndexes":[
{
"IndexArn":"arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-2:610968236798:table/Employee_Details/index/department",
"IndexName":"department",
"IndexSizeBytes":0,
"ItemCount":0,
"KeySchema":[
{
"AttributeName":"employee_id",
"KeyType":"HASH"
},
{
"AttributeName":"department",
"KeyType":"RANGE"
}
],
"Projection":{
"ProjectionType":"KEYS_ONLY"
}
}
],
"ProvisionedThroughput":{
"LastIncreaseDateTime":1590071461.81,
"NumberOfDecreasesToday":0,
"ReadCapacityUnits":5,
"WriteCapacityUnits":5
},
"TableArn":"arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-2:610968236798:table/Employee_Details",
"TableId":"10520308-ae1e-4742-b9d4-fc6aae67191e",
"TableName":"Employee_Details",
"TableSizeBytes":0,
"TableStatus":"UPDATING"
}
}- Retrieve information about the added employee details (items).
Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"tableName":"Employee_Details",
"key":{
"employee_id":{
"S":"001"
},
"name":{
"S":"Jhone Fedrick"
}
}
}Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json "http://localhost:8290/resources/listdetails" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{
"Item":{
"department":{
"S":"Engineering"
},
"name":{
"S":"Jhone Fedrick"
},
"employee_id":{}
}
}
Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"tableName":"Employee_Details",
"key":{
"employee_id":{
"S":"001"
},
"name":{
"S":"Jhone Fedrick"
}
}
}Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json "http://localhost:8290/resources/deletedetails" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{
"Attributes":{
"department":{
"S":"Engineering"
},
"name":{
"S":"Jhone Fedrick"
},
"employee_id":{
"S":"001"
}
},
"ConsumedCapacity":{
"CapacityUnits":2,
"TableName":"Employee_Details"
}
} Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"exclusiveStartTableName":"Employee_Details",
"limit":4
}Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json "http://localhost:8290/resources/listtable" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{
"LastEvaluatedTableName":"TTestMyTablehread",
"TableNames":[
"Results",
"Results1",
"Results123",
"TTestMyTablehread"
]
} Sample request
Save a file called data.json with the following payload.
{
"tableName":"Employee_Details"
}
Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command.
curl -v POST -d @data.json " http://localhost:8290/resources/deletetable" -H "Content-Type:application/json"Expected Response
{
"TableDescription":{
"ItemCount":0,
"ProvisionedThroughput":{
"NumberOfDecreasesToday":0,
"ReadCapacityUnits":12,
"WriteCapacityUnits":12
},
"TableArn":"arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-2:610968236798:table/Employee_Details",
"TableId":"10520308-ae1e-4742-b9d4-fc6aae67191e",
"TableName":"Employee_Details",
"TableSizeBytes":0,
"TableStatus":"DELETING"
}
}